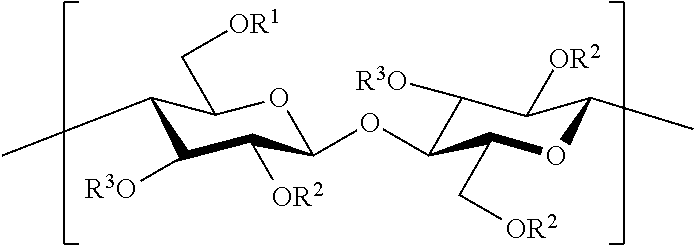
Process for dispersing cellulose esters into elastomeric compositions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0130]In this example, elastomeric compositions were produced using the masterbatch process. A number of different cellulose ester concentrates were prepared and subsequently combined with elastomers to produce the elastomeric compositions.
[0131]In the first stage of the masterbatch process, cellulose esters were bag blended with styrenic block copolymer materials and then fed using a simple volumetric feeder into the chilled feed throat of a Leitstritz twin screw extruder to make cellulose ester concentrates (i.e., masterbatches). The various properties of the cellulose esters and styrenic block copolymer materials utilized in this first stage are depicted in TABLES 1 and 2. All of the recited cellulose esters in TABLE 1 are from Eastman Chemical Company, Kingsport, Tenn. All of the styrenic block copolymers in TABLE 2 are from Kraton Polymers, Houston, Tex. The Leistritz extruder is an 18 mm diameter counter-rotating extruder having an L / D of 38:1. Material was typically extruded ...
example 1 (
Example 1(s)
[0156]In this example, 90 weight percent of Eastman CA 398-3 was melt blended with 10 weight percent of triphenyl phosphate to produce a plasticized cellulose acetate pre-blend. Subsequently, 40 weight percent of this plasticized cellulose acetate was melt blended with 60 weight percent of Kraton FG 1924. The materials were compounded using a medium shear screw design at max zone temperatures of 200° C. and a residence time of less than one minute. The cellulose ester concentrate was combined with the base rubber formulation at a 66.7 / 33.3 weight ratio and mixed in a Brabender mixer. The final formulation contained 33.3 weight percent of base rubber, 40 weight percent of Kraton FG 1924, 20 weight percent of CA 398-3, and 6.67 weight percent of triphenyl phosphate. The particles were evenly dispersed and had particle sizes of less than 1 micron. Note that this material will exhibit minimal flow at 160° C. so any subsequent mixing with a primary elastomer will involve the ...
example 2 (
Example 2(b)
[0166]The carrier elastomer in example 2(b) was Kraton® D1118 rubber, and the cellulose ester was CAB 381-0.1. The twin screw masterbatch (TSMB2B) was added in the 2nd stage of the Banbury mixing. The material properties can be seen in Table 4C, and the data show that the Mooney Viscosity had been reduced compared to the control, the dispersion was similar, and the storage modulus at 30° C. increased. The measured tan delta decreased relative to the comparative example, while the molded groove tear was slightly higher.
Comparative Examples 3(a) and 3(b) and Examples 3(a) through 3(l)
[0167]
TABLE 5A-1Example #CE-3(a)CE-3(b)3(a)3(b)3(c)Buna VSL 5025-2S-SBR1,89.3858.4358.4358.4375.6337.5phr TDAE2,high vinyl (67%of BD), 25% SCB24PBD3 rubber3535353535Ultrasil ® 7000Silica8065656565GR4N234Carbon Black1515151515Si 266Coupling agent6.245.075.075.075.07Tudalen 41925Process08.458.458.453.75AdditiveStearic acidCure Activator1.51.51.51.51.5Stage 2 mix conditions (settings)masterbatchM...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com