Non-human primate model of age-related macular degeneration and method for producing same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0048]A cynomolgus monkey model of AMD was produced to investigate whether or not the model exhibits histological characteristics unique to human AMD in the retina.
[0049]
[0050]50 μl of sodium iodate solution having a concentration of 20 mg / mL or 30 mg / mL was administered into the vitreous body of one eye of a cynomolgus monkey (dosage of 1 mg or 1.5 mg of sodium iodate per vitreous body) under ketamine anesthesia. Furthermore, the sodium iodate solution was prepared by dissolving sodium iodate in water for injection and preliminarily sterilizing by passing through a filter having a pore size of 0.22 μm.
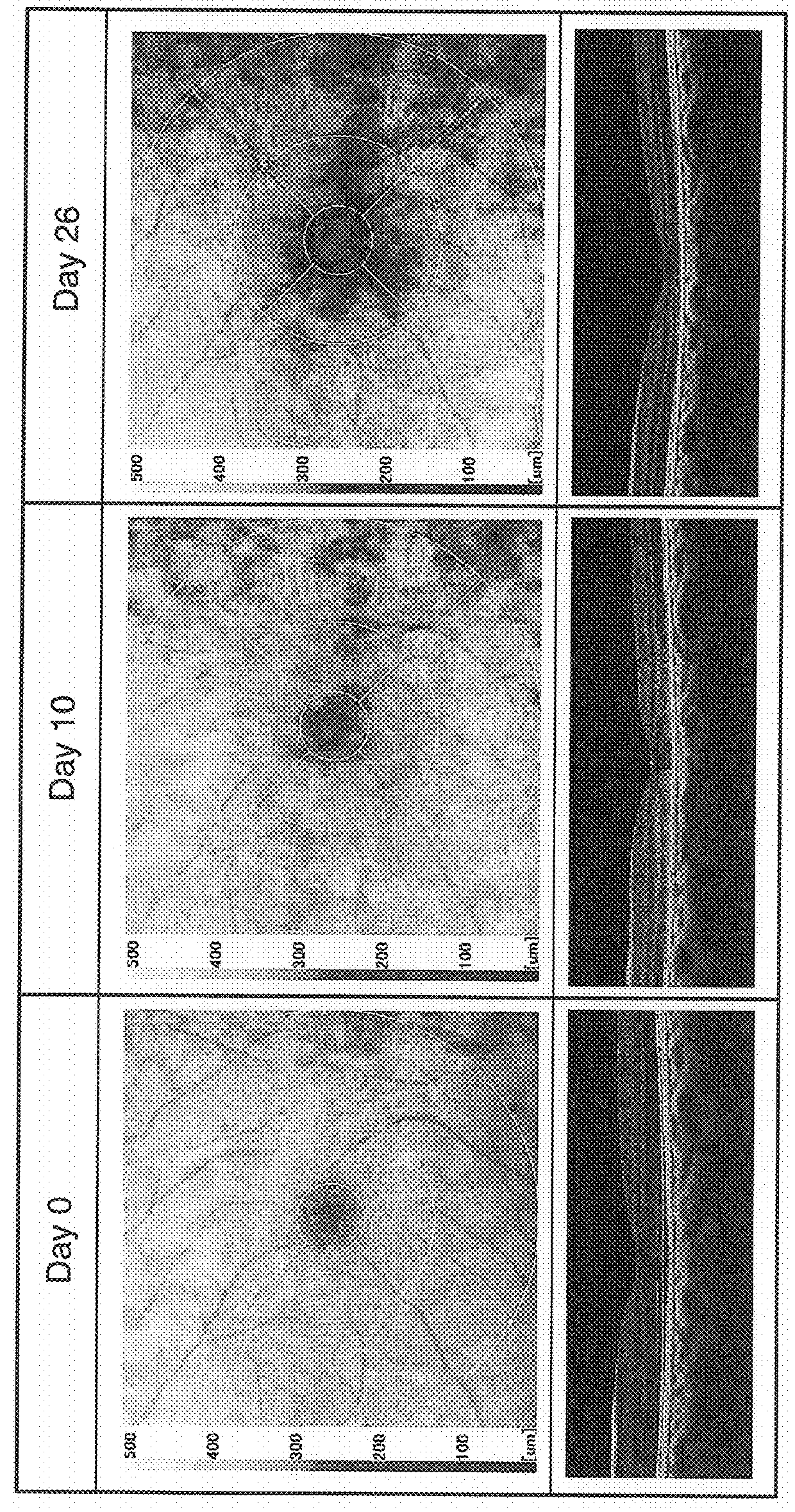
[0051]Retinal thickness of the resulting animal model intravitreally administered sodium iodate was measured prior to administration of the sodium iodate solution (day 0 of administration) and on days 10 and 26 after administration. OCT images of the retina in the vicinity of the central fossa of the macula obtained from these measurements are shown in FIG. 1. The upper row of images ...
example 2
[0053]A cynomolgus monkey model of AMD was produced to investigate whether or not the model exhibits histological characteristics unique to human AMD in the ocular fundus and central fossa of the macula.
[0054]
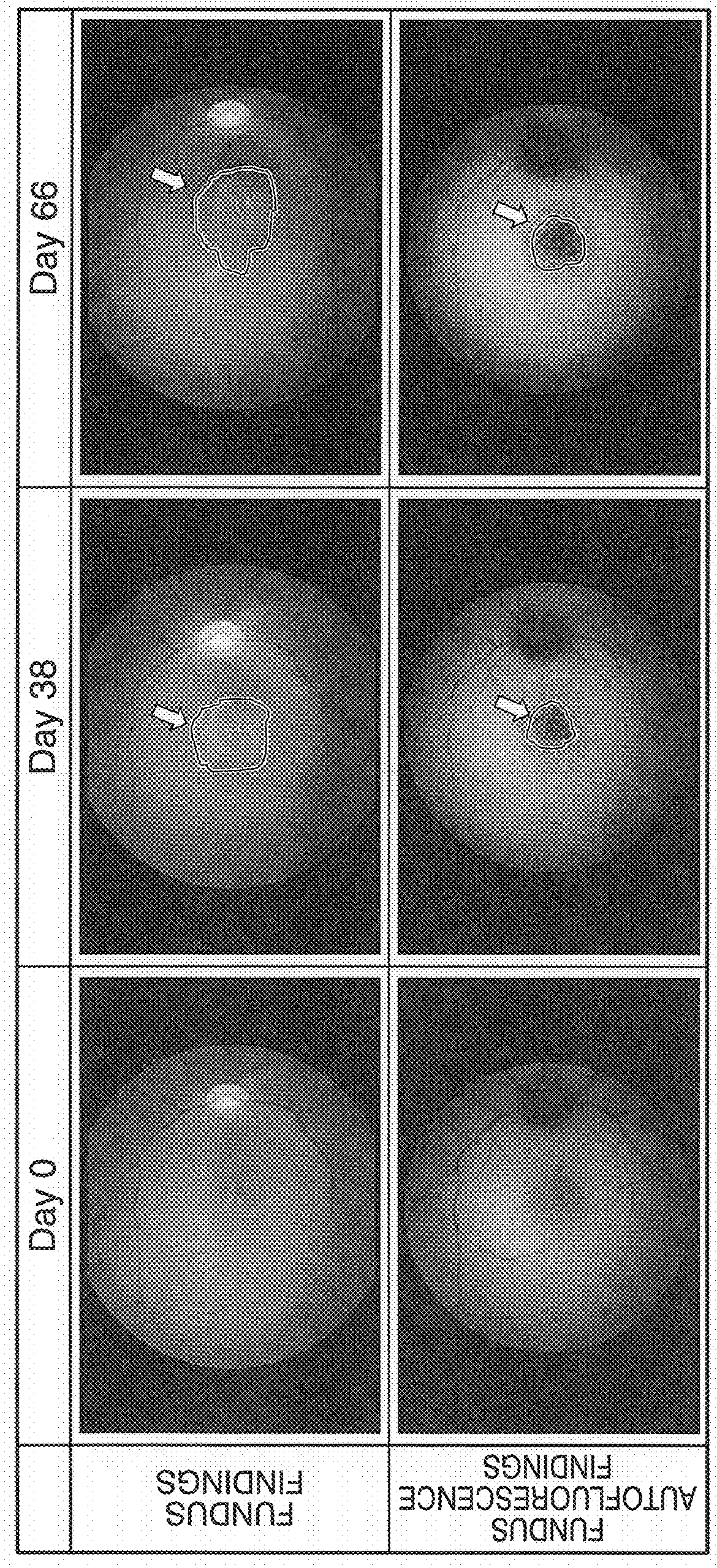
[0055]More specifically, 1.5 mg of sodium iodate per vitreous body were administered into the right eye of a 9-year-old cynomolgus monkey in the same manner as Example 1 to produce an animal model of intravitreal administration of sodium iodate followed by investigating the ocular fundus by funduscopy and fundus autofluorescence prior to administration of the sodium iodate solution (day 0 of administration) and on days 38 and 66 after administration. Funduscopy and fundus autofluorescence were carried out in accordance with routine methods using a fundus camera equipped with an autofluorescence imaging function. In addition, the animal model also underwent fluorescein angiography on day 66 after administration. Fluorescein angiography was carried out in accordance with routine ...
reference example 1
[0062]A cynomolgus monkey model of light-induced retinopathy was produced to investigate the morphology of the retinal tissue of that model by HE staining.
[0063]
[0064]One eye of a cynomolgus monkey immobilized while facing upward was illuminated for 30 minutes with blue light at an illumination intensity of 1800 lux and wavelength of 460 nm from directly overhead at a distance of 5 cm from the eye using a variable wavelength light source. This procedure was carried out for 3 days to produce an animal model of light-induced retinopathy.
[0065]
[0066]Tissue at sites surrounding the central fossa of the resulting animal model of light-induced retinopathy was subjected to HE staining to investigate the morphology of the RPE layer. HE staining was carried out in the same manner as Example 2.
[0067]Images of the HE-stained tissue at sites surrounding the central fossa are shown in FIG. 6. Significant degeneration of the RPE layer was not observed. Detachment of the photoreceptor cell layer f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com