Semiconductor device
a technology of semiconductors and devices, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical equipment, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the operation of semiconductor devices, so as to facilitate the improvement of reverse withstand voltage, facilitate the improvement, and facilitate the preventing the waveform of turnoff voltage and the waveform of turnoff current from oscillating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
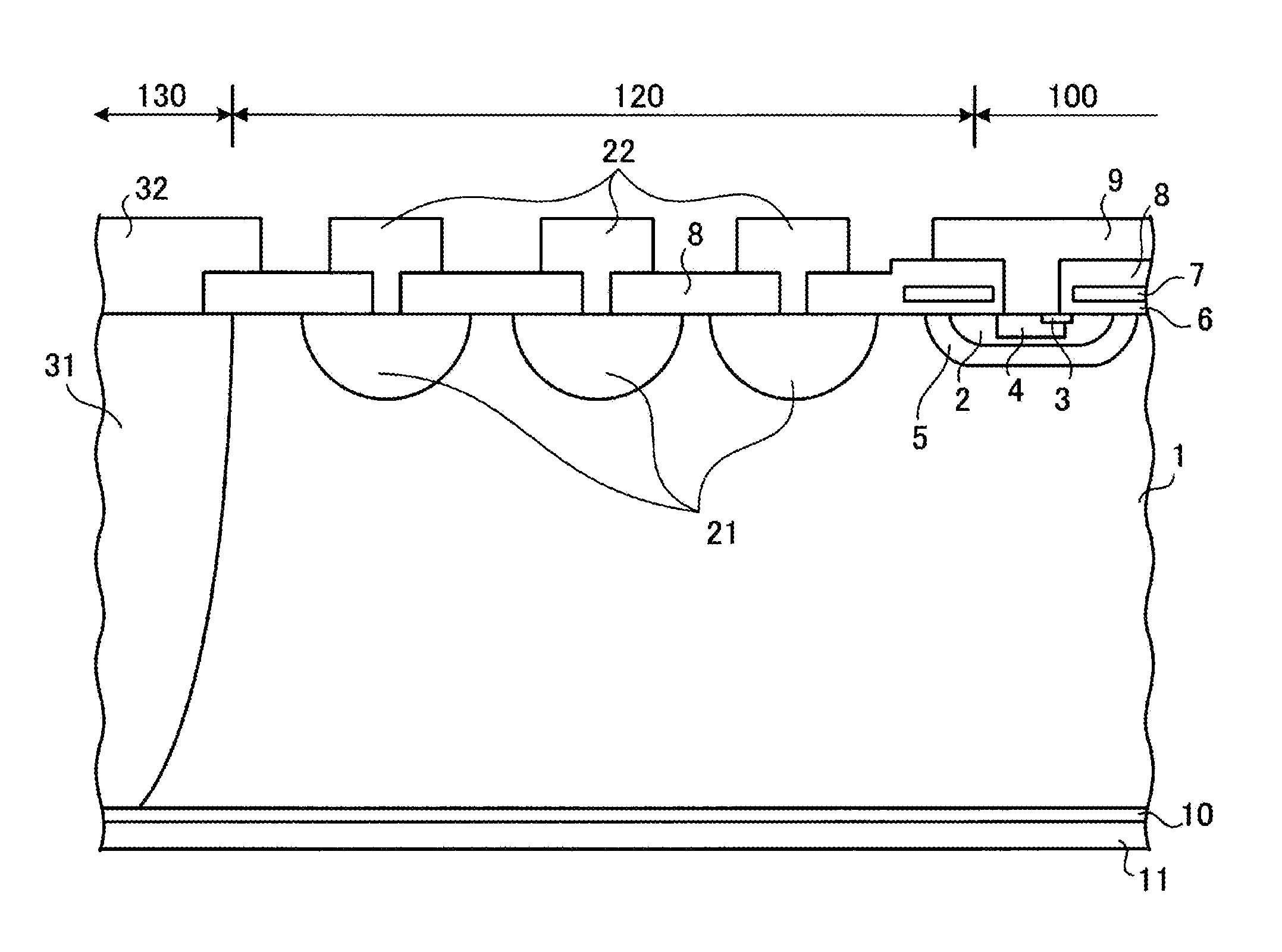
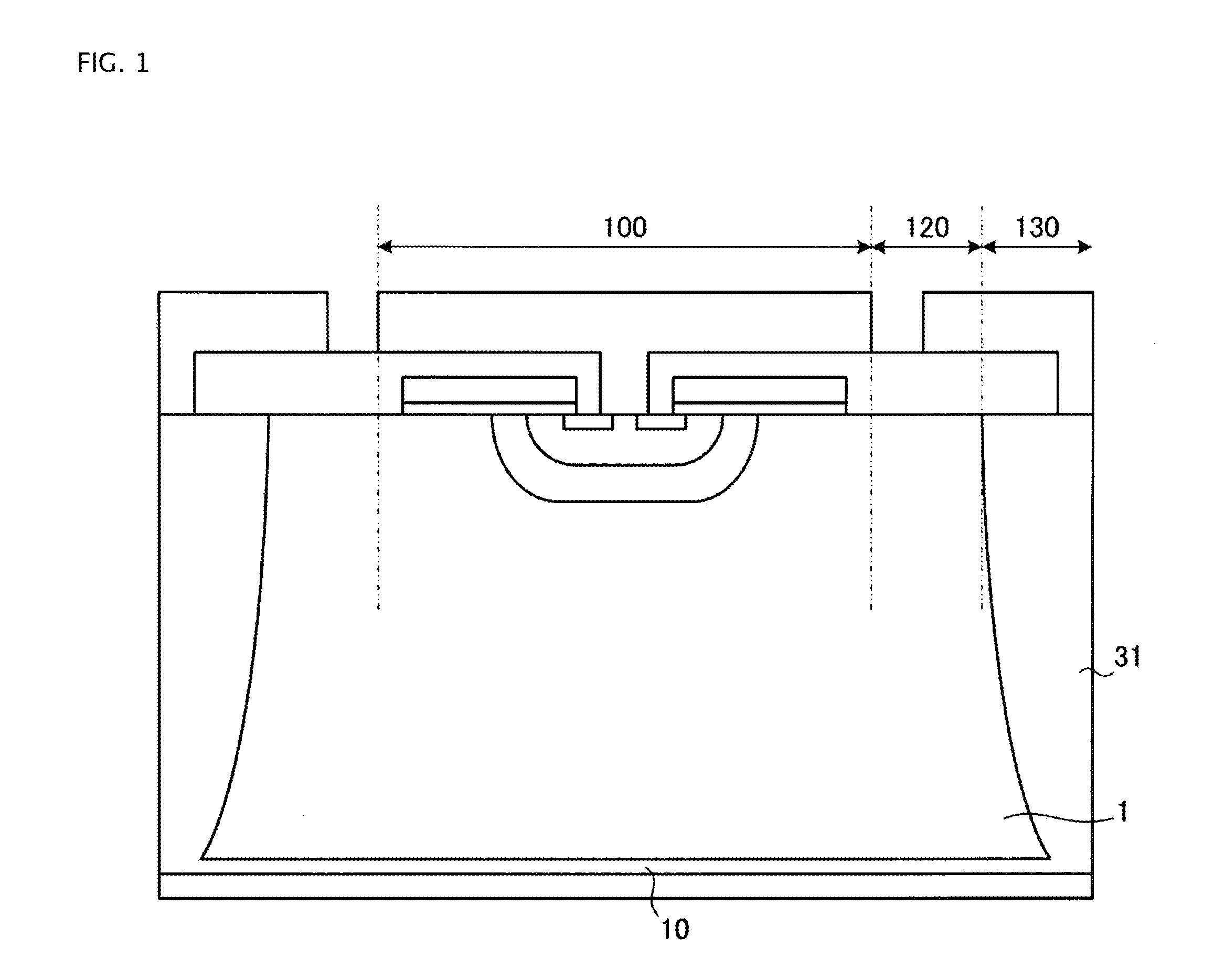
FIG. 1 is the cross sectional view of a reverse blocking IGBT according to the invention.
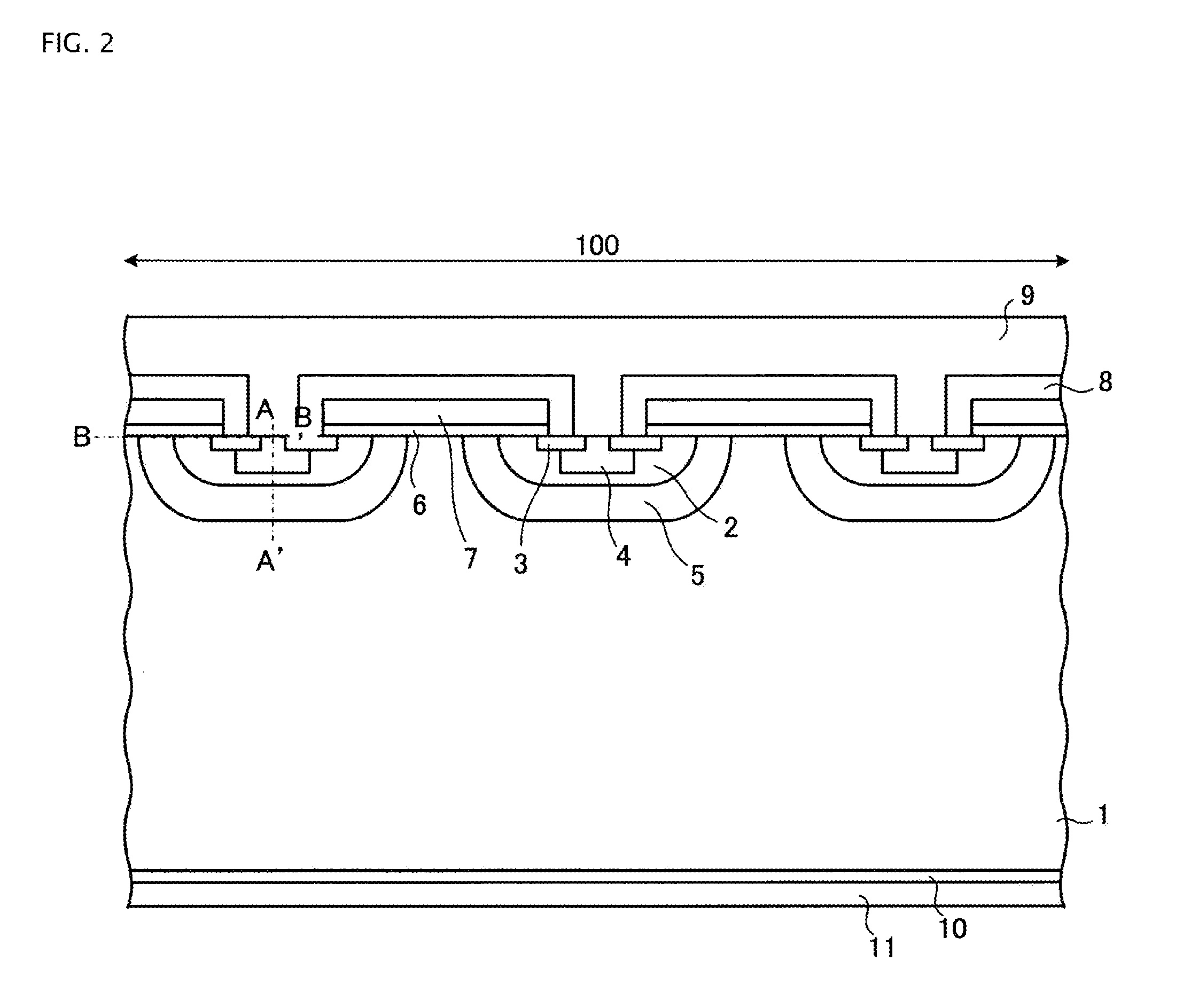
Referring now to FIG. 1, the reverse blocking IGBT according to the invention includes a semiconductor substrate working for n−-type (first conductivity type) drift region 1; active region 100 in the semiconductor substrate; breakdown withstanding region 120 outside active region 100; and separation section 130 outside breakdown withstanding region 120. It is effective for the semiconductor substrate to be 90 μm in thickness or thicker so as not to adversely affect the performances of the reverse blocking IGBT of the 600 V breakdown voltage class. In active region 100, a vertical IGBT structure is formed. The vertical IGBT structure includes an emitter-gate region formed on the front surface side of drift region 1 and p-type (second conductivity type) collector region 10 on the back surface side of drift region 1. Active region 100 will be described later in detail.
Drift region 1 corresponds to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com