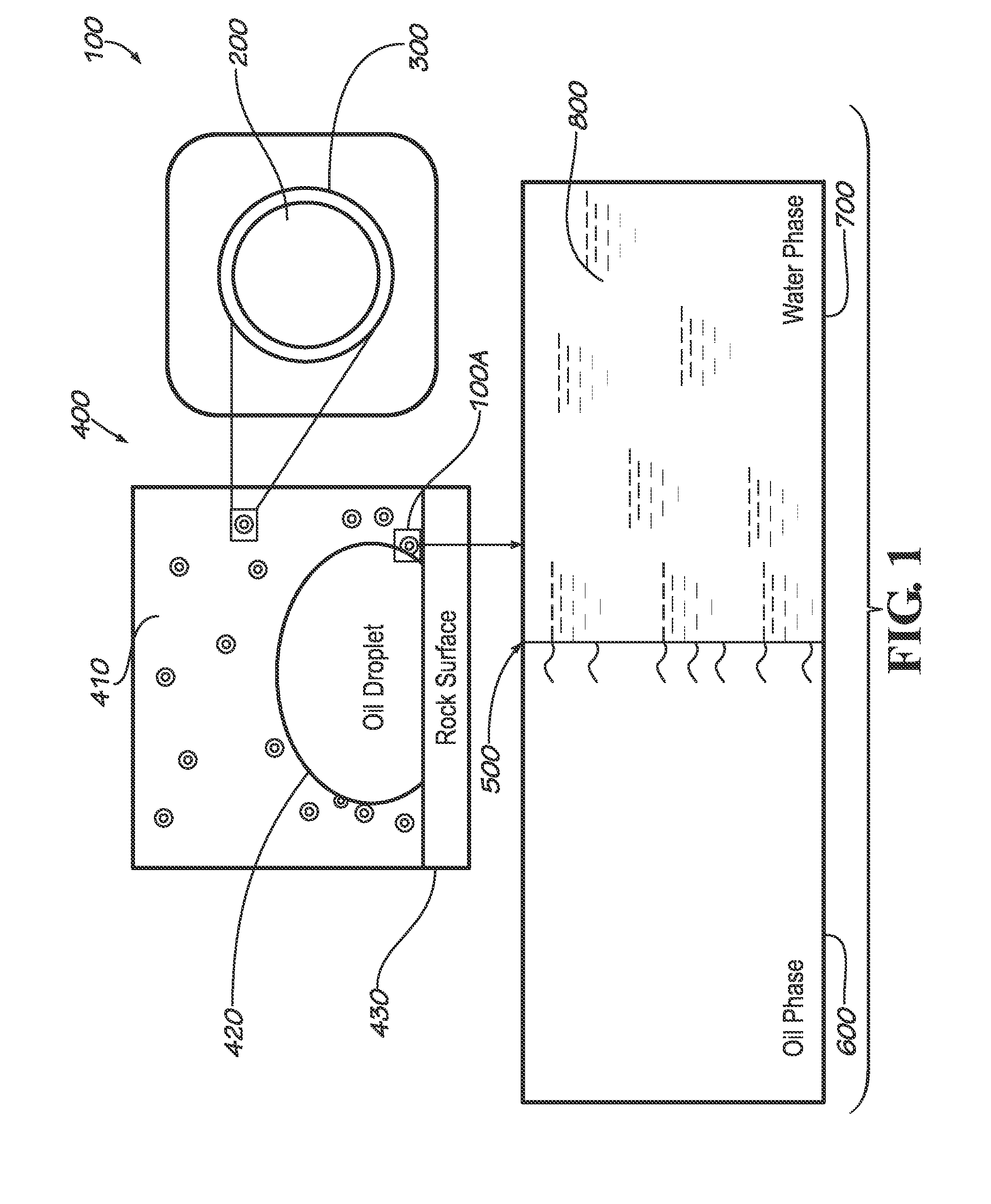
Smart polymer flooding process
a polymer flooding and polymer technology, applied in the direction of earthwork drilling, wellbore/well accessories, drilling composition, etc., can solve the problem of small particles that may be required, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of polymer used and increasing eor efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
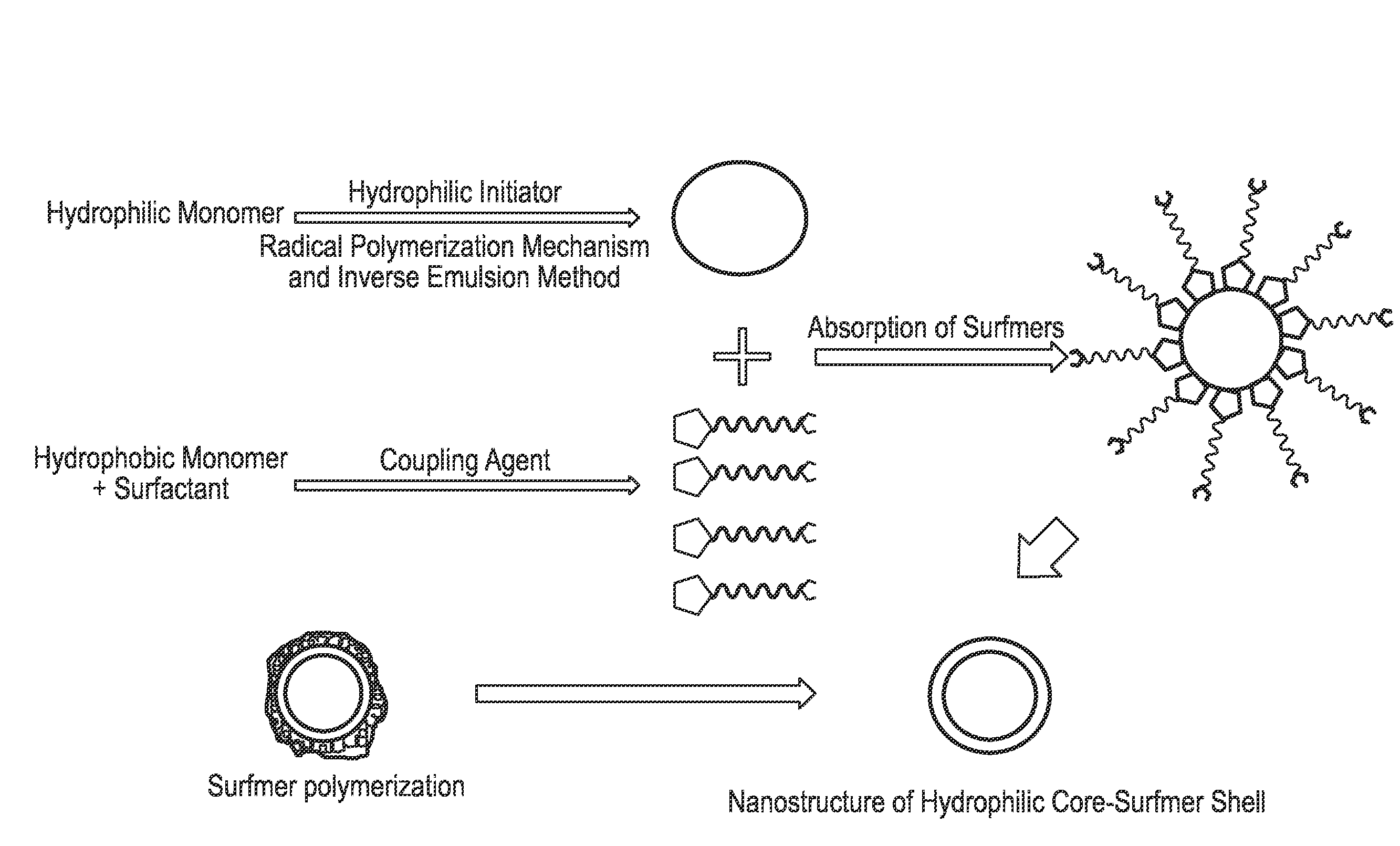
Nanostructure of Hydrophilic Core-Block Copolymer Shell (PAM / PAM-c-PS)
[0085]In this exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a first, 60 ml of hexane solvent and 0.0035 ml of a surfactant sorbitane monooleate (span 80) in a reactor are mixed by a mechanical mixer at a speed of about 2000 rpm. Then, an aqueous solution, including 5 g acrylamide and 20 ml water, is added to the previous solution under mixing and nitrogen purging by the microinjection method that produce emulsion of nanoparticles in the organic phase. After the completion of a water phase emulsion in organic thinner, the redox initiator system, including ferrous sulfate and potassium per sulfate, is added to the emulsion system with amounts 0.001688 and 0.0007225 g, respectively, at a temperature of about −15° C. With the injection of the initiator, the core polymerization process starts and the required time for completion of this process is about 30 minutes. At that time 0.2 ml styrene monomers are added to t...
example 2
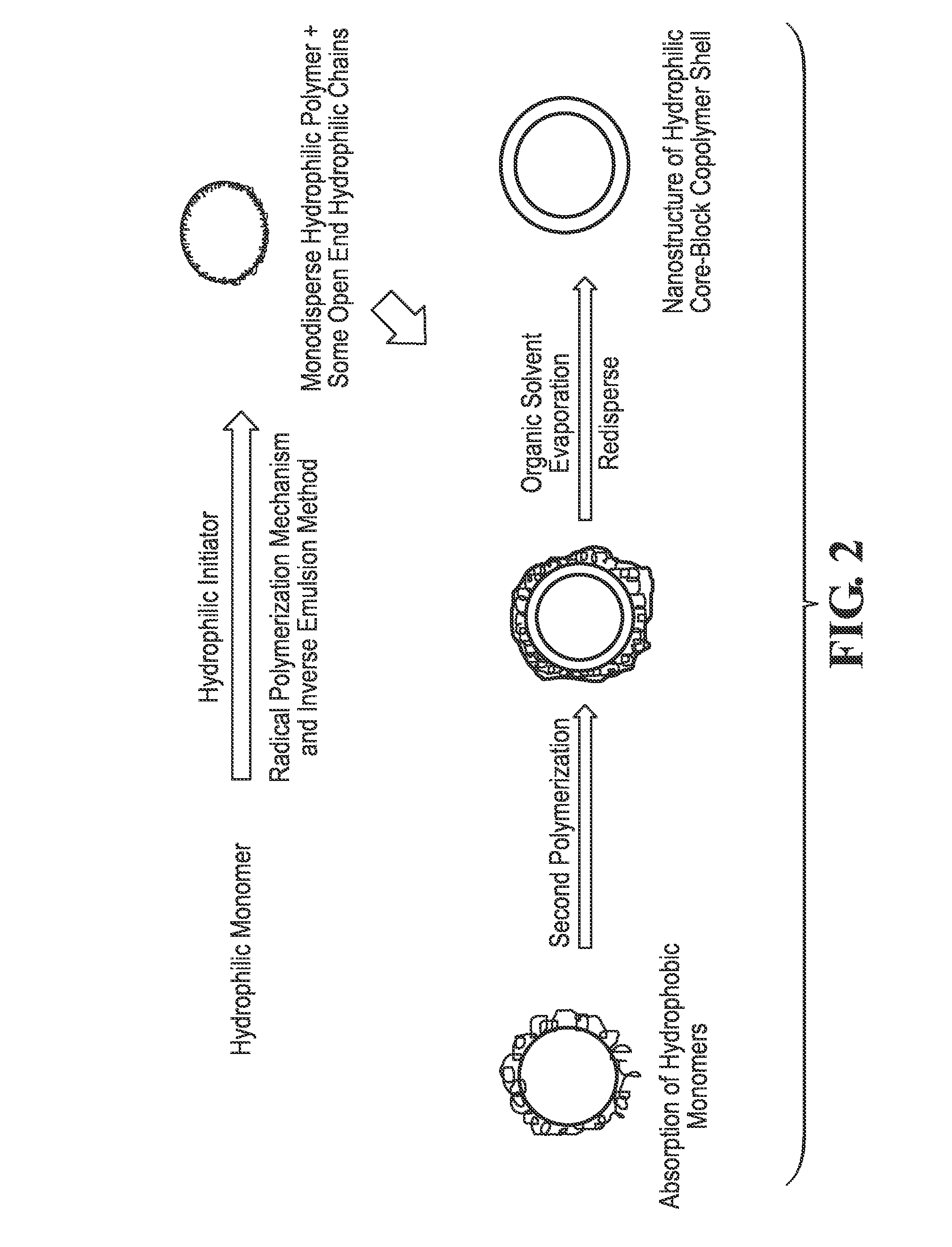
Nanostructure of Hydrophilic Core-Block Copolymer Shell (TVP / PAM-c-PS)
[0090]A thermoviscosifying water soluble polymer (TVP) with the molecular weight of 5 million Daltons was synthesized by radical copolymerization of acrylamide with a newly-developed thermo sensitive monomer, MPAD. At this time 0.4 ml styrene monomers were added to the reaction environment. The chains which reached to the termination step make the core polymer, and surviving long chains make block copolymers that include internal hydrophilic and external hydrophobic parts. The chain transfer should be considered in a special time (e.g., shell polymerization time: 15 min) to prevent high propagation of the polymer chains. The polystyrene layer is soluble in hexane solvent, and should be removed from the reactor, which prevents the tenacity of the particles and changing of the size distribution. This removal is preferably done via a low speed rotary as a solvent evaporator. Then, the remaining materials are spraye...
example 3
Nanostructure of Hydrophilic Core-Surfmer Shell (PAM / Surfactant-PS)
[0095]Polymerized surfactants, including dodecylsulfate (SDS) as an internal part and styrene monomer as an external part are synthesized as follows. An aqueous solution of SDS corresponding to 1:1 molar ratio with respect to styrene is mixed with the salt of styrene based. The interchange of ions produces the precipitation of the sulfate salt of styrene because of the much lower solubility of this salt in water at room temperature. Salt purification was performed by saturation of an aqueous solution at temperature 50° C. Then the solution is cooled under normal conditions. After refrigeration of the supernatant at 4° C. for 5 hours, the solid is recovered by filtration on a filter paper and dried under vacuum at 40° C.
[0096]For producing core nanoparticles, 30 ml of Toluene and 0.043 g of the synthesized surfmer are mixed strongly via a high speed homogenizer to produce a stable micelle system in the reactor. Then...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com