Article for Magnetic Heat Exchange and Method for Manufacturing an Article for Magnetic Heat Exchange
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
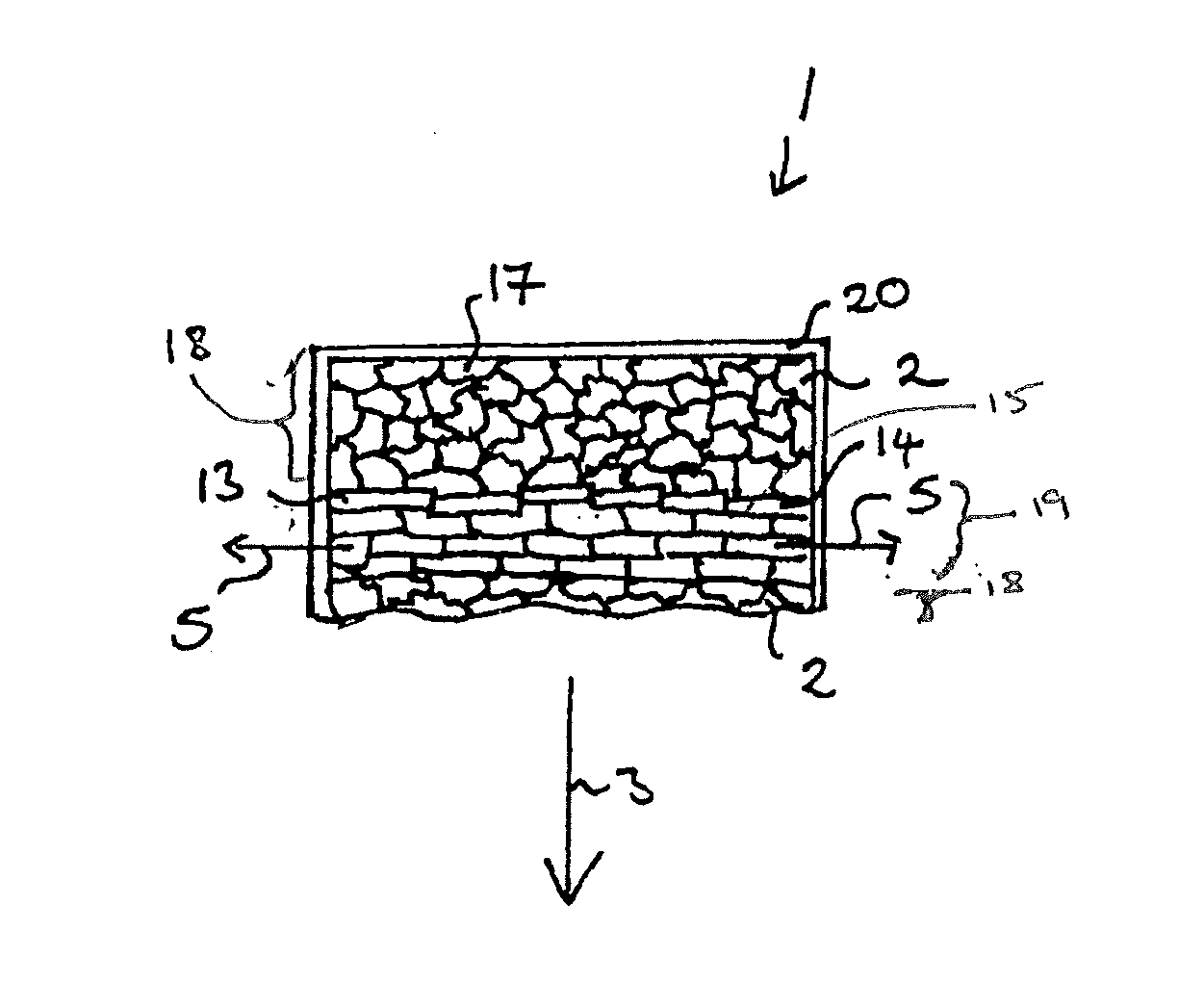
[0103]In the second embodiment illustrated in FIG. 4, the grains 14 of the magnetocalorically passive phase 13 also have a generally plate-like form. The grains 14 are also arranged in the article 1 with a preferred orientation such that their long direction 15 extends in directions generally parallel to the second length b of the article 1 and in directions generally perpendicular to the coolant flow direction 3.
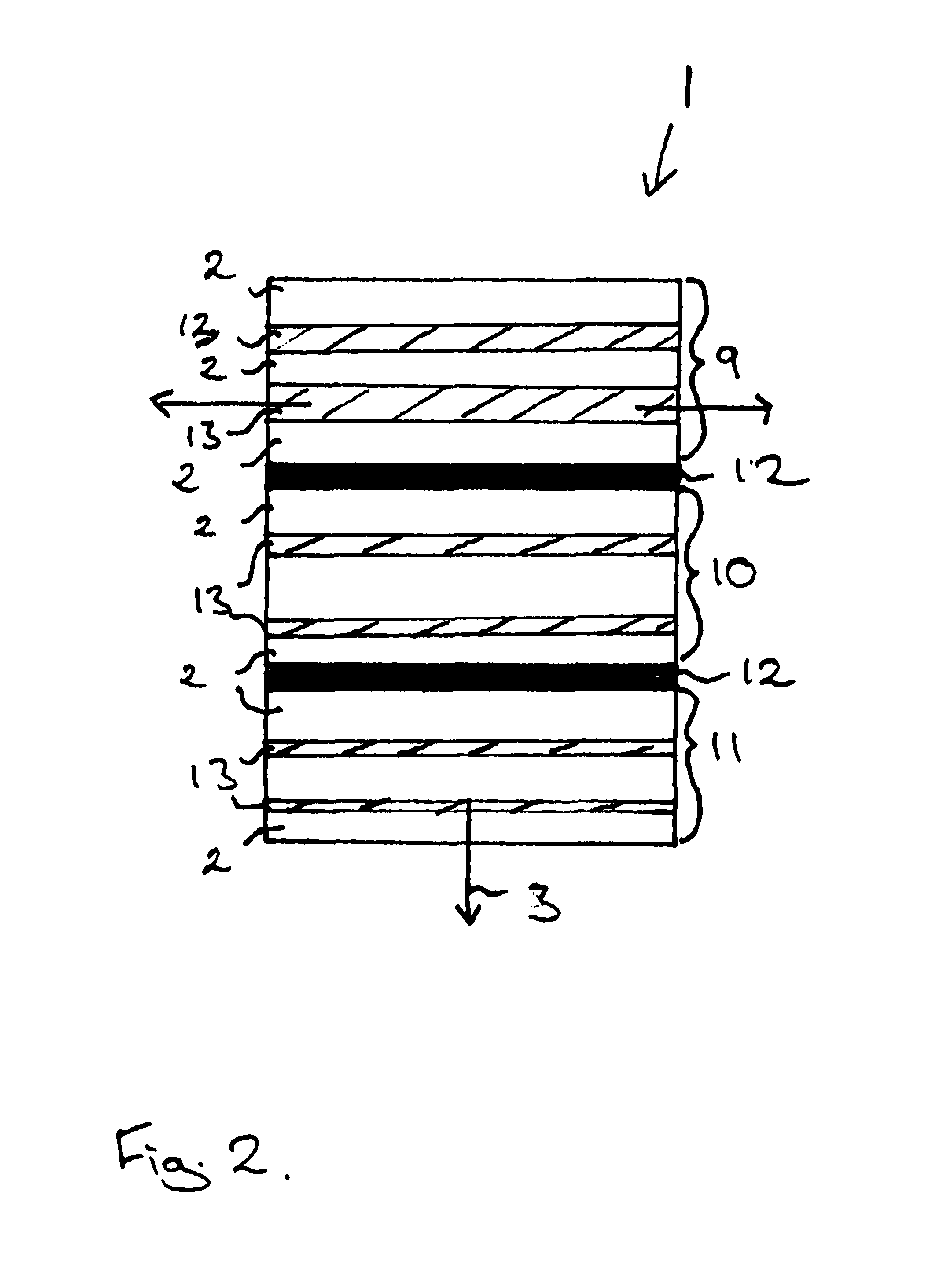
[0104]In the second embodiment of FIG. 4, as in the embodiment of FIG. 2, the anisotropic thermal conductivity of the article 1 is provided by a layered structure in which layers 18 consisting essentially of a magnetocalorically active phase 2 are interleaved with layers 19 consisting essentially of a magnetocalorically passive phase 13. In the embodiment illustrated in FIG. 4, the anisotropic average thermal conductivity of the article 1 is provided macroscopically.
[0105]A single layer 19 of a magnetocalorically passive phase 13 sandwiched between two layers 18 of magnetoc...
fourth embodiment
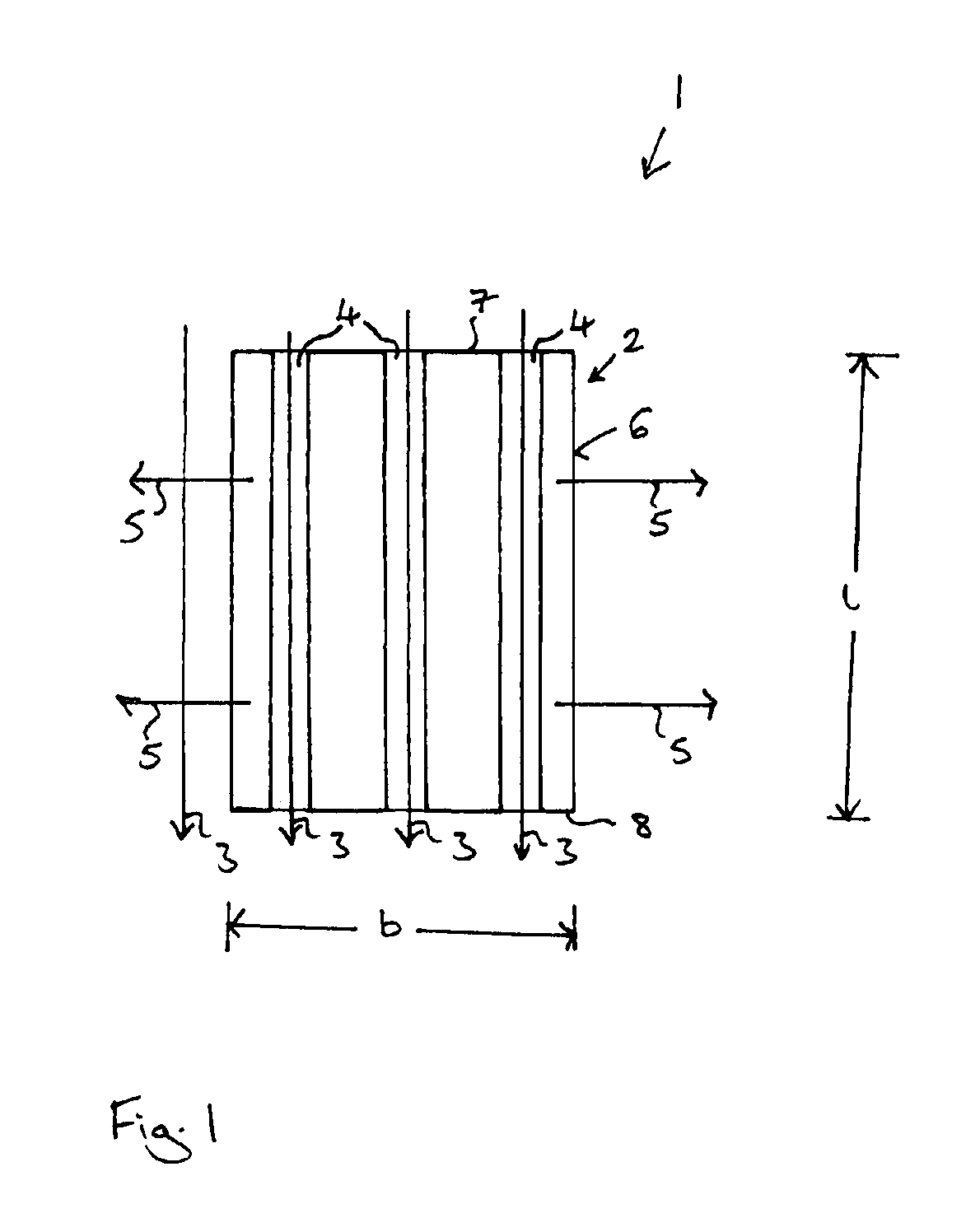
[0116]FIG. 6 illustrates an embodiment of an article 1 for use as the working component of a magnetic heat exchange system according to a
[0117]The article 1 of the fourth embodiment comprises a plurality of grains 17 of a magnetocalorically active phase 2 and a plurality of grains 14 of a magnetocalorically passive phase 13. For illustrative purposes only, the grains 17 are unshaded and the grains 14 are shaded black. On average, each of the grains 14 and / or 17 has a shape which is generally isotropic (e.g., generally spherical). In this embodiment, the article 1 has anisotropic thermal conductivity due to the preferred orientation of the isotropically-shaped grains 14 of the magnetocalorically passive phase 13.
[0118]The generally spherical grains 14 of the magnetocalorically passive phase 13 comprises a ferromagnetic material, in this case iron. The grains 14 are arranged in a plurality of rows or chains 24 having a long direction which extends in directions generally parallel to t...
fifth embodiment
[0123]FIG. 7 illustrates an article 1′ for use as the working component of a magnetic heat exchange system according to a
[0124]The article 1′ of the fifth embodiment consists essentially of one or more magnetocalorically active phases 2. For purposes of illustration, these phases are depicted as unshaded areas. The article 1′ of the fifth embodiment is free from magnetocalorically passive phases. The anisotropic average thermal conductivity of the article 1′ is provided, in this embodiment, by an anisotropic distribution of the density of the article 1′ and, in particular, and anisotropic distribution of the porosity of the article 1′.
[0125]The article 1′ of the fifth embodiment includes a plurality of layers of which five are illustrated in FIG. 7. Three first layers 25 have a relatively low porosity and two second layers 26, which are arranged between adjacent first layers 25, include a higher degree of porosity than that of the first layers 25. In the illustration of FIG. 7, the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com