Methods of detecting lung cancer
a lung cancer and detection method technology, applied in the field of detecting lung cancer, can solve the problems of lung cancer being only correctly diagnosed, and lung cancer being difficult to diagnos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
5.1 Example 1
Small RNA Levels in Lung Primary Tumors Determined by Microarray
Selected Cohort
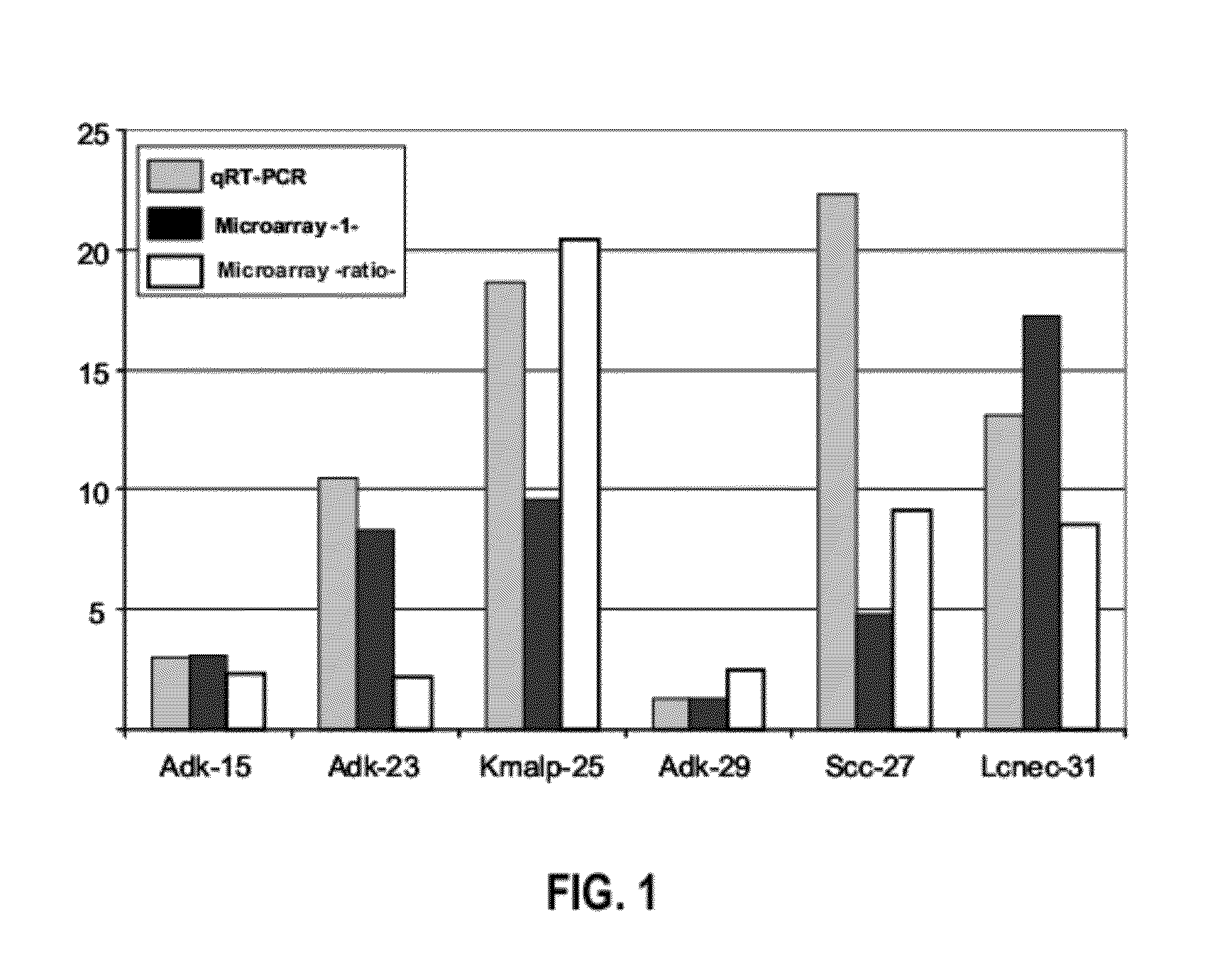
[0259]Thirteen patients diagnosed with lung cancer were included in the cohort, nine men and four women. Seven of the patients had never been smokers, and six had a history of heavy smoking. Because squamous cell lung cancer and non-squamous cell lung cancer are two of the most frequent lung cancer types (more than 70% of all lung cancers), three patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma (Epi-4, Kmalp-21, Kmalp-25) and six patients diagnosed with non-squamous cell carcinoma (Adk-2, Adk-9, Adk-10, Adk-15, Adk-23 and Adk-29) were included. In addition, one patient diagnosed with a carcinoid (Car-13), one diagnosed with a carcinoma sarcomatoide (Ksarc-19), one diagnosed with a small cell lung cancer (Scc-27), and one diagnosed with a large cell neuroendocrine cancer (Lcnec-31) were also selected. Table 1 shows a list of the patients in the cohort and various clinical characteristics of eac...
example 2
5.2 Example 2
Small RNA Levels in Lung Primary Tumors Determined by qRT-PCR
[0289]A TaqMan® quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR; Applied Biosystems) assay was used to measure small U2 in the same small RNA samples used for the microarray experiment in Example 1. The small RNA RNU44 was used as an endogenous control (Amaral F C et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94: 320-323 (2009)). Small RNA from primary tumors of six patients (Adk-15, Adk-23, Kmalp-25, Adk-29, Scc-27 and Lcnec-31) and from the adjacent normal tissue from three of those patients (Adk-15, Adk-23 and Scc-27) were used in the analysis.
[0290]The fold changes in the levels of small U2 in primary tumors were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method (Livak and Schmittgen, Methods, 25: 402-408 (2001)), and using the average of small U2 levels in the 3 adjacent normal tissues as a reference. The results are shown in Table 5.
TABLE 5qRT-PCR quantification of small U2 in tissue samplesSAMPLEU2RNU44ΔCt = U2 Ct −ΔΔCt = U2 ΔCt −IDDESCRIP.CtCtRNU44 C...
example 3
5.3 Example 3
Small RNA Levels Determined by qRT-PCR in Larger Cohort
Selected Cohort
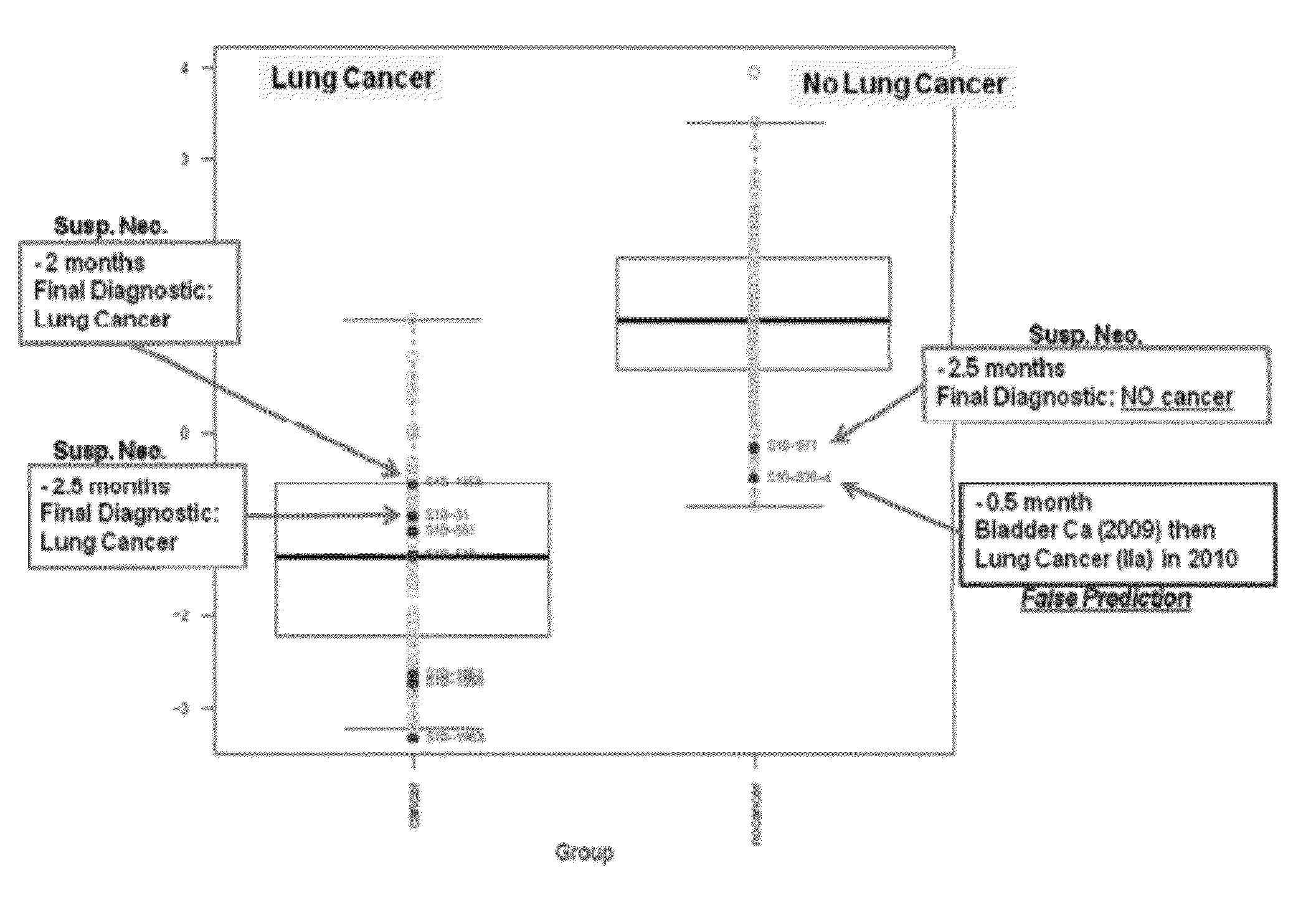
[0296]Thirty-six individuals were selected, 24 of which had been diagnosed with lung cancer, and 12 of which were healthy. This study demonstrates that small U2 can be used as an early detection marker for lung cancer using a minimally invasive assay.
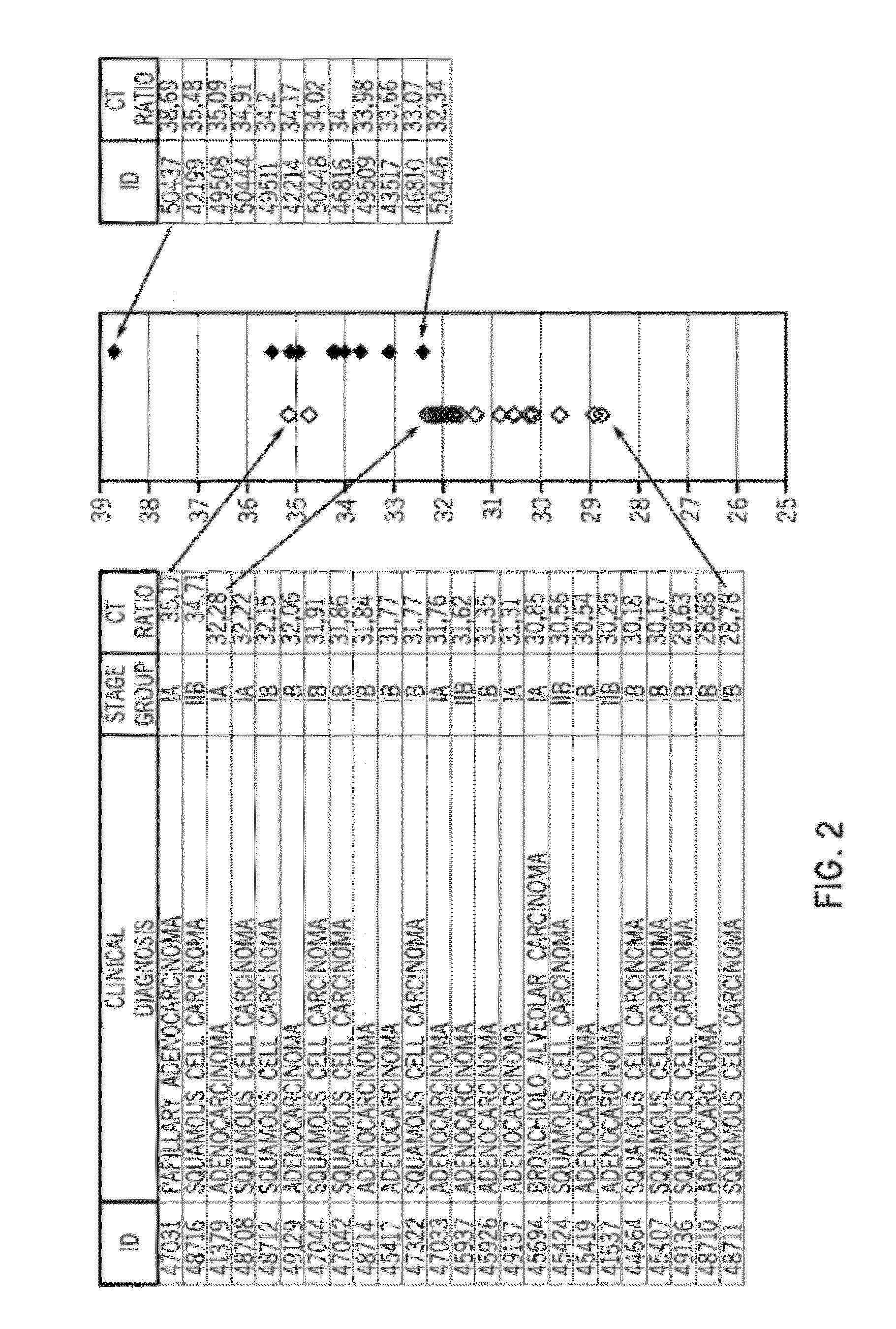
[0297]The 24 lung cancer patients had early-stage lung cancer: six were diagnosed with stage IA lung cancer, 14 with stage IB, and four with stage IIB. The cohort included 16 men and eight women. Sixteen of the patients were smokers, one was a former smoker, and seven had never been smokers. None of the patients had been diagnosed with diabetes, infectious disease, other cancers, obesity, or cardiac problems. None of the patients were taking medication at the time the tissue was collected. Table 7 shows 24 patients with lung cancer in the cohort and various clinical characteristics of each patient.
TABLE 7Clinical characteristics of lung cancer patients in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com