Use of microvesicles in analyzing kras mutations
a technology of kras mutation and microvesicles, which is applied in the field of medical diagnosis, prognosis, treatment efficacy, and patient monitoring, can solve the problems of insufficient sensitivity of the method, inconvenient use, and complicated methods,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0155]Method of Analyzing Kras mutations using microvesicles isolated from serum and plasma samples.
[0156]Following proper protocols, serum and plasma samples from 12 colorectal cancer patients were obtained for the following analysis.
[0157]To isolate microvesicles, 0.6-2 milliliter serum was filtered through a 0.8 μm filter to remove any cell contamination. Microvesicles were then pelleted by ultracentrifugation at 110,000×g for 70 minutes.
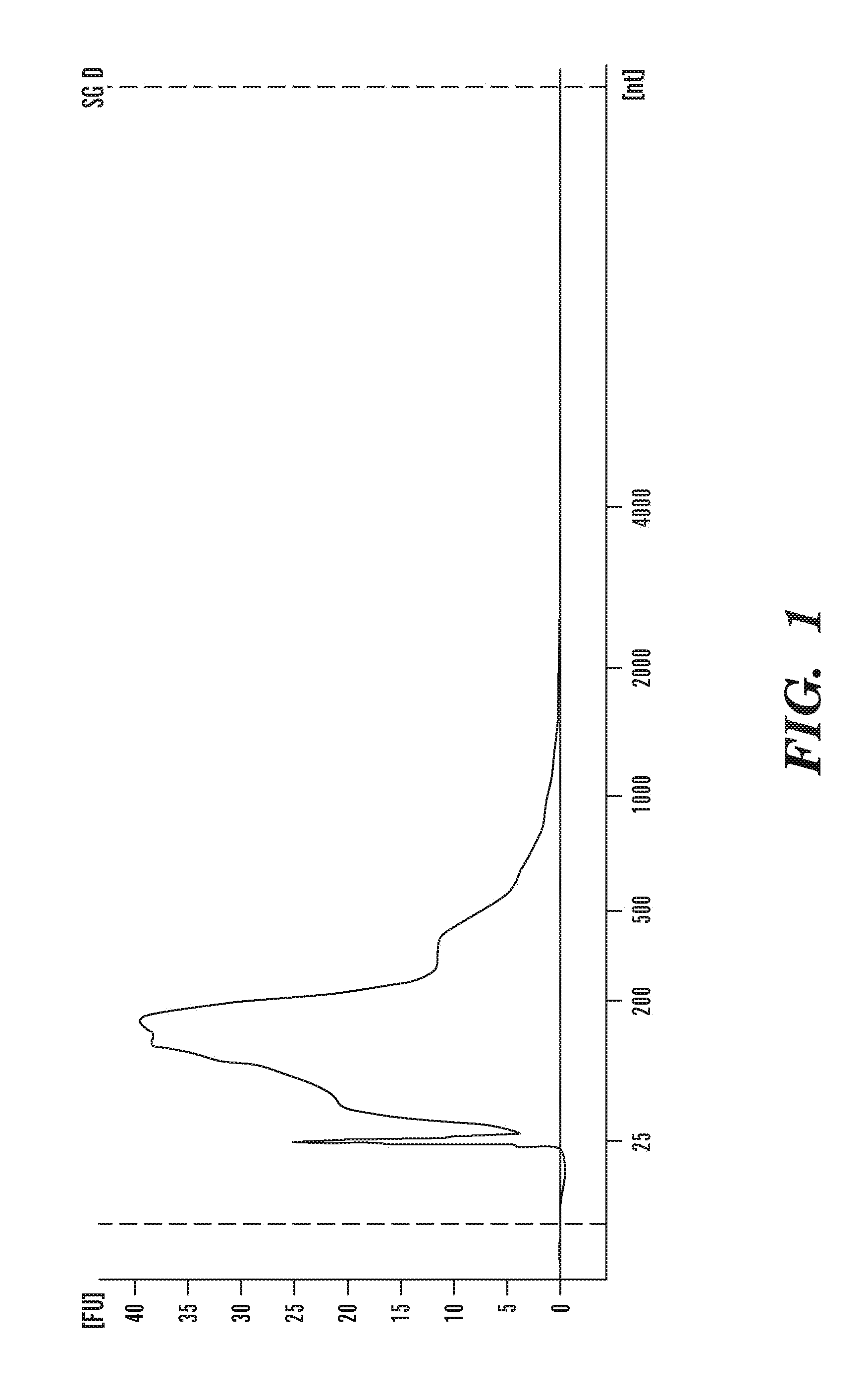
[0158]For the extraction of RNA from microvesicles, the pelleted microvesicles were incubated in an RNAse inhibitor solution for 20 minutes at room temperature. The RNase inhibitor can be obtained from various known vendors, e.g., SUPERase-In (Ambion Inc). Total RNA was then extracted from the RNAse-treated microvesicles using miRNeasy RNA extraction kit (Qiagen). Alternatively, various commercial RNA extraction kits such as the QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit from Qiagen, QIAamp viral RNA mini kit (Qiagen) and the MirVana RNA isolation kit from Ambion...
example 2
[0163]Positive and Negative Control Reactions For the Detection of Kras Exon 4 and Kras G12A Mutations.
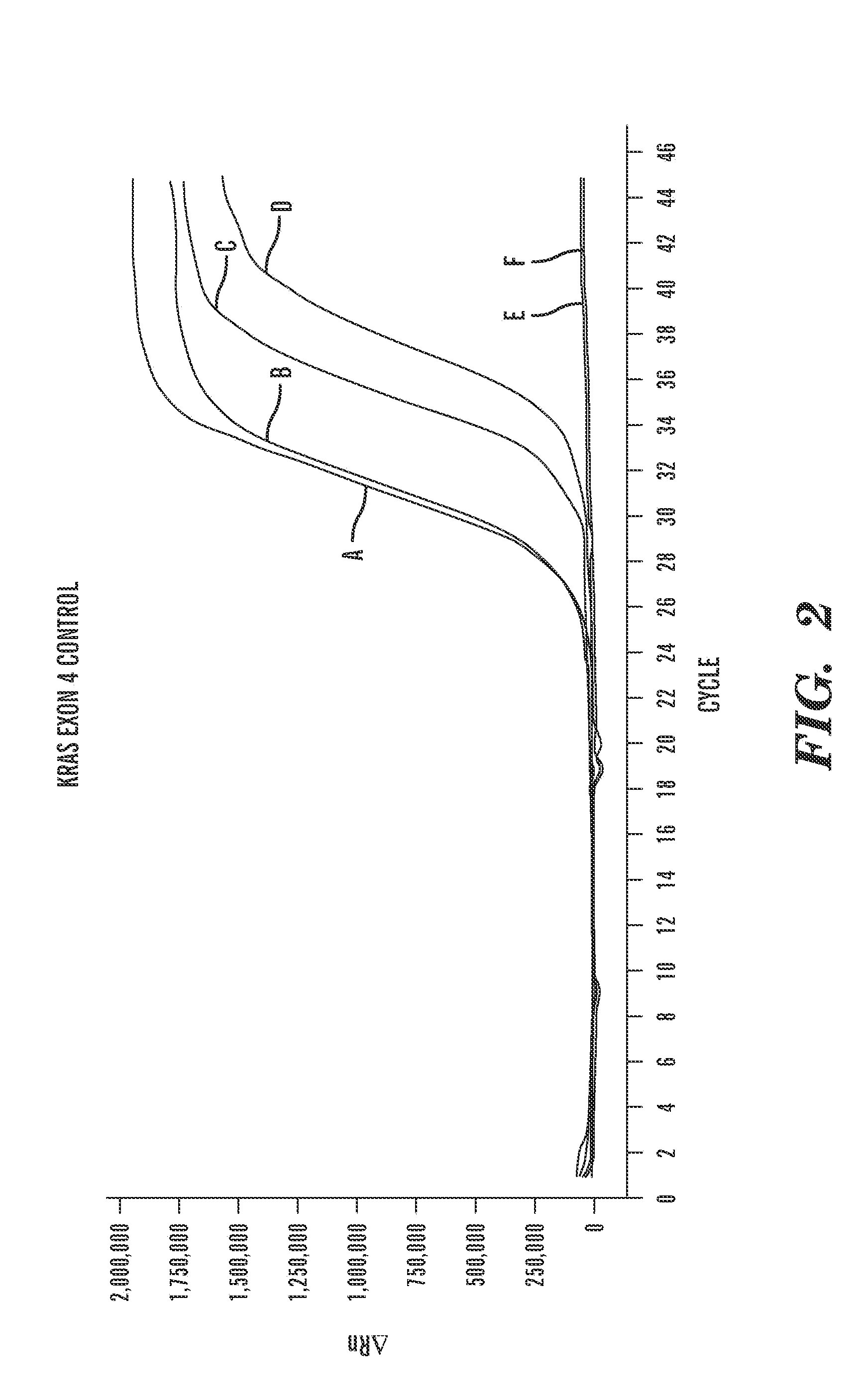
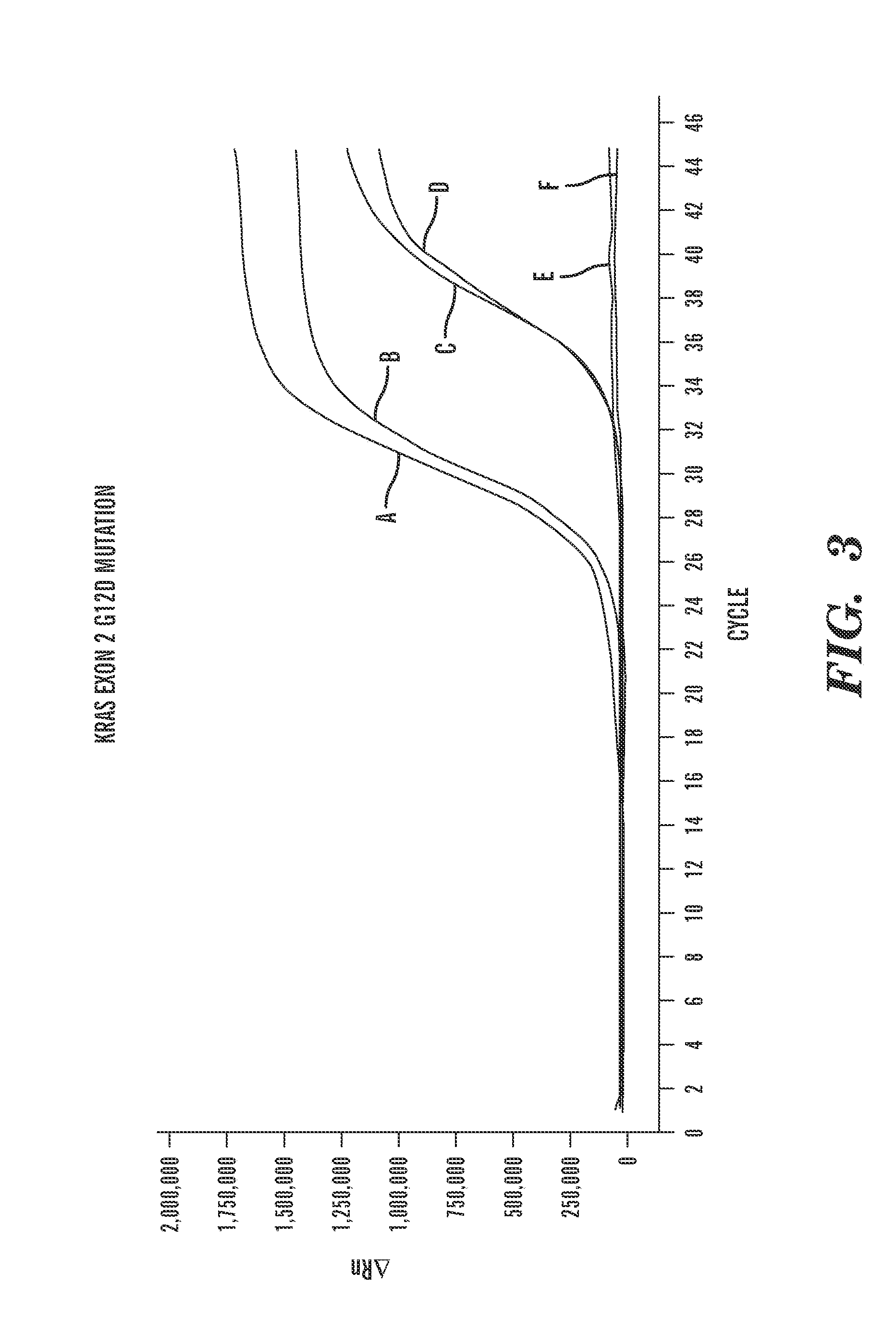
[0164]Scorpion® Kras mutation detection PCR reactions to detect Kras Exon 4 were performed on positive and negative controls (FIG. 4(a)). Scorpion® Kras mutation detection PCR reactions to detect Kras G12A mutations were performed on positive and negative controls (FIG. 4(b)). As is shown in FIG. 4, the positive controls can be detected and the negative controls cannot.
example 3
[0165]DNase pre-treatment in method of analyzing Kras Exon 4 in RNA and DNA associated with microvesicles isolated from serum and plasma samples.
[0166]Following proper protocols, serum and plasma samples were obtained for the following analysis, from a patient diagnosed with colorectal cancer and having a Kras G12A mutation, confirmed by pathology evaluation of a biopsy.
[0167]Microvesicles were isolated as described previously in Example 1. Prior to isolation of nucleic acids from the microvesicles, a subset of the isolated microvesicles was pre-treated with DNase (Turbo™ DNase (Ambion®)) in order to eliminate or substantially eliminate any DNA located on the surface of the microvesicles or outside of the microvesicles. The remaining subset of microvesicles was left untreated. Samples of nucleic acid (both RNA and DNA) were obtained for analysis as described previously in Example 1. The RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA, as described in Example 1. The purified cDNA (FIG. 5(a)) a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com