Apical Instrument Port
a technology of surgical procedures and catheters, applied in the direction of epicardial electrodes, surgical instruments for cooling, catheters, etc., can solve the problems of less than desirable, limited size of catheters and tools used for percutaneous cardiac procedures, and difficulty in precisely positioning the working end of the catheter at the area in the heart where treatment is carried out, so as to minimize blood loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
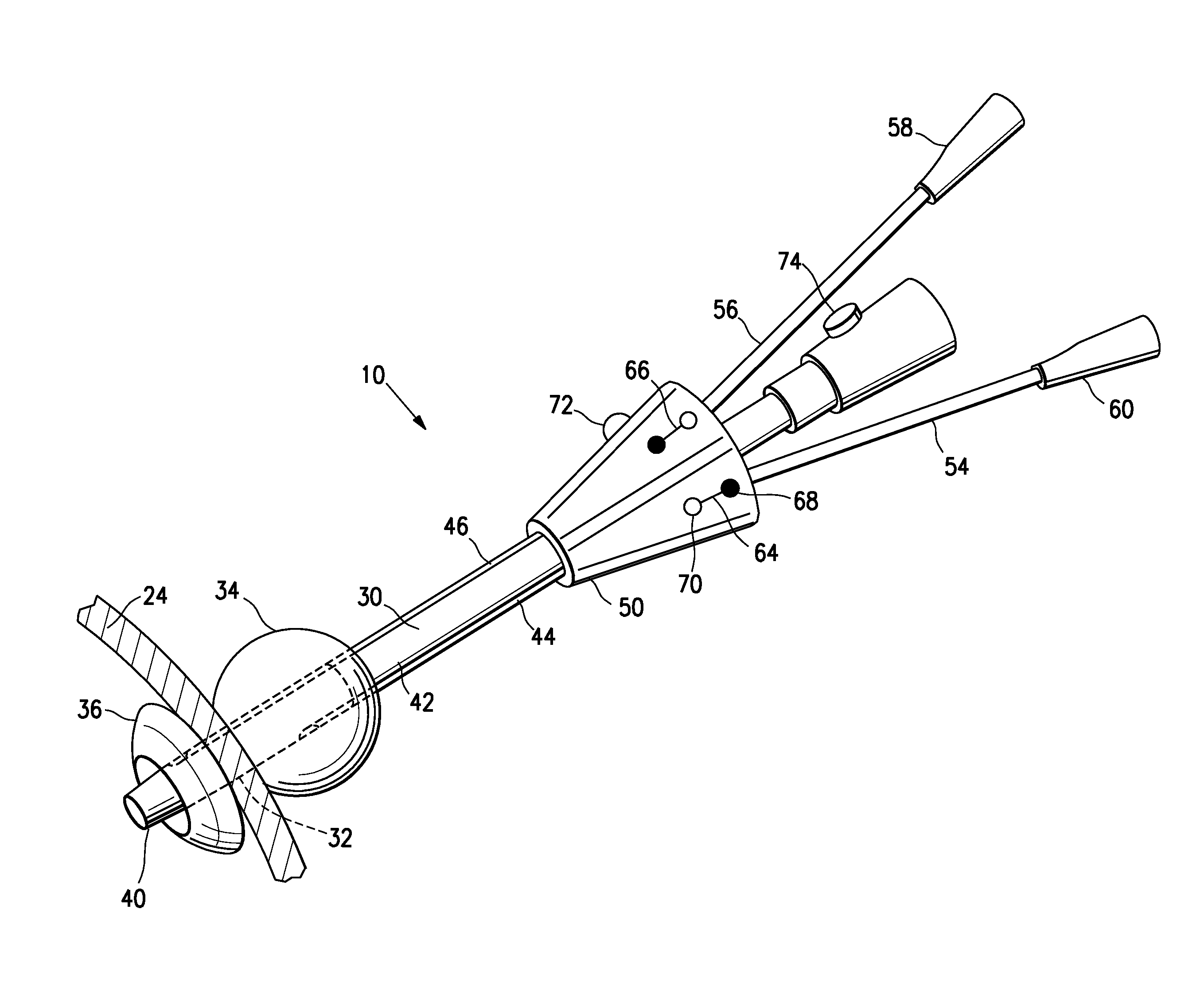
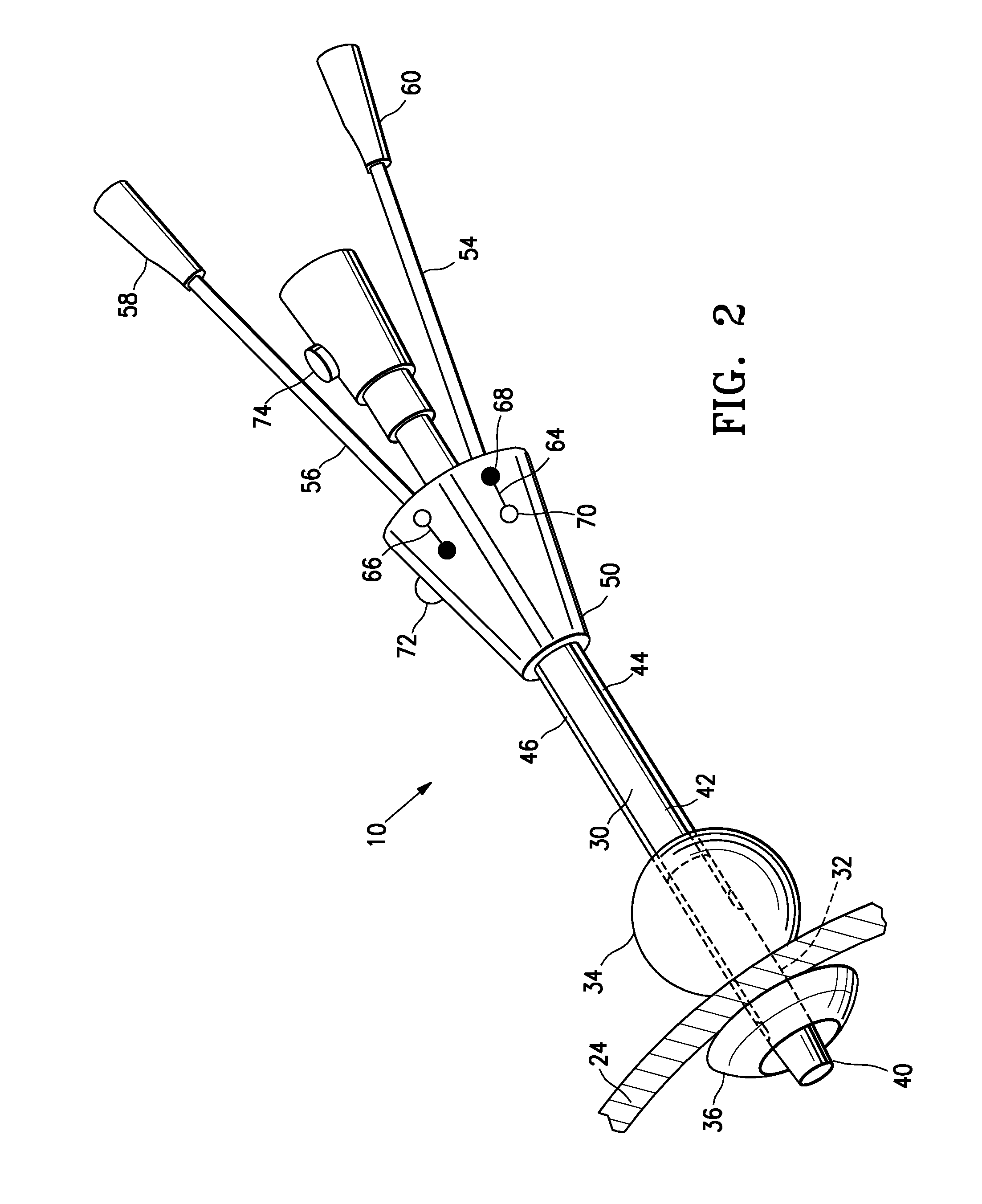
[0021]The instrument port embodying features of the invention allows a physician to gain access to the interior of the heart in a minimally invasive manner, so that a surgical procedure can be performed in the interior of the patient's heart. The instrument port is designed to be temporarily implanted through an apical region of the patient's heart wall and to allow passage of one or more instruments into the heart while minimizing blood loss out of the heart.
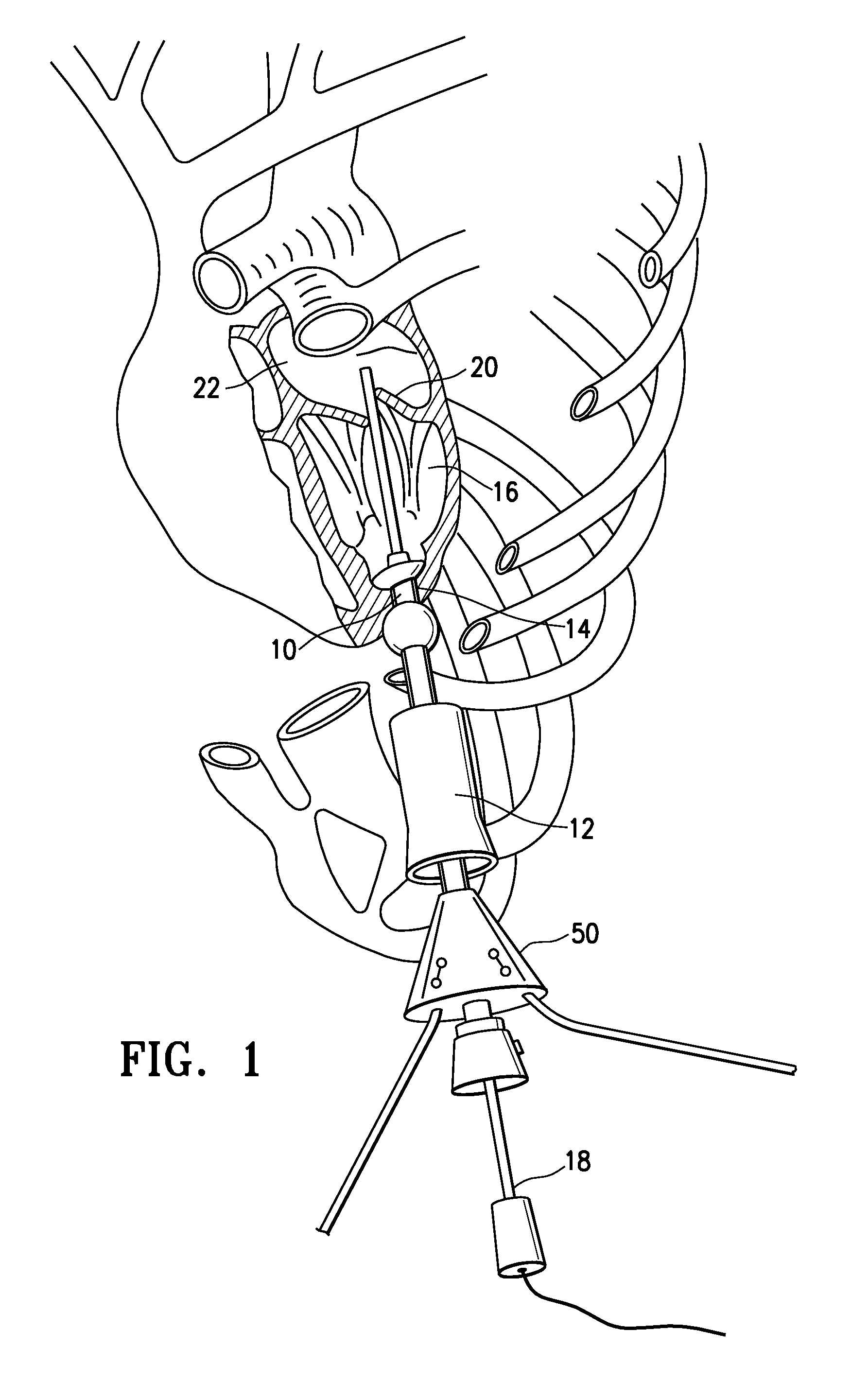
[0022]FIG. 1 illustrates the instrument port 10 as used to facilitate delivery of an ablation catheter or other instrument into or through the left atrium of a patient's heart. The instrument port is shown inserted through the apex of the left ventricle of the patient's heart to facilitate access to the left ventricle and left atrium. Although the instrument port 10 is shown for delivery of an ablation catheter, it can be used with a wide variety of instruments and in a wide variety of minimally invasive procedures.
[0023]As des...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com