Therapy for kidney disease and/or heart failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Intravenous (IV) Infusion of Vessel Dilator (VD) Peptide
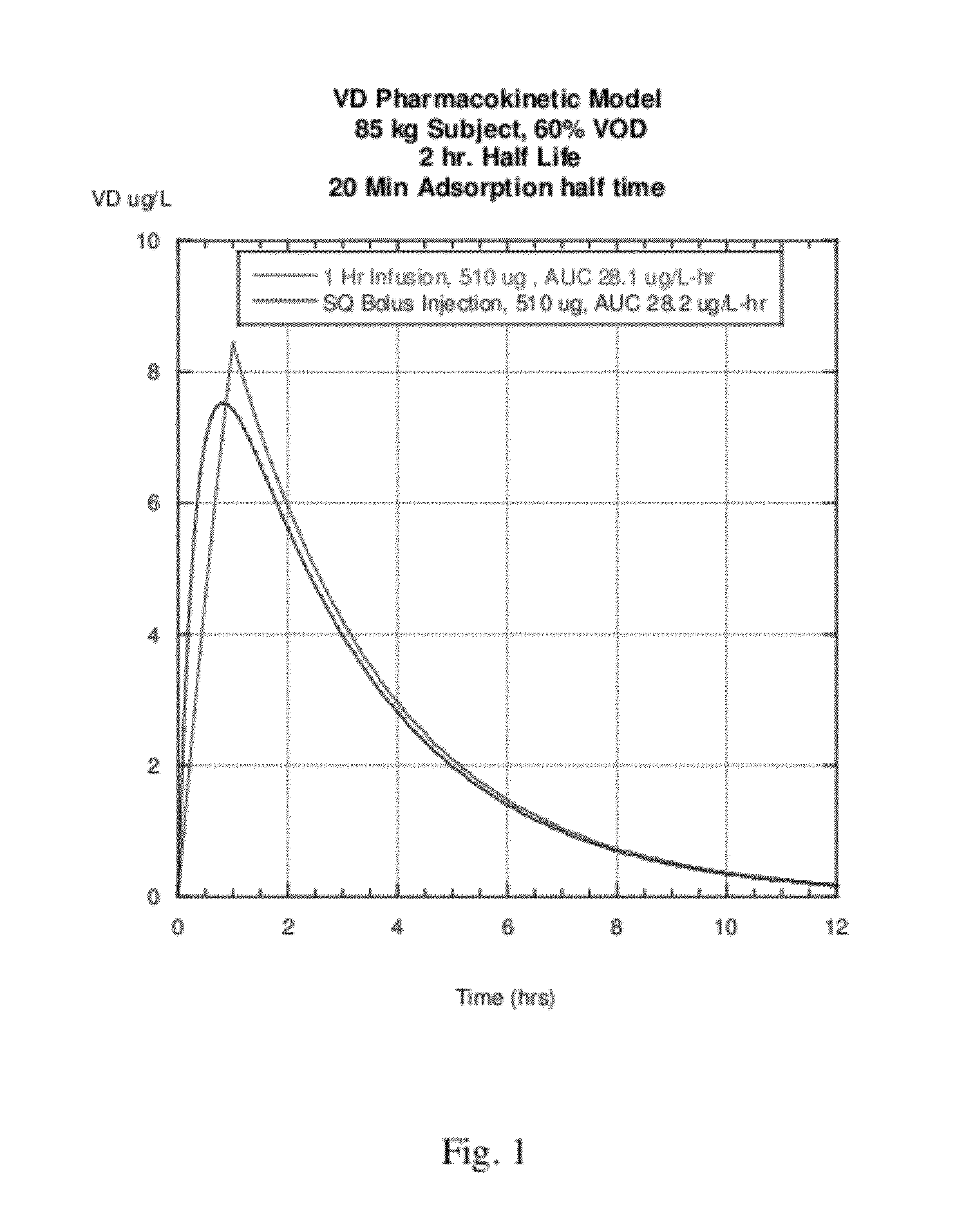
[0244]A study can be performed examining the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the vessel dilator (VD) peptide following intravenous (IV) infusion lasting 1 hour. The half life of the VD peptide for this route of administration is estimated to be about 20 minutes. Subjects are divided into two dose groups: (1) 50 ng / kg·min infusion rate and (2) 100 ng / kg-min infusion rate. For an 85 kg subject, the total dose delivered at 50 ng / kg·min is 255 μg, and at 100 ng / kg·min, the total dose delivered is 510 μg. The pharmacokinetic model for this IV infusion is shown in FIG. 3. As shown in the graph, the peak plasma levels reached are 17.7 and 35.5 ng / ml for the 50 and 100 ng / kg-min doses, respectively.
[0245]Administration of the peptide can be varied to achieve different models of exposure of the patient to the peptide. For example, in certain embodiment models, an 85 kg subject can receive a bolus dose of peptide to reach a peak...
example 2
Modeling Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Vessel Dilator (VD) Protein
[0255]Using an IV infusion model, a two-part study can be performed to determine the pharmacokinetics of subcutaneously delivered Vessel Dilator (VD) peptide and to establish a relationship between the pharmacokinetics of VD and the subsequent pharmacodynamics, particularly related to hemodynamics and kidney function. In a first part of the study, a number of subjects can be dosed subcutaneously with VD. A full range of noninvasive measurements can be obtained. The first study can thereby result in establishing pharmacokinetic parameters in the subjects at certain doses.
[0256]A second part of the study can be run on 16 subjects, all of whom are fitted with right heart catheters to measure hemodynamics. This stage can be run in two doses. The nominal doses can be chosen to mimic the peak plasma levels reached by IV infusion and subcutaneous (SQ) bolus administration of the first part of the study described h...
example 3
Determination of Pharmacokinetic Behavior of Vessel Dilator (VD) Peptide
[0259]An alternative study can be performed to establish a dosing for the VD peptide, where the VD peptide is detected in blood extracted from a subject by liquid chromatograph (LC)-mass spectrometry (MS) methods or LC-MS-MS methods. It is desired to study the pharmacokinetic behavior of VD by SQ administration at the lowest feasible range of doses while still allowing for adequate ability to detect VD peptide in the blood plasma.
[0260]Up to 18 subjects can be enrolled in the study, where the subjects can be divided into two groups with a goal of at least 8 evaluable subjects in each group. The first 8 subjects can be dosed for 6-12 hours by SQ infusion with VD peptide at a rate that will lead to a plasma concentration of 10 ng / mL above baseline, which is about half of the peak plasma concentration reached during a 1 hr IV infusion at 50 ng / kg·min. A second set of subjects can receive a higher dose for 6-12 hour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com