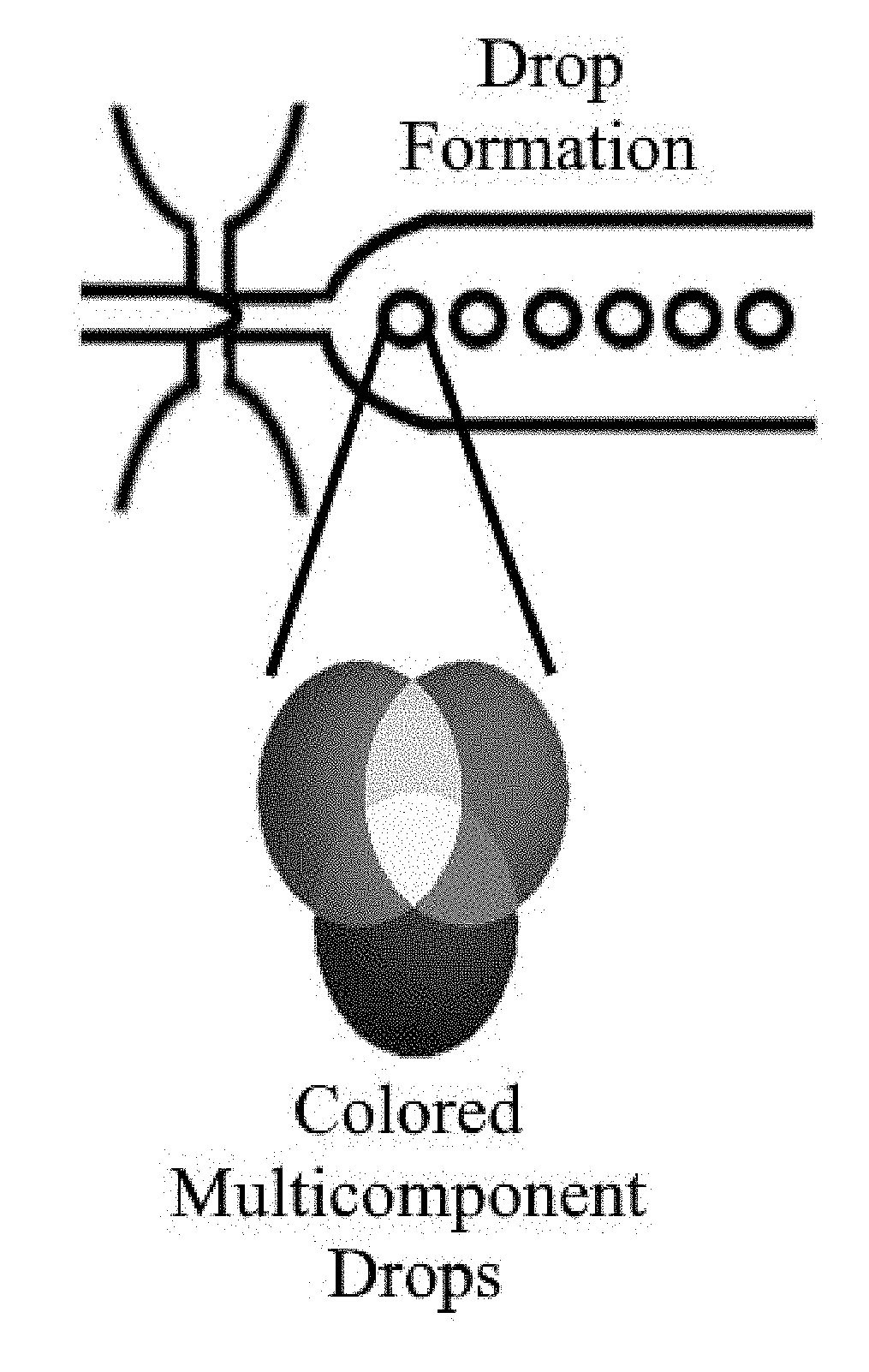
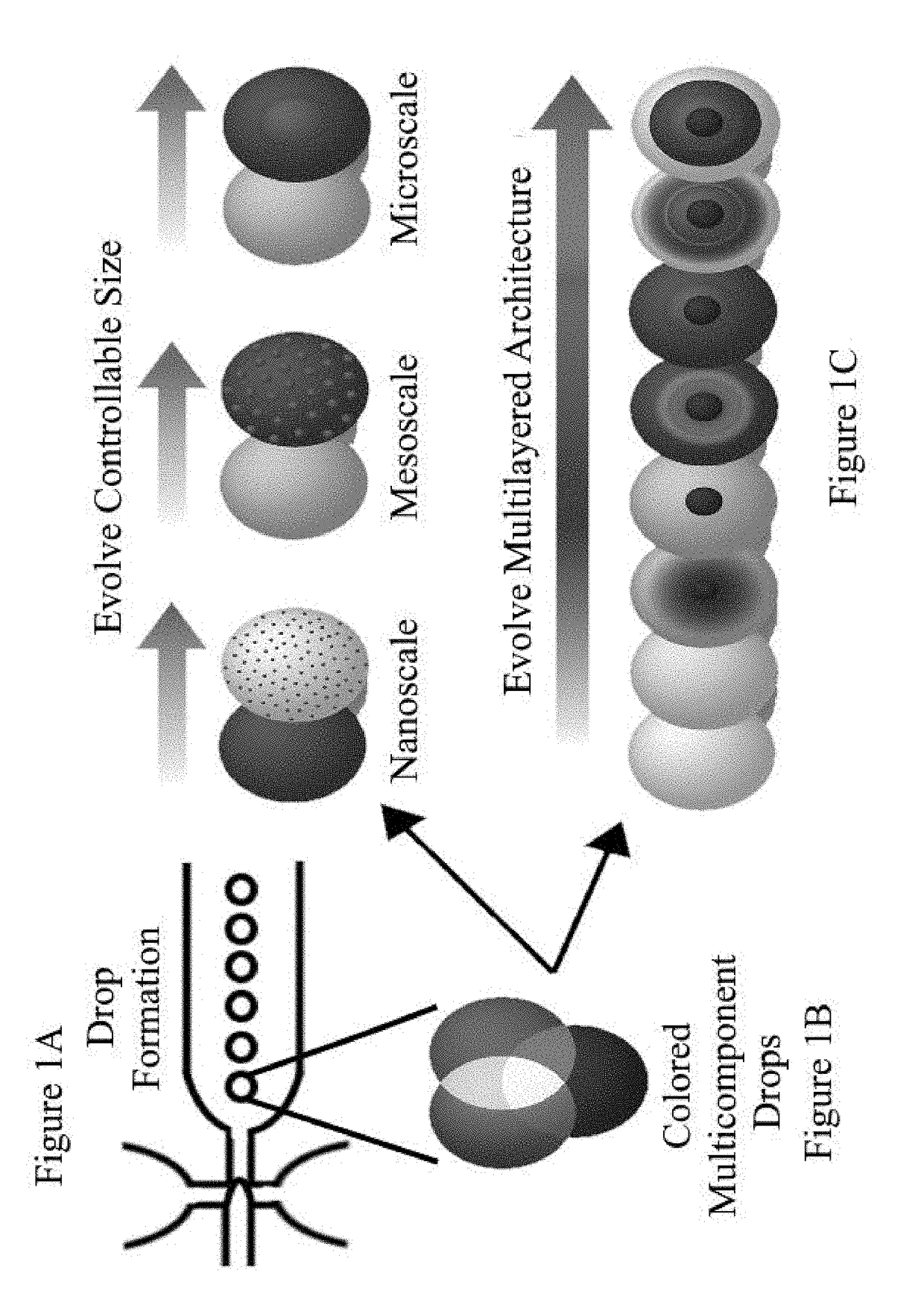
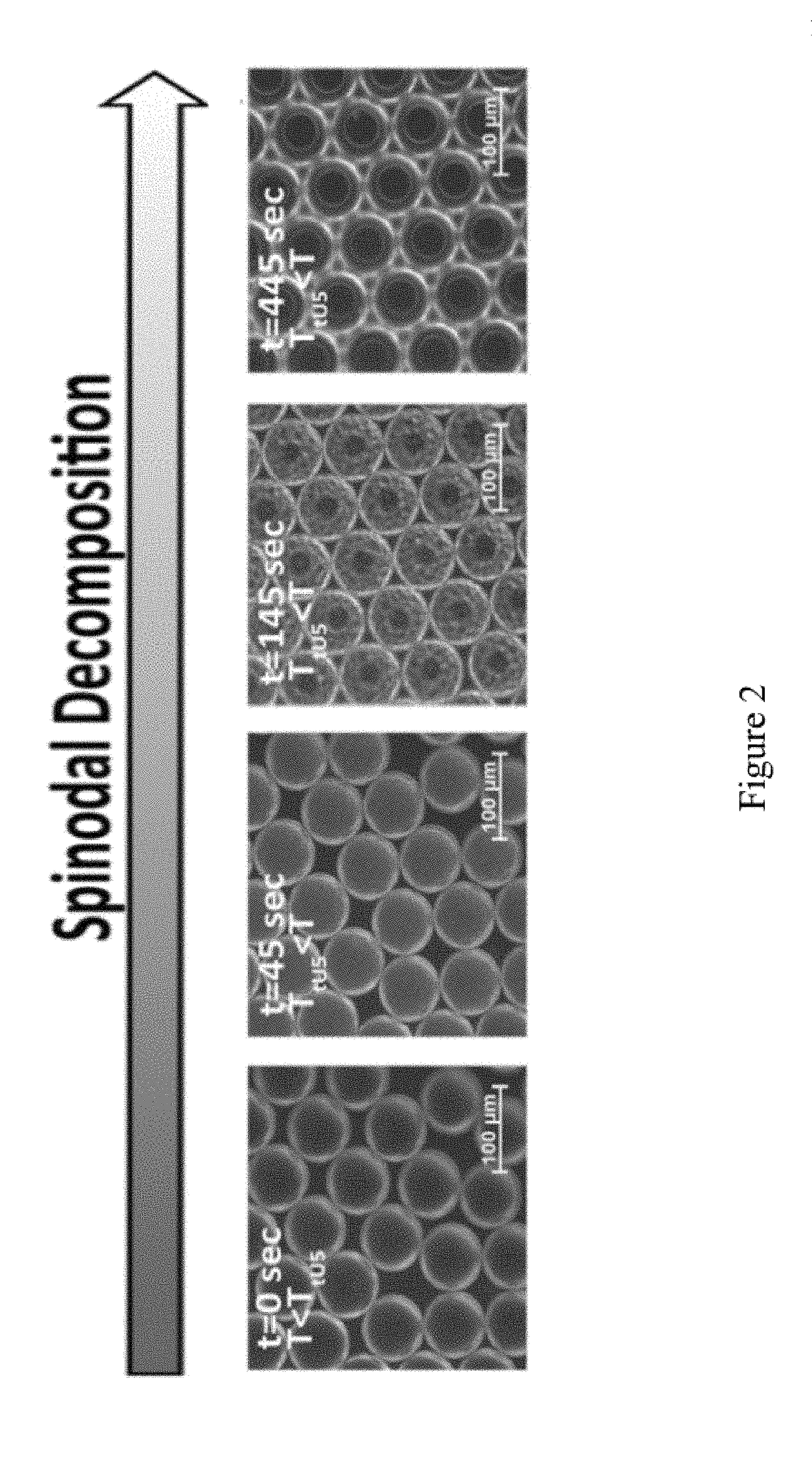
Programmable liquid, gel and biohybrid compartments and methods of use
a technology of biohybrid compartments and liquids, applied in the field of programmable liquids, gels and biohybrid compartments and methods of use, can solve the problems of complex and specialized fluidic devices, inability to broaden the platform for in vitro programming of hierarchical multi-phase structures, and limited approaches to varying extents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021]For the purposes of promoting an understanding of the principles of the present disclosure, reference will now be made to preferred embodiments and specific language will be used to describe the same. It will nevertheless be understood that no limitation of the scope of the disclosure is thereby intended, such alteration and further modifications of the disclosure as illustrated herein, being contemplated as would normally occur to one skilled in the art to which the disclosure relates.
[0022]Articles “a” and “an” are used herein to refer to one or to more than one (i.e. at least one) of the grammatical object of the article. By way of example, “an element” means at least one element and can include more than one element.
[0023]Unless otherwise defined, all technical terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this disclosure belongs.
[0024]The presently disclosed invention provides the ability to program the self-as...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase separation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydrophilic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydrophobic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com