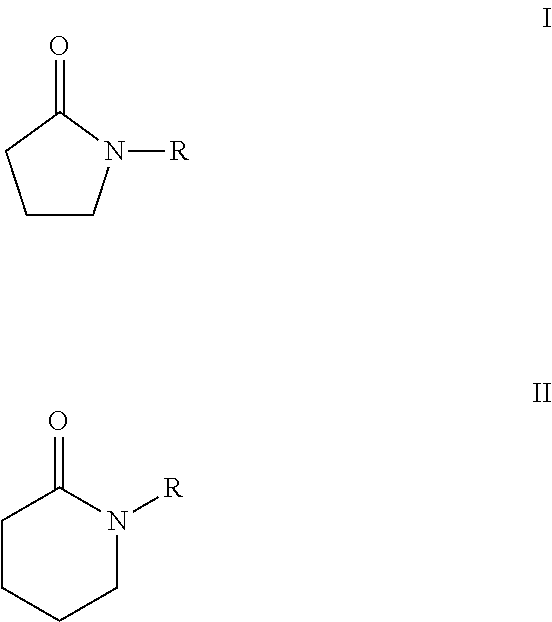
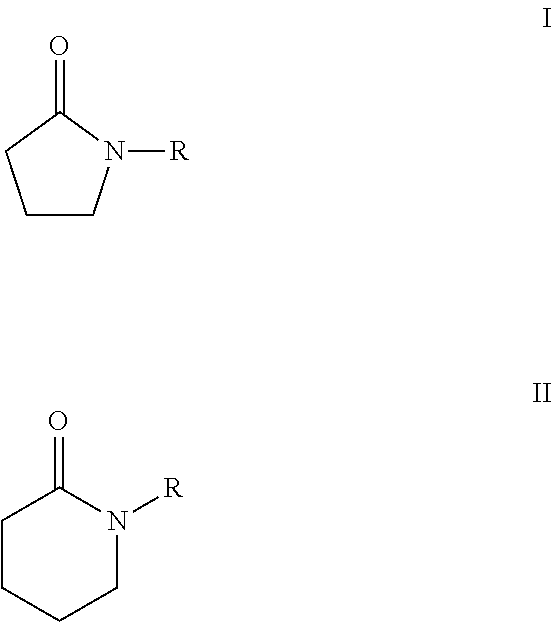
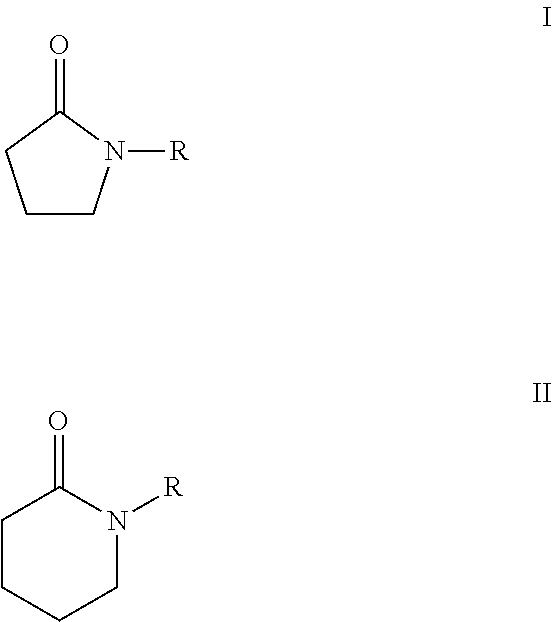
Processes for making cyclohexane compounds
a technology of cyclohexane and process steps, which is applied in the preparation of organic compounds, carboxylic preparations by ozone oxidation, and organic chemistry. it can solve problems such as additional process steps, and achieve favorable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0069]Hydrogenation of benzenecarboxylic Acids to cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids
[0070]Except as otherwise stated in the individual examples, the following procedures were used for hydrogenation of benzenecarboxylic acids to cyclohexanecarboxylic acids. A 100 ml autoclave configured in a high pressure AUTO-MATE System Model 4590 (H.E.L. Inc., Grand Rapids, Mich.) with a drop-in catalyst basket (volume 7 ml) was used. The catalyst was placed in the basket in an amount equal to the lesser of 2.0 grams or the amount that would fit in the basket. The autoclave was then pressurized to 1500 psig with nitrogen. Nitrogen was slowly vented then the feed manifold to the reactor was then purged twice with by passing hydrogen gas through at atmospheric temperature. To activate the catalyst, the reactor was then purged three times by pressurizing with hydrogen to 150 psig, then venting to ambient pressure each time. Agitation at 450 rpm commenced and the reactor was heated to 150° C. Hydrogen was th...
examples 1 and 2
TPA hydrogenation to CHDA in NMP / water as a Solvent
[0077]The catalyst used was 1% Ru loaded on 1 / 4″ carbon granules (1% Ru / C, Lot # SE09051, BASF Corporation, Iselin, N.J.). The solvent in Example 1 was a mixture of 50 parts NMP and 16 parts deionized water. The solvent in Example 2 was NMP. The filtered resultant solution was analyzed by the GC method described above to quantify TPA, CHDA and other byproducts. Results are presented in Table 1 below.
TABLE 1TPA hydrogenation to CHDA in the presence ofNMP as a solvent.TPACHDAMassExampleConversion %Selectivity %Balance %186718624596.593
[0078]The results shown in Table 1 suggest that NMP is a suitable solvent for highly selective production of CHDA from TPA. In the presence of water, although the conversion increases, the selectivity drops from 96% to 71%, the conversion increases from 45% to 86%. GC-MS was conducted for Example 2. The GC wt. % accountability for Example 2 was 101.4% and the cis / trans ratio of product CHDA was 4.4.
example 3
TPA hydrogenation to CHDA in NEP as a Solvent.
[0081]Example 2 was repeated but instead of N-methyl 2-pyrrolidone (NMP) as a solvent, N-ethyl 2-pyrrolidone (NEP) was used as a solvent. The GC wt. % accountability for Example 4 was 91.3% and the cis / trans ratio of product CHDA was 4.6.
TABLE 3TPA hydrogenation to CHDA in the presence of NEP as a solvent.TPACHDAMassExampleSolventConversion %Selectivity %Balance %3NEP71.682.395
[0082]As can be seen from the result in Table 3, NEP is a suitable solvent for TPA hydrogenation to CHDA much like NMP.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com