Methods of manufacturing bioactive gels from extracellular matrix material
a bioactive gel and extracellular matrix technology, applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of additional regulatory barriers to marketing, degradation of gel bioactivity, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing the number of purification steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
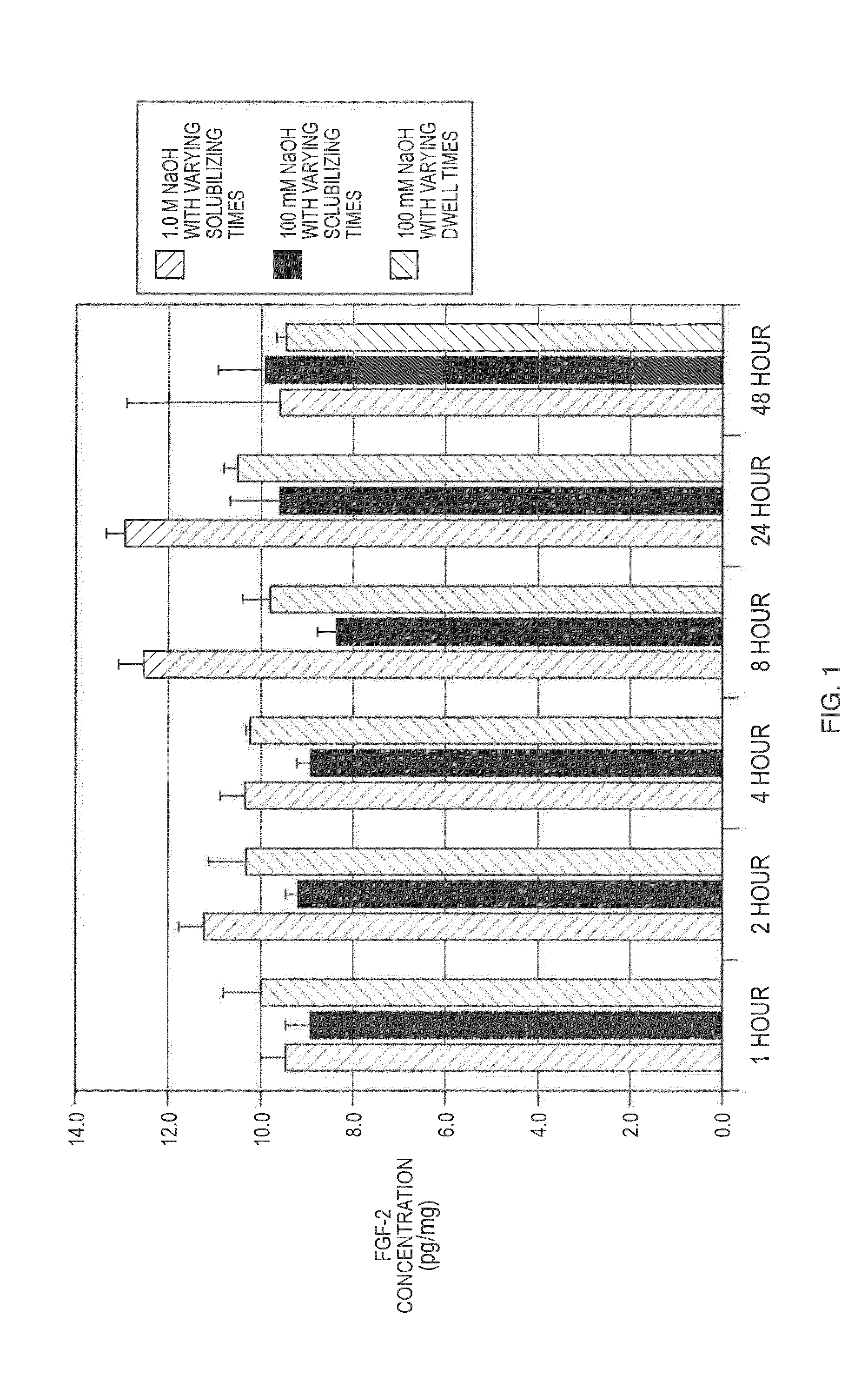
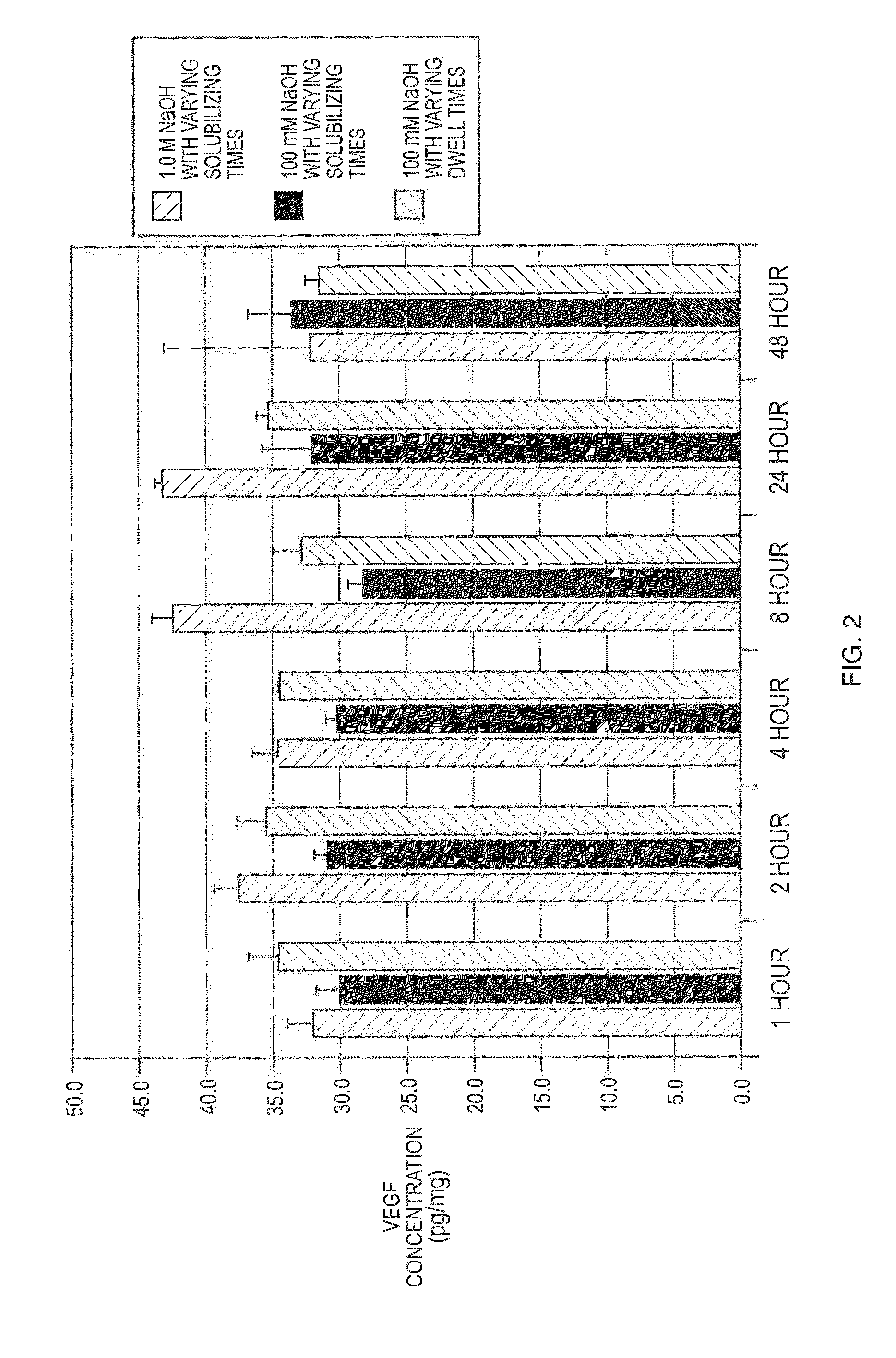
[0011]The present invention is directed to methods of manufacturing bioactive gels from ECM, i.e., gels which retain bioactivity, and can serve as scaffolds for preclinical and clinical tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches to tissue reconstruction. As will be described in detail below, these manufacturing methods take advantage of a new recognition that bioactive gels from ECM can be created by treating a particularized ECM in a basic environment, which when neutralized with acid provides bioactive gels.
[0012]In accordance with the inventive methods, the ECM may be derived from native mammalian tissues including but not limited to submucosa, dermis, epithelial basement membrane, aponeurosis, fascia, tendon, ligament, smooth and skeletal muscle and treatment site-specific ECM. The native mammalian tissue source may be porcine, bovine, ovine, allogenic, or autogenic, for example. For example, the ECM may be SIS (small intestinal submucosa), UBS (urinary bladder subm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com