Methods and compositions for treating myelofibrosis
a technology of compositions and myelofibrosis, applied in the field of methods and compositions for treating myelofibrosis, can solve the problems of unmet needs for effective therapies, high treatment-related mortality, and many other currently available treatments that are not effective in reversing the process of myelofibrosis, and achieve the effects of reducing splenomegaly, fibrosis, and extramedullary hematopoiesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
n of ActRIIB-Fc Fusion Proteins
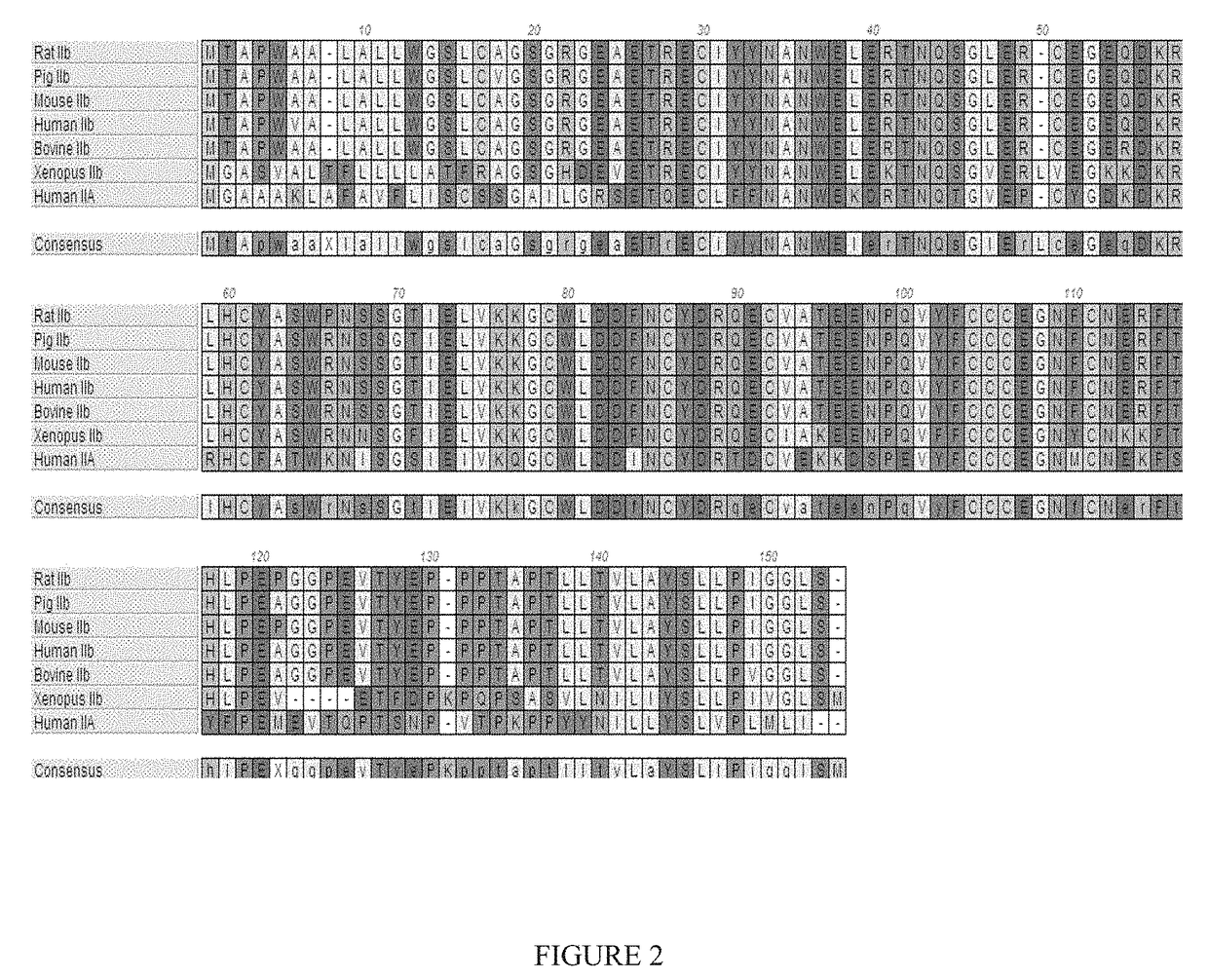
[0275]Applicants constructed a soluble ActRIIB fusion protein that has the extracellular domain of human ActRIIB fused to a human or mouse Fc domain with a minimal linker (three glycine amino acids) in between. The constructs are referred to as ActRIIB-hFc and ActRIIB-Fc, respectively.
[0276]ActRIIB-hFc is shown below as purified from CHO cell lines (SEQ ID NO: 24):
GRGEAETRECIYYNANWELERTNQSGLERCEGEQDKRLHCYASWRNSSGTIELVKKGCWLDDENCYDRQECVATEENPQVYFCCCEGNECNERFTHLPEAGGPEVTYEPPPTAPTGGGTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLEPPKPKDTLMIS
[0277]The ActRIIB-hFc and ActRIIB-Fc proteins were expressed in CHO cell lines. Three different leader sequences were considered: (i) Honey bee mellitin (HBML):
(SEQ ID NO: 21)MKFLVNVALVFMVVYISYIYA,
ii) Tissue plasminogen activator (TPA):
(SEQ ID NO: 22)MDAMKRGLCCVLLLCGAVFVSP,
and (iii) Native:
(SEQ ID NO: 23)MGAAAKLAFAVFLISCSSGA.
[0278]The selected form employs the TPA leader and has the following unprocessed amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 25):
MDAMK...
example 2
n of a GDF Trap
[0292]Applicants constructed a GDF trap as follows. A polypeptide having a modified extracellular domain of ActRIIB (amino acids 20-134 of SEQ ID NO: 1 with an L79D substitution) with greatly reduced activin A binding relative to GDF11 and / or myostatin (as a consequence of a leucine-to-aspartate substitution at position 79 in SEQ ID NO:1) was fused to a human or mouse Fc domain with a minimal linker (three glycine amino acids) in between. The constructs are referred to as ActRIIB(L79D 20-134)-hFc and ActRIIB(L79D 20-134)-Fc, respectively. Alternative forms with a glutamate rather than an aspartate at position 79 performed similarly (L79E). Alternative forms with an alanine rather than a valine at position 226 with respect to SEQ ID NO: 44, below were also generated and performed equivalently in all respects tested. The aspartate at position 79 (relative to SEQ ID NO: 1, or position 60 relative to SEQ ID NO: 29) is indicated with double underlining below. The valine at...
example 3
for GDF-11- and Activin-Mediated Signaling
[0300]An A-204 reporter gene assay was used to evaluate the effects of ActRIIB-Fc proteins and GDF traps on signaling by GDF-11 and activin A. Cell line: human rhabdomyosarcoma (derived from muscle). Reporter vector: pGL3(CAGA)12 (described in Dennler et al, 1998, EMBO 17: 3091-3100). The CAGA12 motif is present in TGF-beta responsive genes (e.g., PAI-1 gene), so this vector is of general use for factors signaling through SMAD2 and 3.
[0301]Day 1: Split A-204 cells into 48-well plate.
[0302]Day 2: A-204 cells transfected with 10 ug pGL3(CAGA)12 or pGL3(CAGA)12(10 ug)+pRLCMV (1 μg) and Fugene.
[0303]Day 3: Add factors (diluted into medium+0.1% BSA). Inhibitors need to be preincubated with factors for 1 hr before adding to cells. Six hrs later, cells were rinsed with PBS and lysed.
[0304]This is followed by a luciferase assay. In the absence of any inhibitors, activin A showed 10-fold stimulation of reporter gene expression and an ED50˜2 ng / ml. GD...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com