Patents
Literature
114 results about "Non human primate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-human primates occur mostly in Central and South America, Africa, and southern Asia. A few species exist as far north in the Americas as southern Mexico, and as far north in Asia as northern Japan. The Primates order is divided informally into three main groupings: prosimians, monkeys of the New World,...
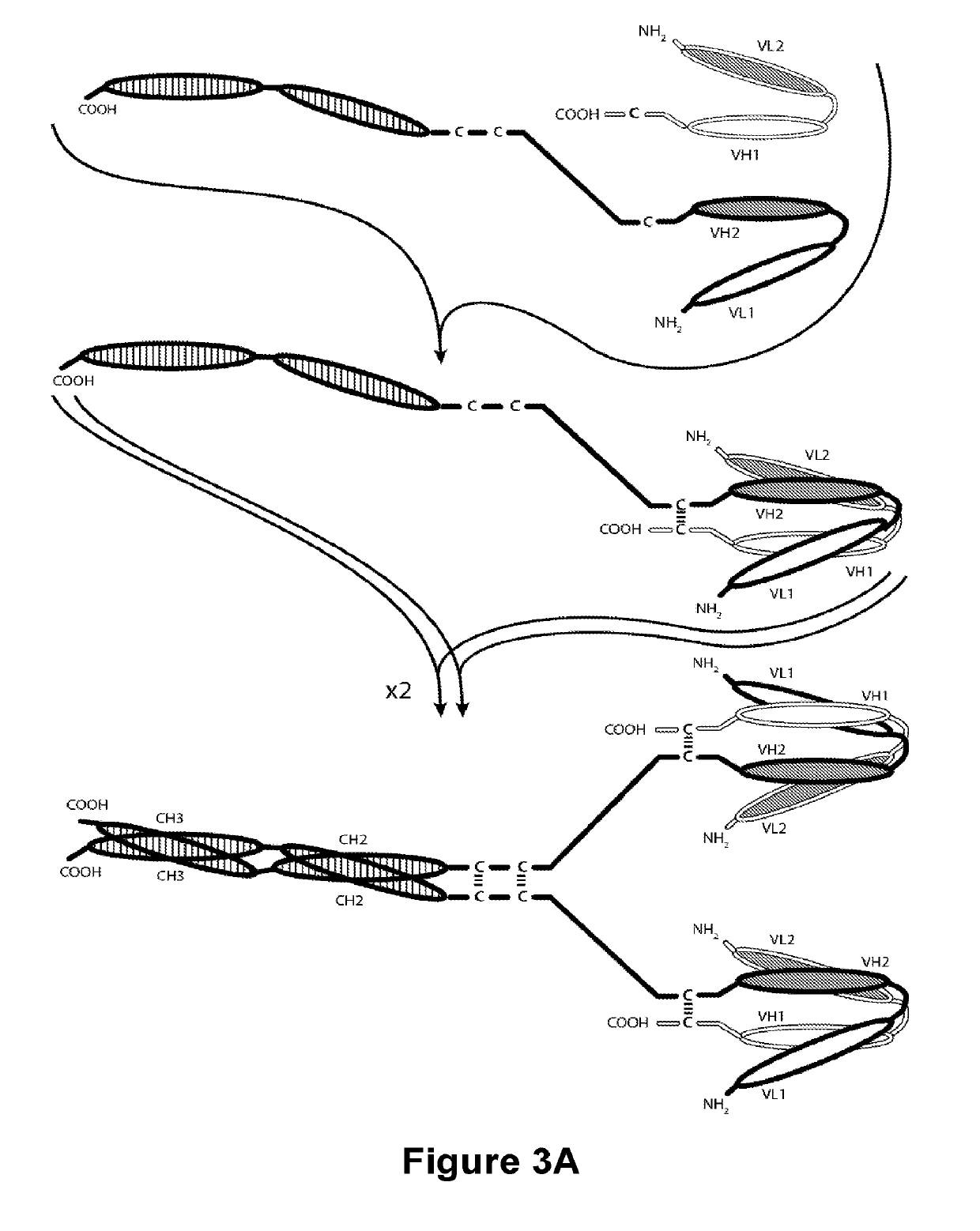
Gynogenetic or androgenetic production of pluripotent cells and cell lines, and use thereof to produce differentiated cells and tissues
InactiveUS20040014206A1Rejection is prevented and reducedEliminate, orMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimateEmbryo
Methods for obtaining pluripotent (embryonic stem) cells from parthenogenetic embryos, especially primates, are provided. These cells are useful for producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs, especially human and non-human primate cells, tissues and organs.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
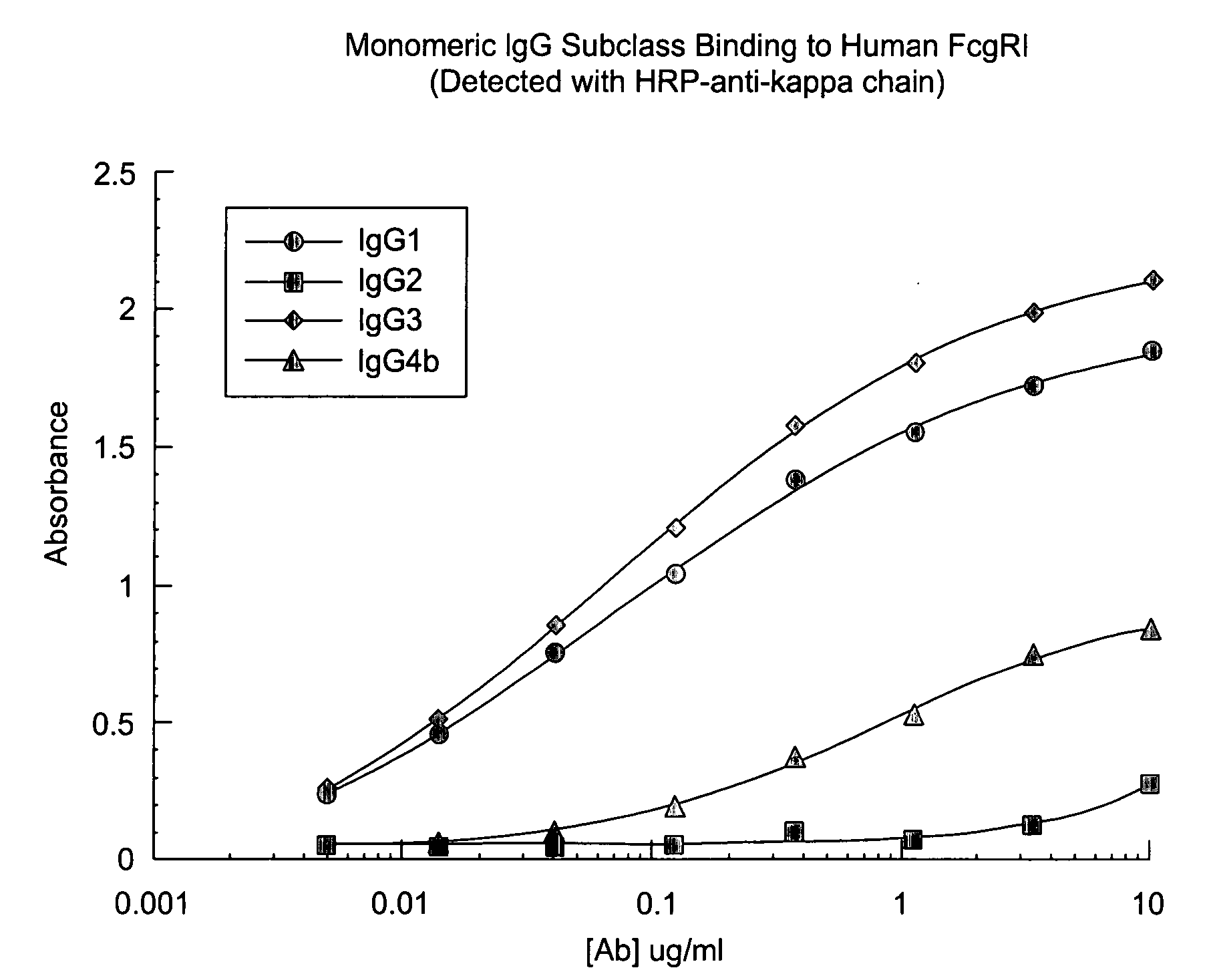
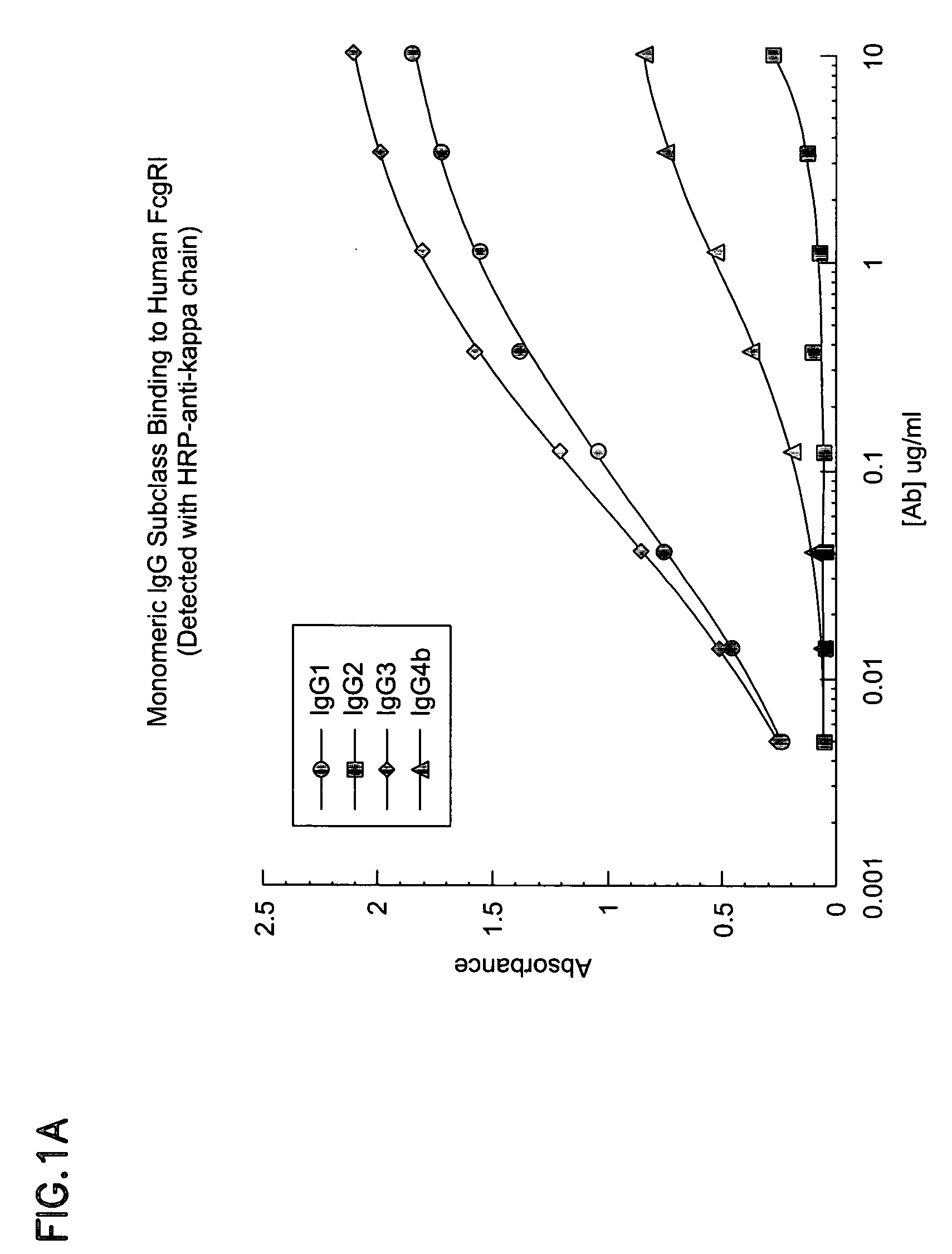
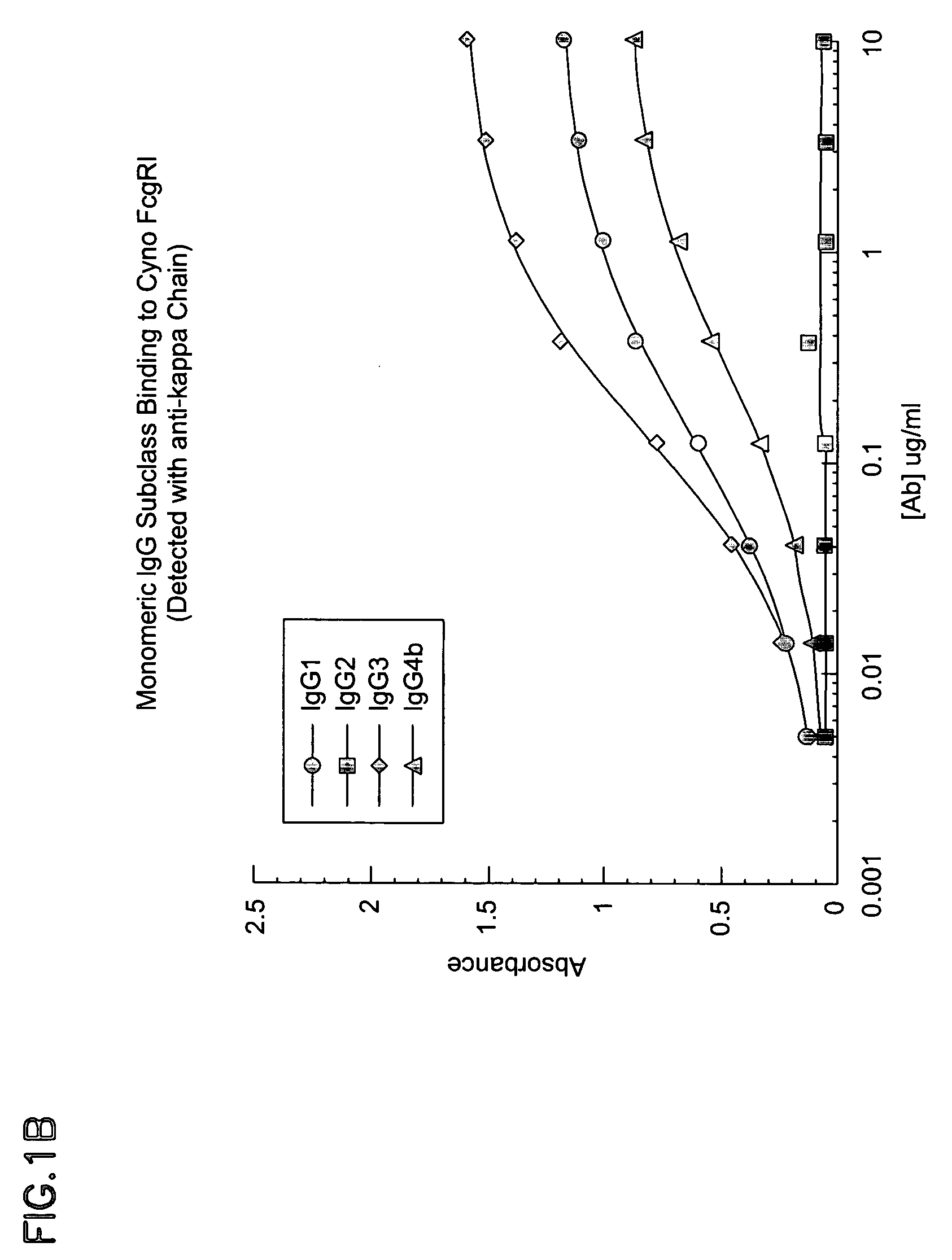
Non-human primate Fc receptors and methods of use
InactiveUS20050054046A1Improve stabilityFacilitate oligomerizationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The invention provides isolated non-human primate Fc receptor polypeptides, the nucleic acid molecules encoding the Fc receptor polypeptides, and the processes for production of recombinant forms of the Fc receptor polypeptides, including fusions, variants, and derivatives thereof. The invention also provides methods for evaluating the safety, efficacy and biological properties of Fc region containing molecules using the non-human primate Fc receptor polypeptides.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for establishing fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model on basis of CRISPR gene knockout technology
InactiveCN103642836APredictive effectReduce the risk of research and developmentVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryDiseaseFragile X chromosome
The invention discloses a method for establishing a fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model on the basis of a CRISPR gene knockout technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a FMR1 gene knockout machin model; (2) carrying out identification and related functional analysis on the machin model; (3) carrying out tests on the nerve characteristics and learning and memorizing ability of the machin model. The method utilizes a CRISPR gene knockout technology to establish a fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model. The model fills the blank of non-human primate model, can effectively stimulate the pathological process of human diseases, can be used as an optimum animal model for researching human diseases, can effectively predict the effect of novel vaccine, novel drug or novel diagnostic reagent in clinical applications, and thus greatly reduces the risk of novel drug development.
Owner:SUZHOU TONGSHAN BIO TECH
Gynogenetic or androgenetic production of pluripotent cells and cell lines, and use thereof to produce differentiated cells and tissues
InactiveUS20030129745A1Rejection is prevented and reducedEliminate, orMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimateEmbryo
Methods for obtaining pluripotent (embryonic stem) cells from parthenogenetic embryos, especially primates, are provided. These cells are useful for producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs, especially human and non-human primate cells, tissues and organs.
Owner:ROBL JAMES M +2
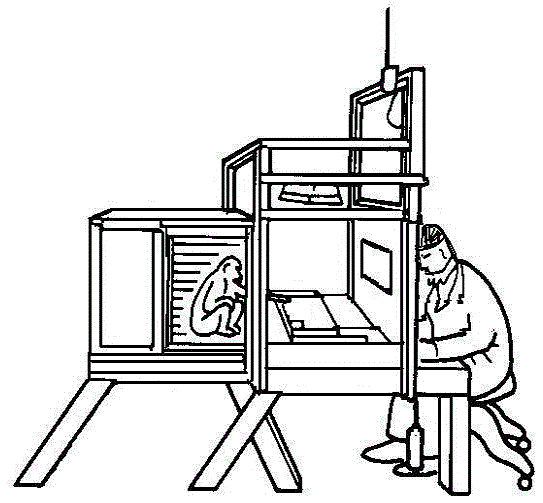
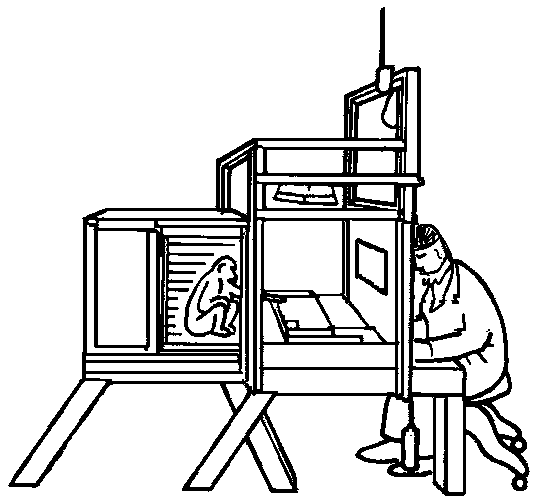
Automatic device for evaluating memory function of primate experimental animal
ActiveCN104663490AIncrease motivation to eatAvoid interferenceTaming and training devicesDiseaseBrain function
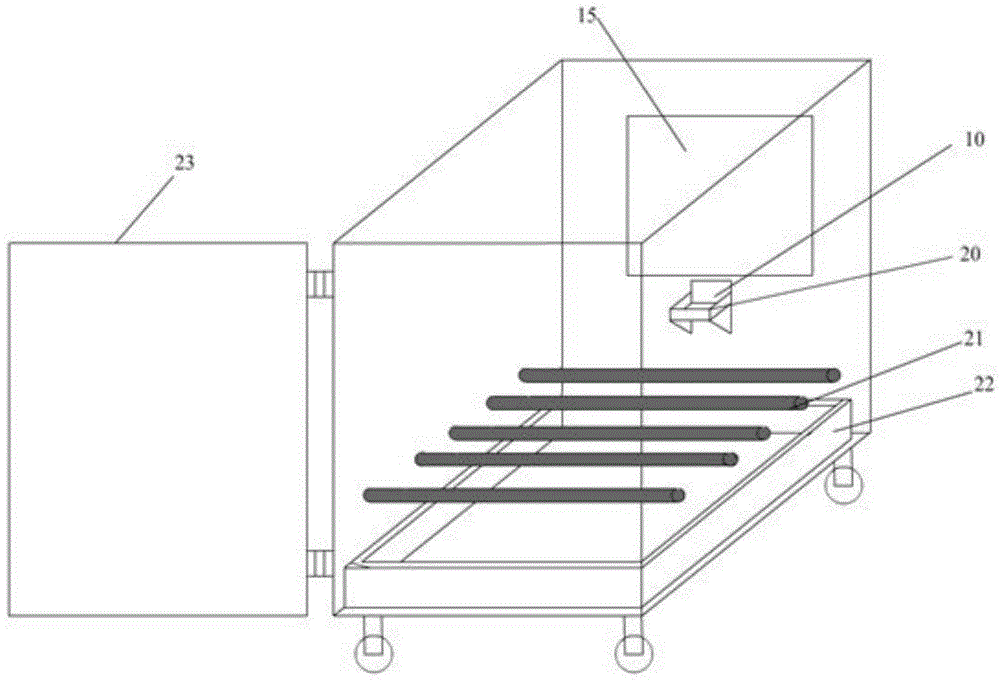
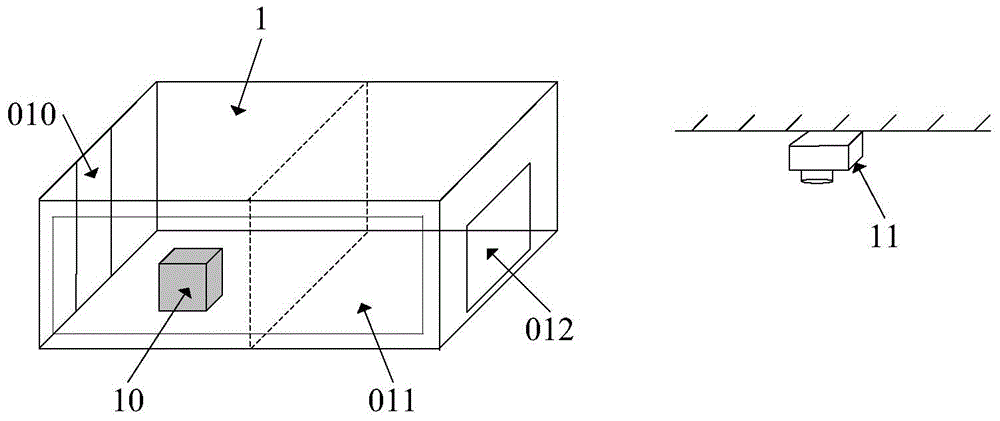
The invention discloses an automatic device for evaluating the memory function of a primate experimental animal and a method for evaluating the memory function of the primate experimental animal. The device comprises an experimental operation cage (1), a touch display screen (15), a horizontal exhibition stand (12), an infrared ray sensing automatic award food distributor (16) and a main control computer (19). Through interactive operation of the touch display screen and the animal, direct interactive operation between experiment personnel and the animal is avoided, and the evaluation of the cognitive ability is more objective. Through the device, the brain function can be evaluated subjectively according to a judgment made by a tester. The device and the method are particularly suitable for evaluating the cognitive memory of primate animals, particularly old non-human primate experimental animals and disease model non-human primate experimental animals.
Owner:广西南宁灵康赛诺科生物科技有限公司
In vitro differentiation of hematopoietic cells from primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20080108044A1Dead animal preservationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHematopoietic cellCytokine
Methods and compositions of CD45-positive hematopoietic cells and hemangioblasts derived b)y culturing human or non-human primate embryonic stem cells under serum-free conditions in cytokine-rich differentiation medium containing fibroblast growth factor or a related growth factor.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for in vitro mass amplification of human mature high-activity dendritic cells and application thereof
ActiveCN108546679AHigh activityImprove proliferative abilityVirus peptidesAntiviralsGene ModificationDendritic cell proliferation
Owner:CELARTICS BIOPHARMA CO LTD
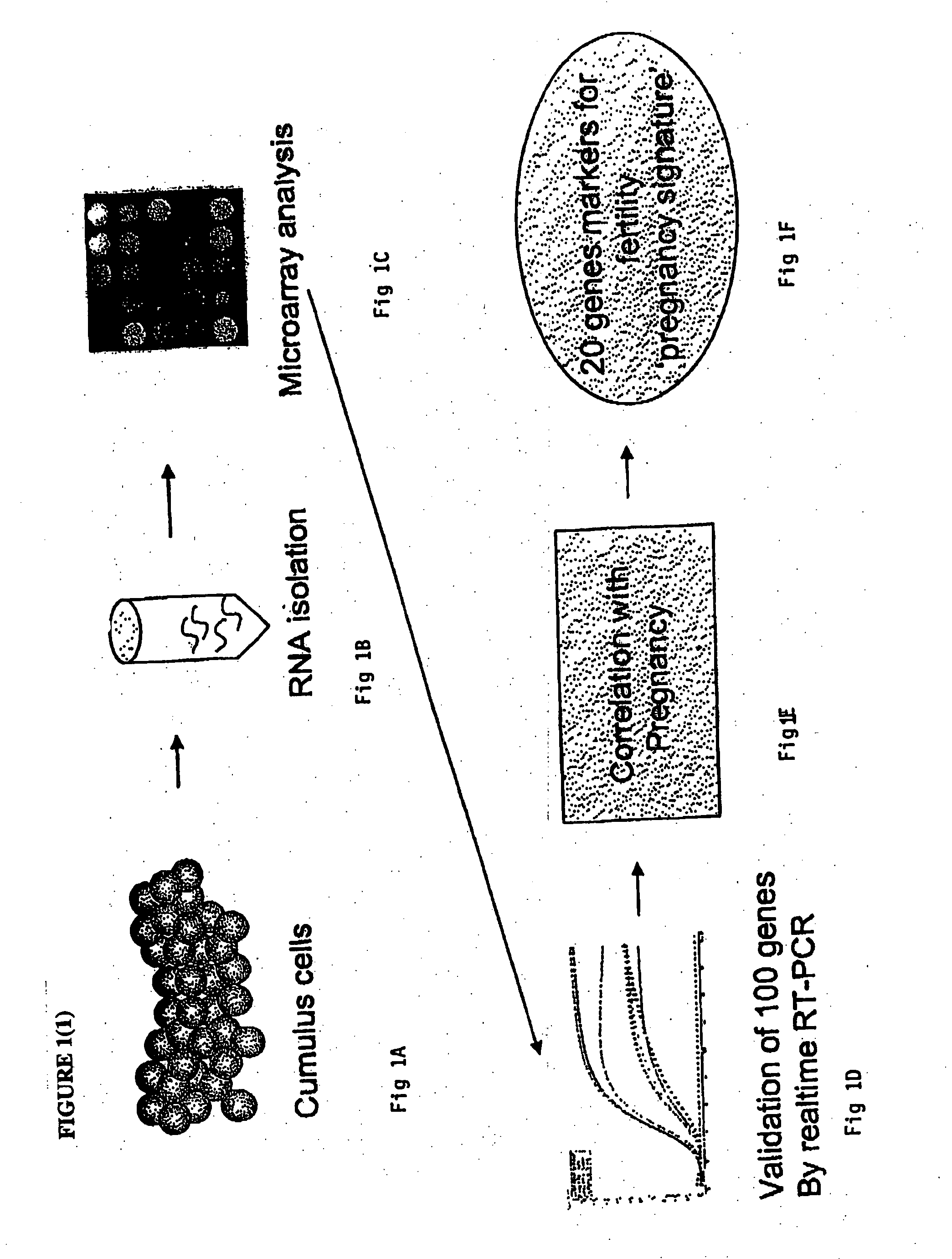
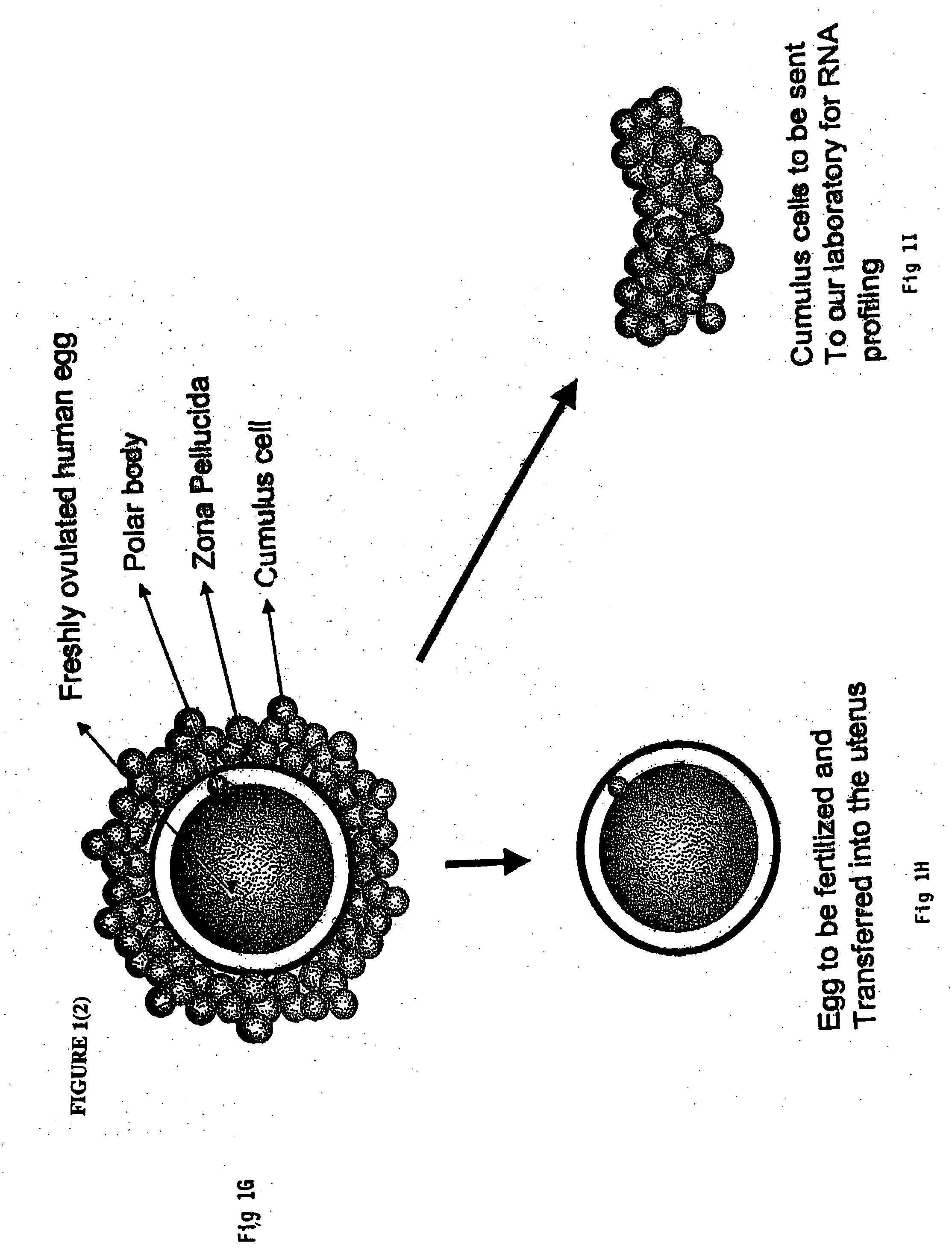
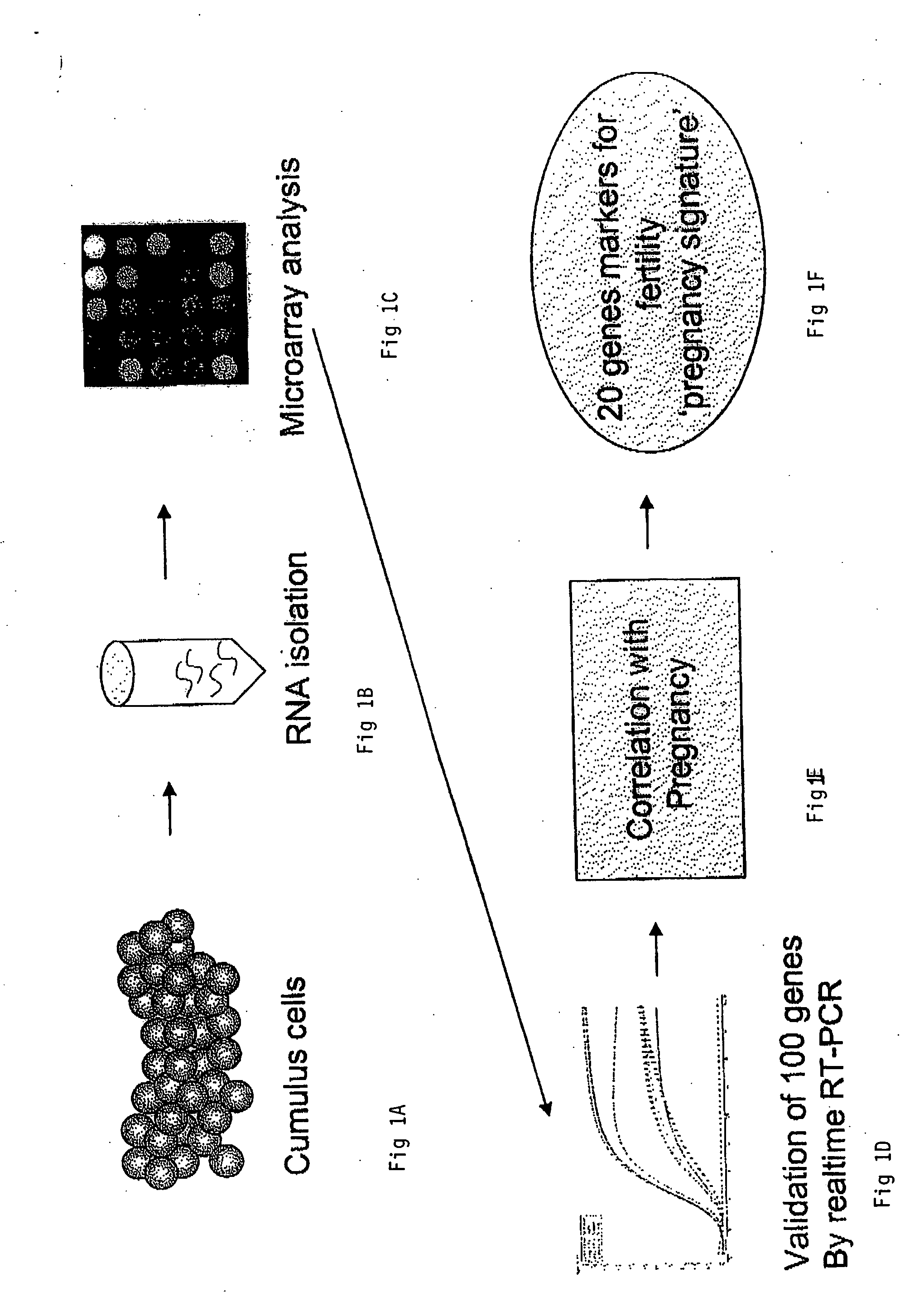
Identification of genes or polypeptides the expression of which correlates to fertility, ovarian function and/or fetal/newborn viability
InactiveUS20070238111A1Good curative effectImprove abilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseAutoimmune disease
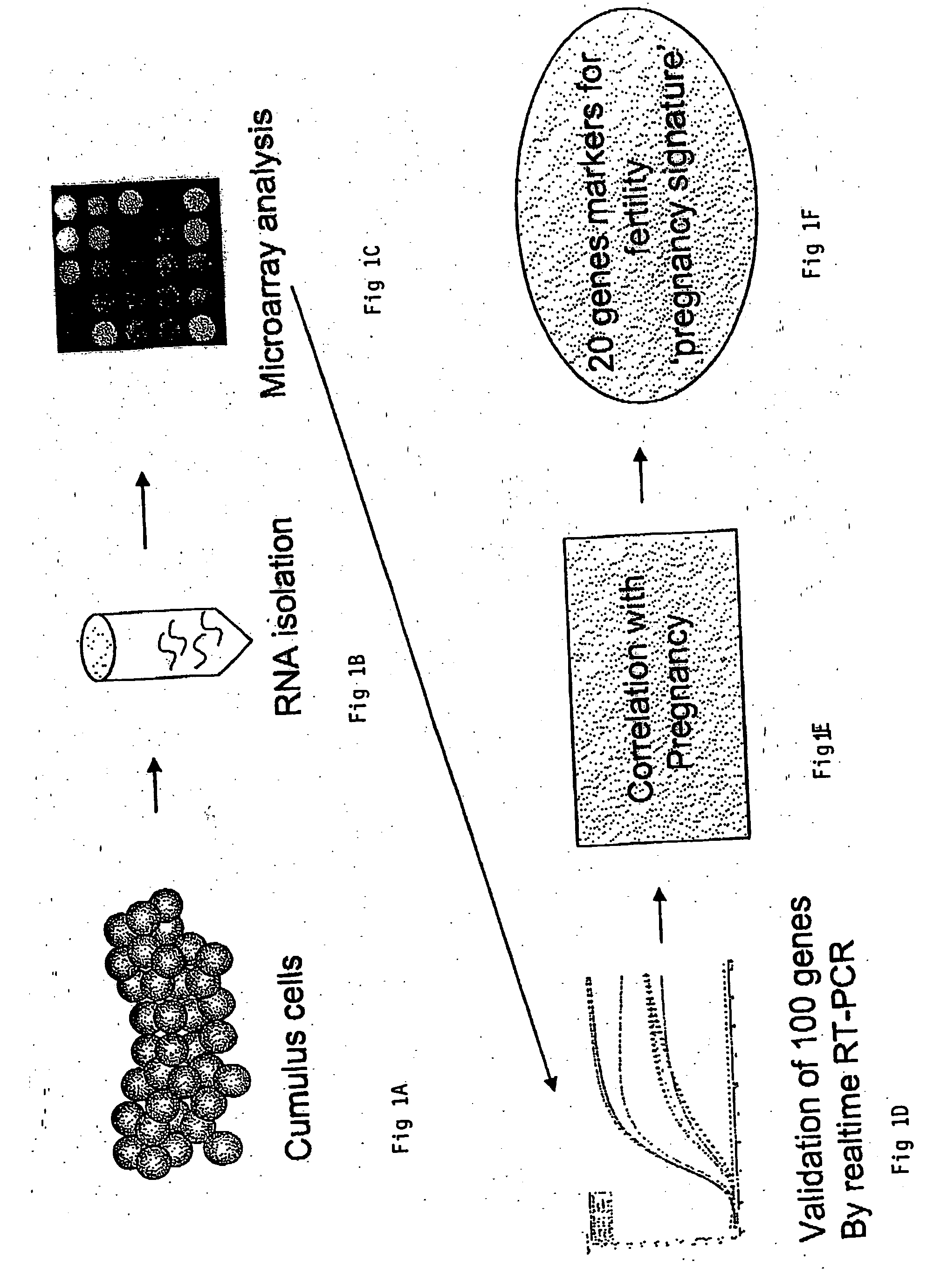
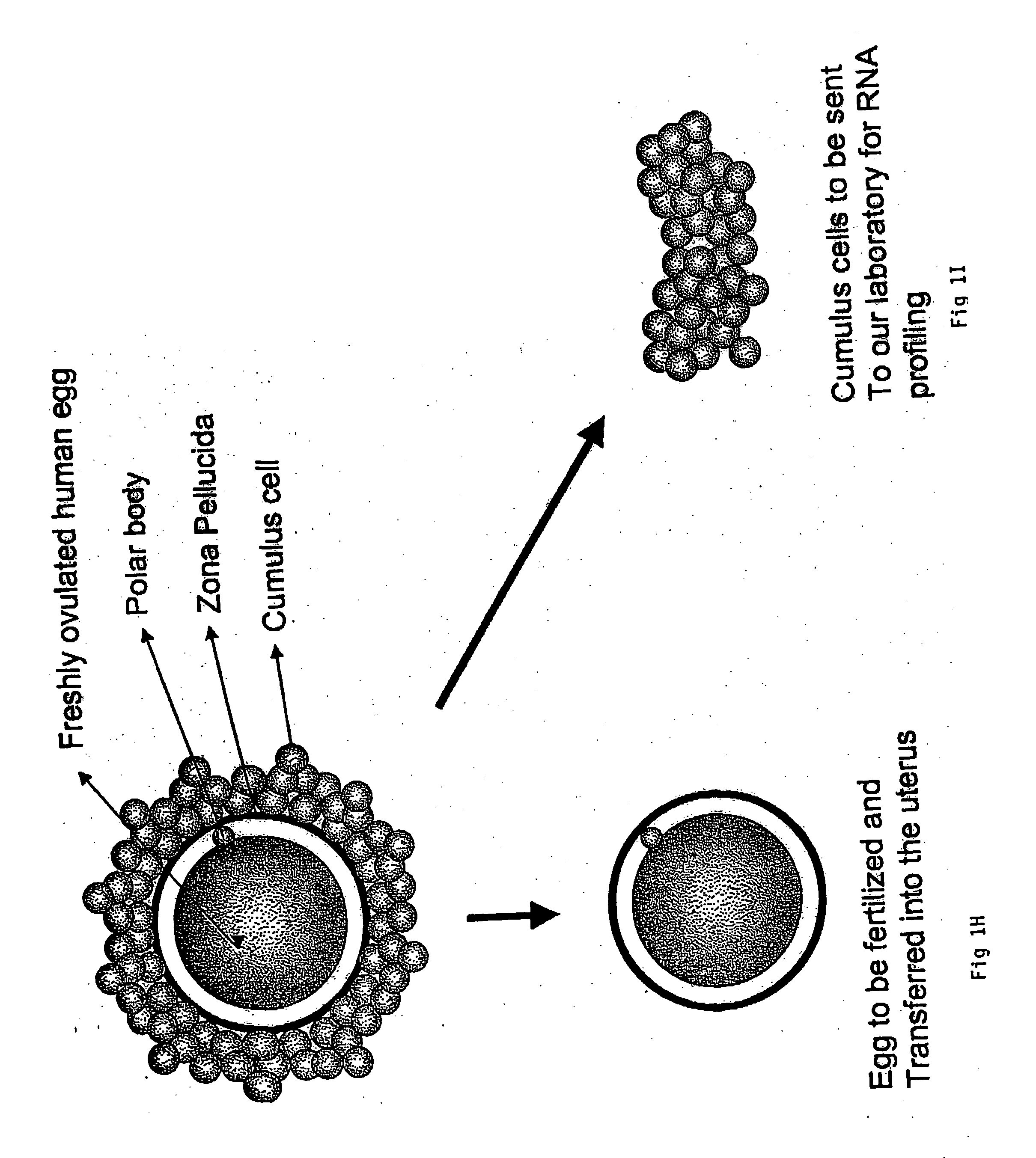
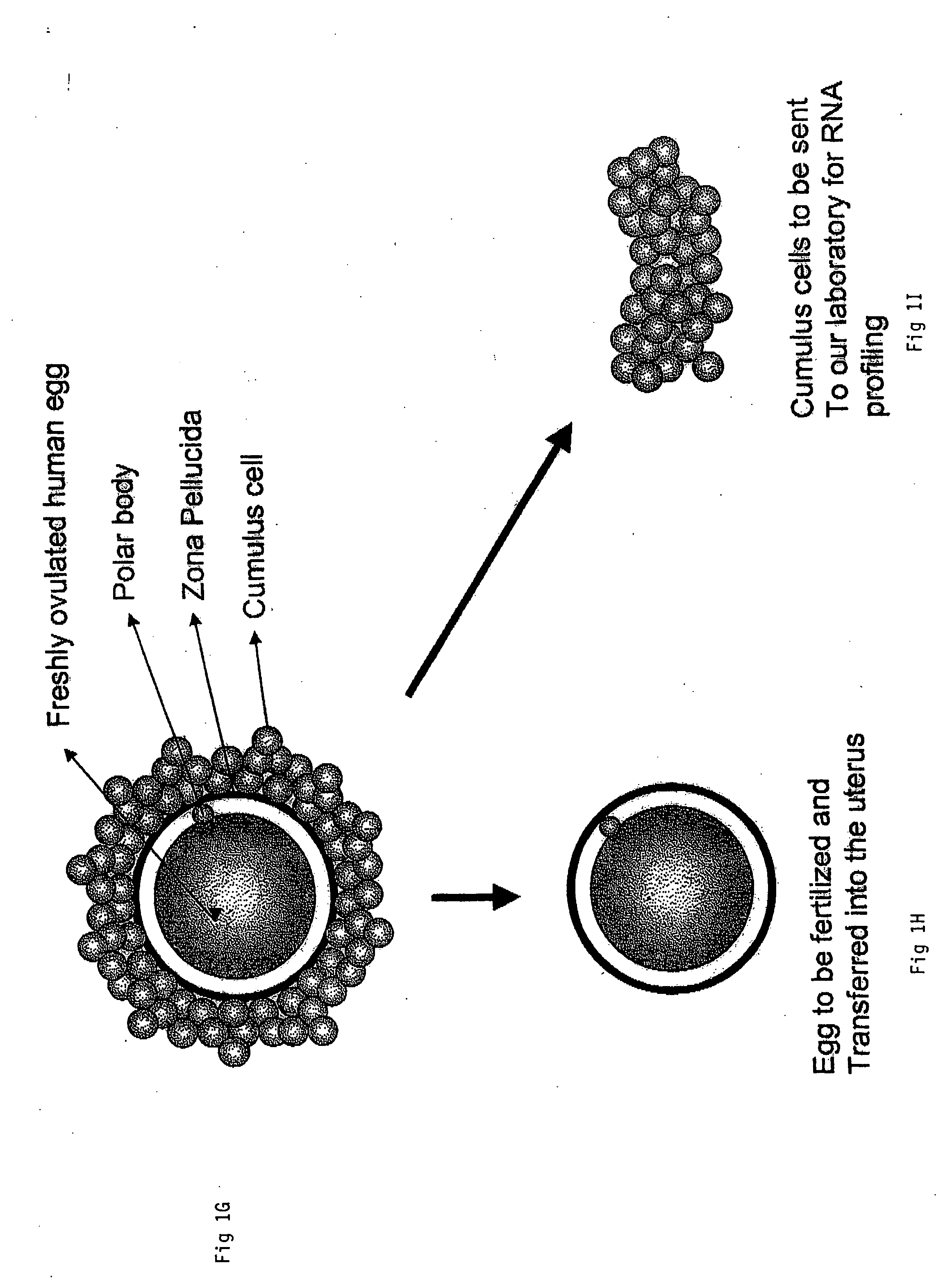
A genetic means of determining whether a female subject produces "pregnancy competent" oocytes is provided. The means comprises detecting the level of expression of one or more genes that are expressed at characteristic levels (upregulated or downregulated) in cumulus cells derived from pregnancy competent oocytes. This characteristic gene expression level, or pattern referred to herein as the "pregnancy signature", also can be used to identify subjects with underlying conditions that impair or prevent the development of a viable pregnancy, e.g., pre-menopausal condition, other hormonal dysfunction, ovarian dysfunction, ovarian cyst, cancer or other cell proliferation disorder, autoimmune disease and the like. Microarrays containing "pregnancy signature" genes or corresponding polypeptides provide another preferred aspect of the invention. Still further, the subject invention can be used to derive animal models, e.g., non-human primate animal models, for the evaluation of the efficacy of putative female fertility treatments.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
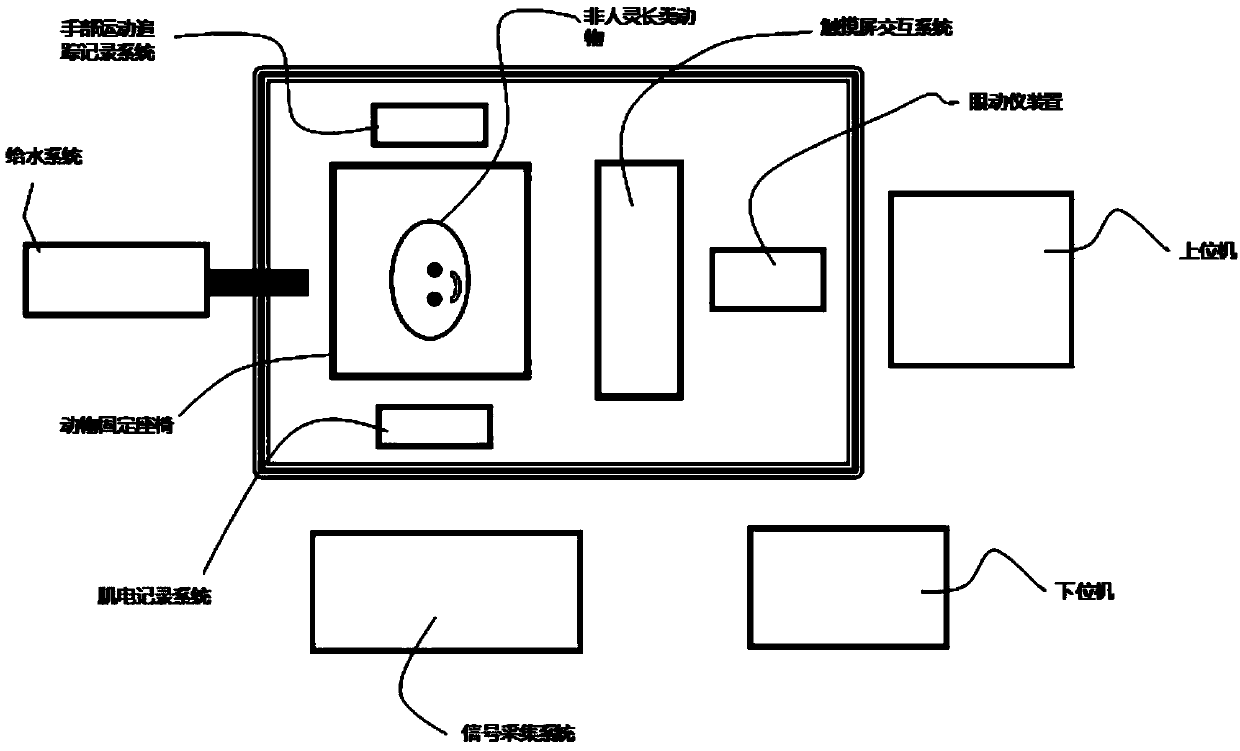
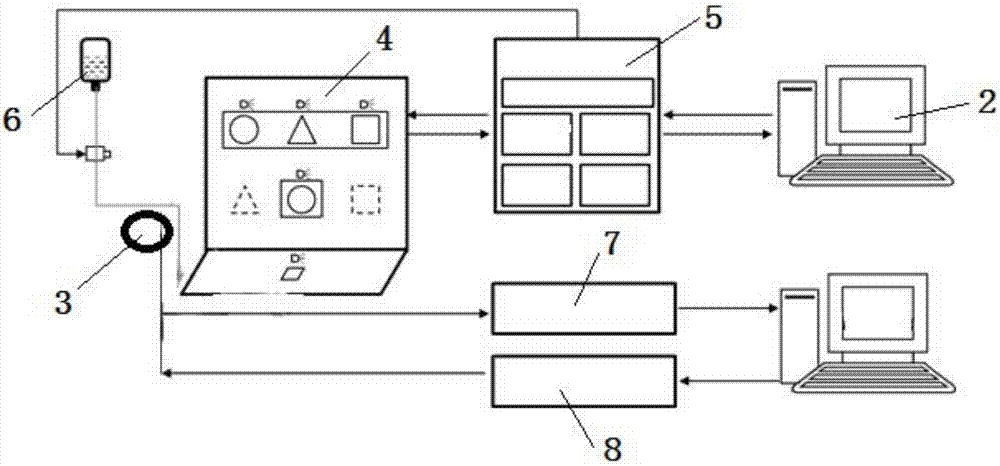
Research system for motion and cognitive functions of non-human primates based on touch screen
InactiveCN109566447AReasonable designVersatileTaming and training devicesInteraction systemsHearing perception
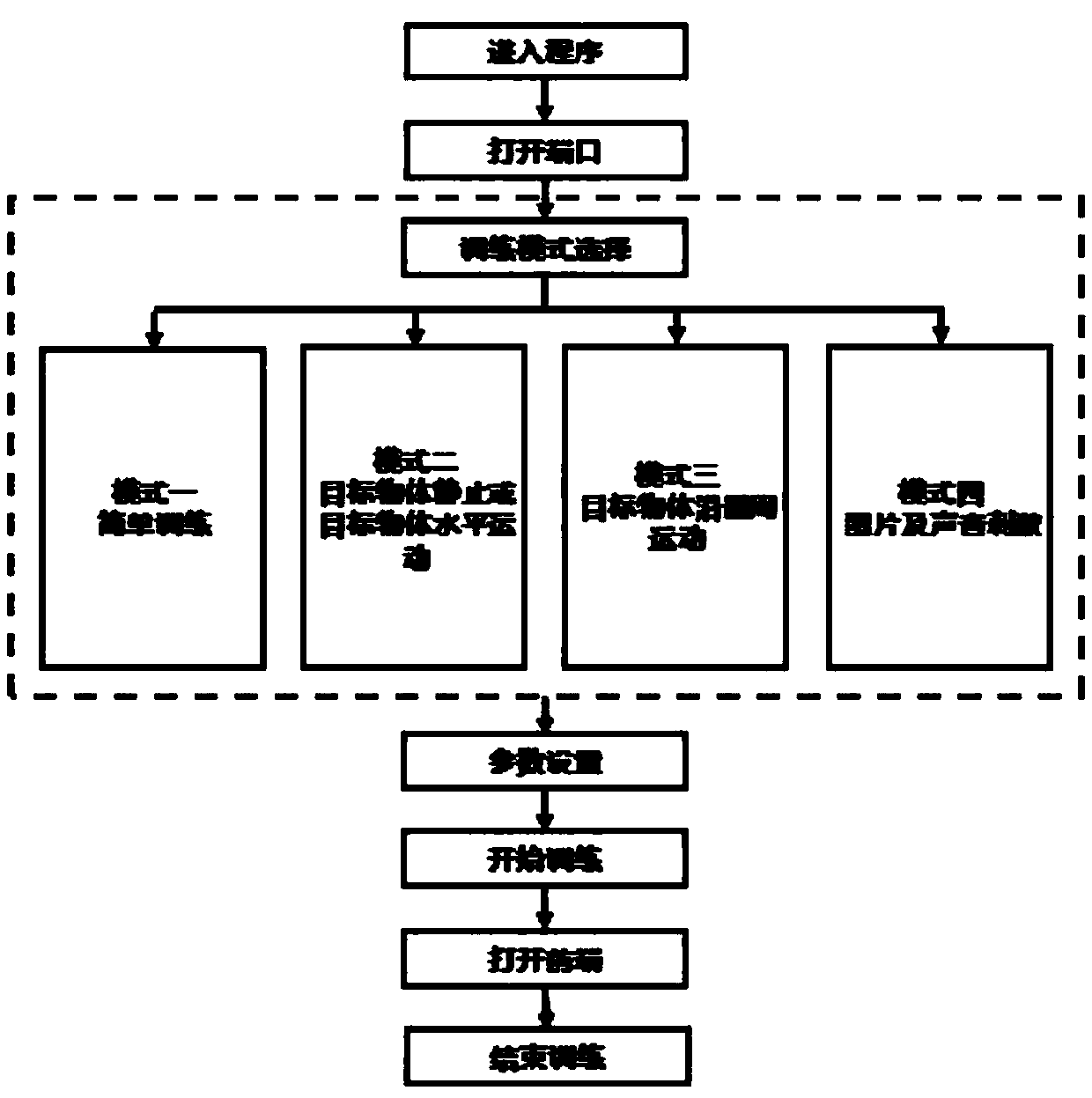
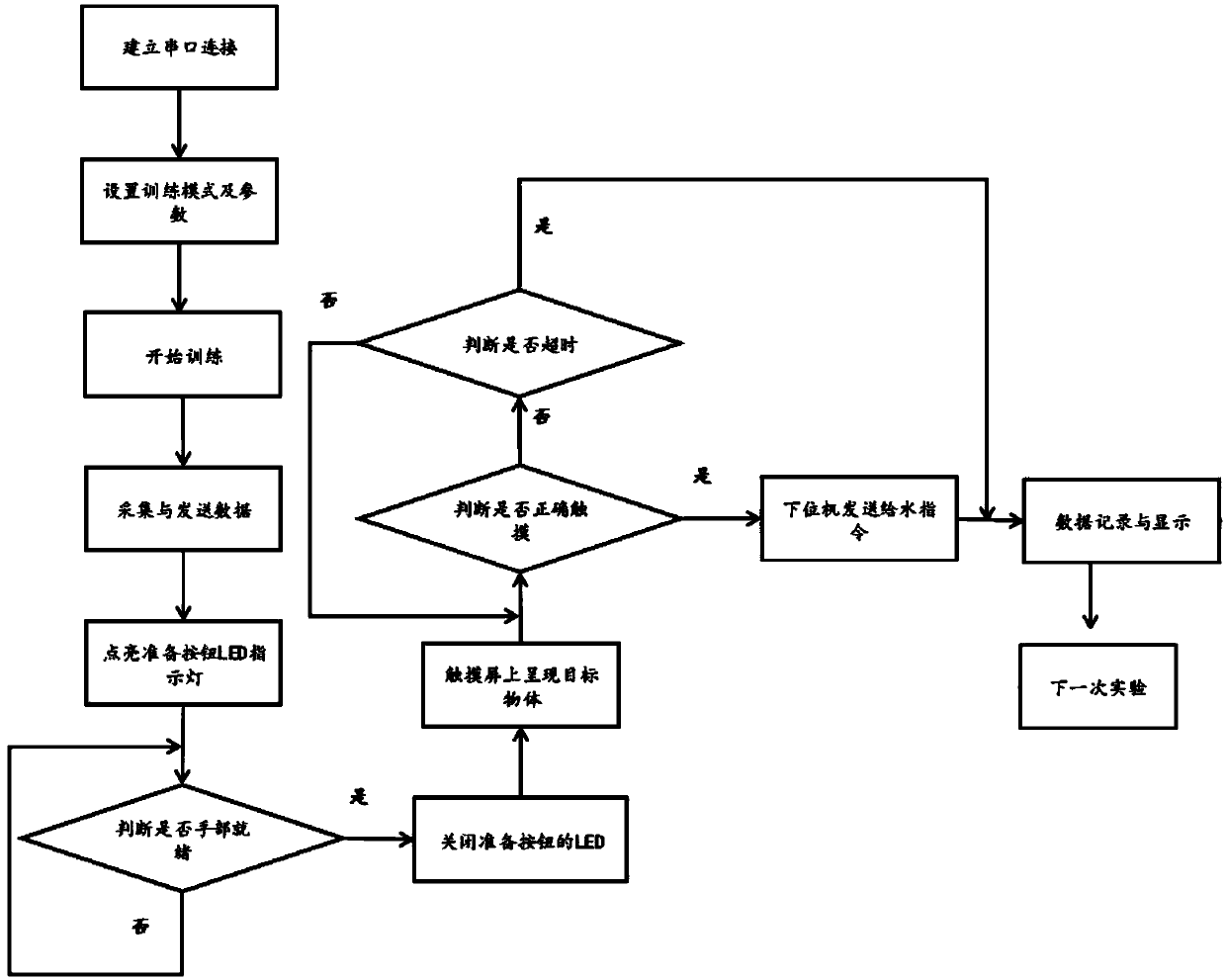
The invention discloses a research system for motion and cognitive functions of non-human primates based on a touch screen, and belongs to the field of biology. The system comprises an animal fixing seat, a touch screen interaction system, a water supply system, an ophthalmoscope device, a hand motion tracking and recording system, an electromyographic recording system, a signal acquisition system, a lower computer and an upper computer. The system can be used for a plurality of training modes, can adjust various important parameters on line, can accurately record the time of each stage in themotion execution process, can synchronously extract the characteristic vector of the motion direction of a tested eyeball, the electromyographic signals of a plurality of muscles on the arm, the movement track of a hand and the electrical activity of a cerebral nerve, The system is reasonable in design, can be used for neural electrophysiological research related to functions of vision, hearing,motion and the like, a multifunctional automatic animal behavior training method greatly improves the training speed, and facilitates design of related experimental paradigm and later data acquisitionand processing.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
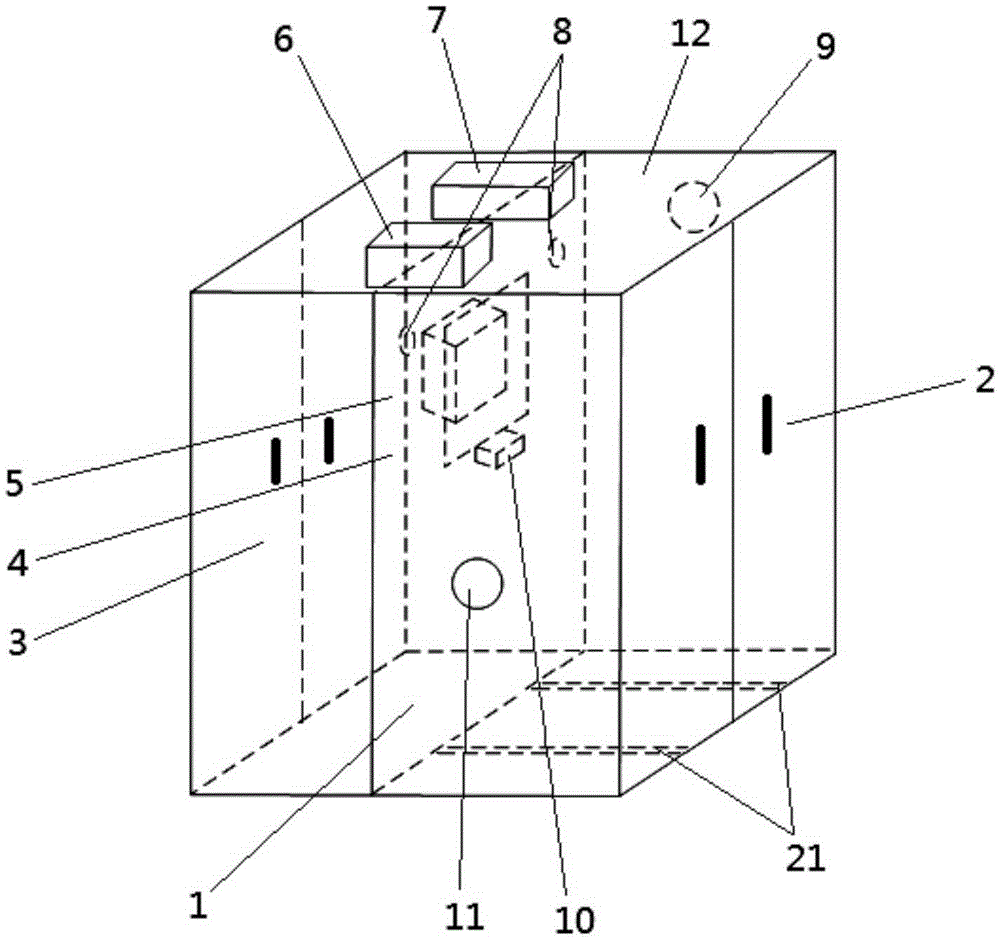
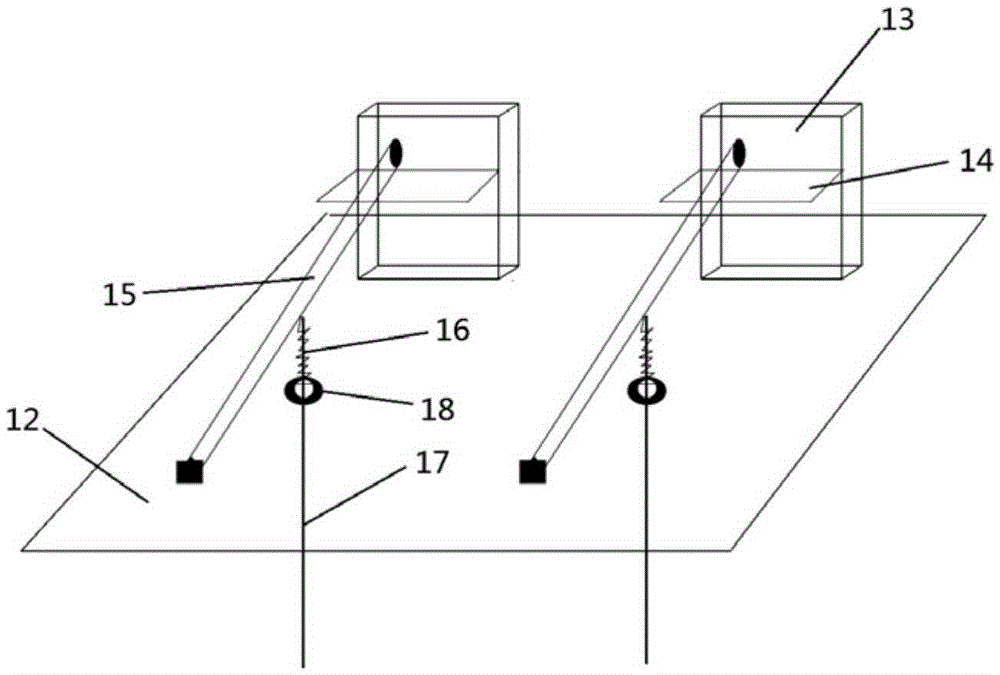
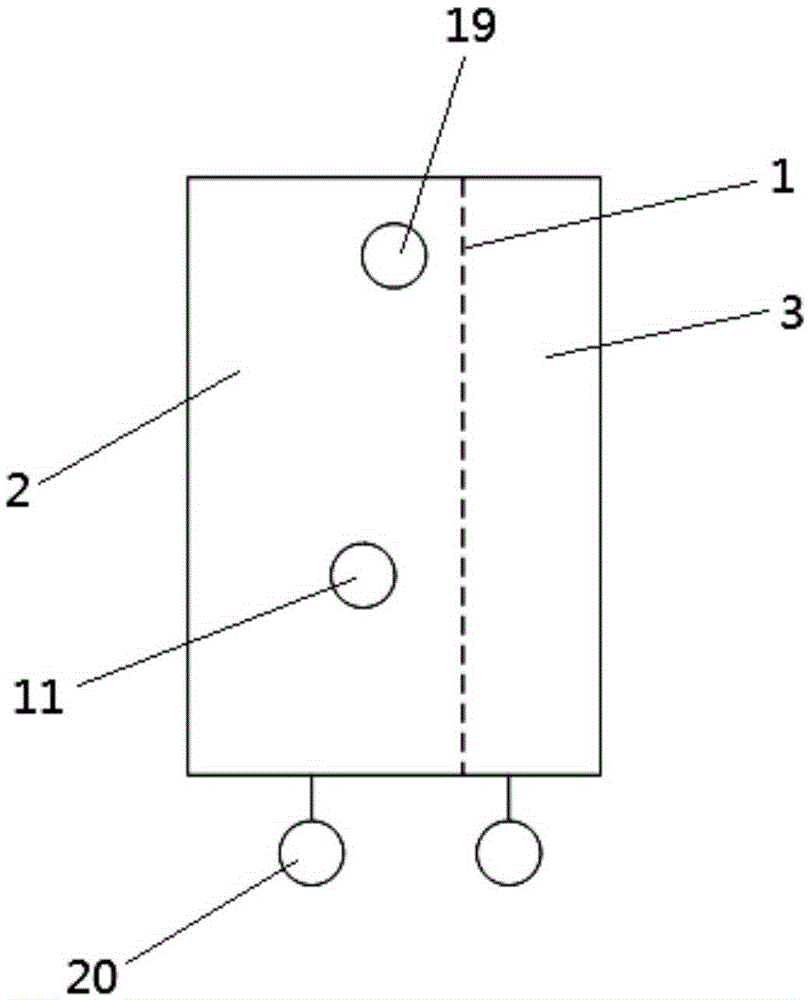
Non-human primate social behavior testing device
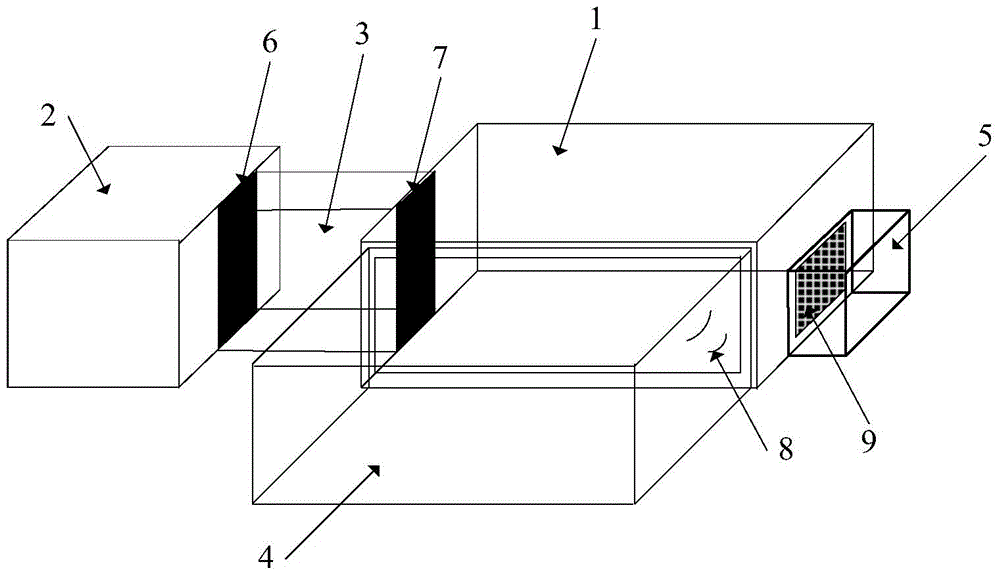
An embodiment of the invention discloses a non-human primate social behavior testing device. The non-human primate social behavior testing device comprises a behavior testing box, a first animal accommodation box, a channel which communicates the first side of the testing box and a first animal accommodation box, a behavior observation chamber which is communicated with the second side of the behavior testing box and a second animal accommodation box which is communicated with a third side of the behavior testing box. The non-human primate social behavior testing device can provide an experimental testing device and a measurement criteria for a social behavior research of non-human primates.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
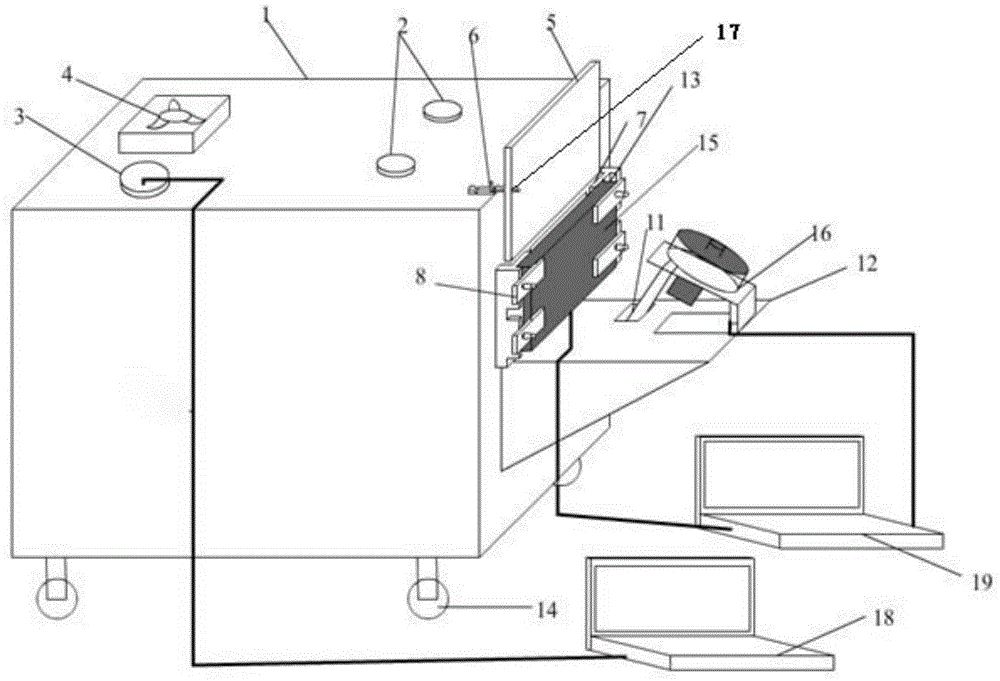
Integrated coil, special for non-human primates, in magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveCN105286864AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove spatial resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsParallel imagingEngineering
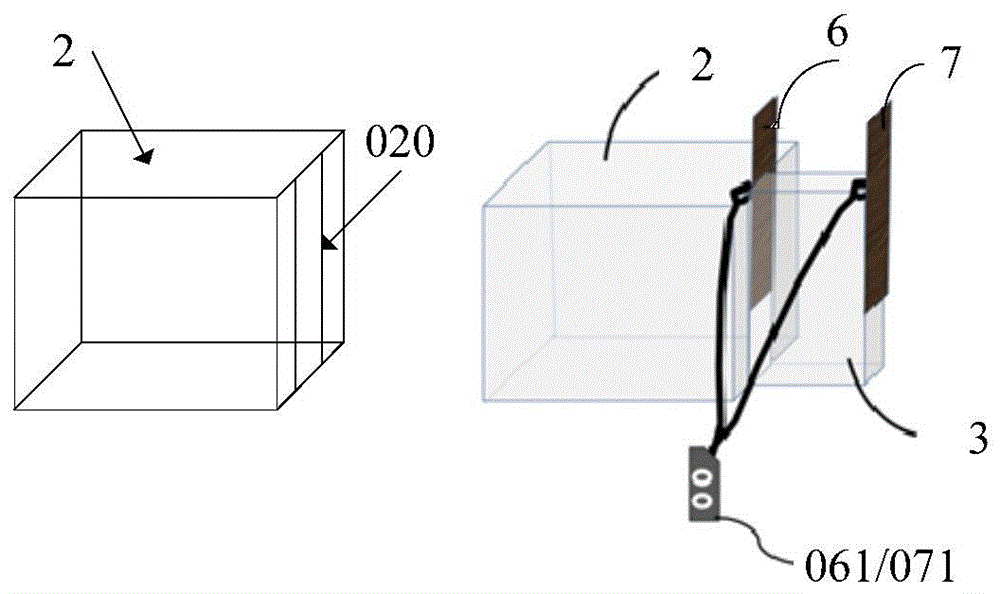
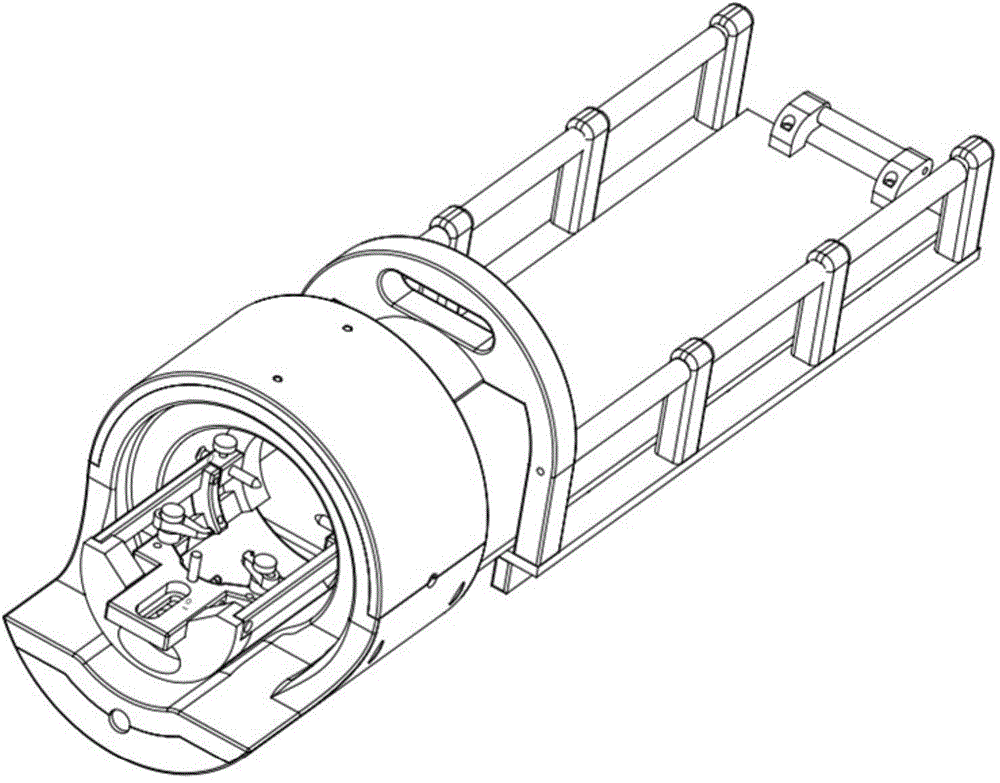
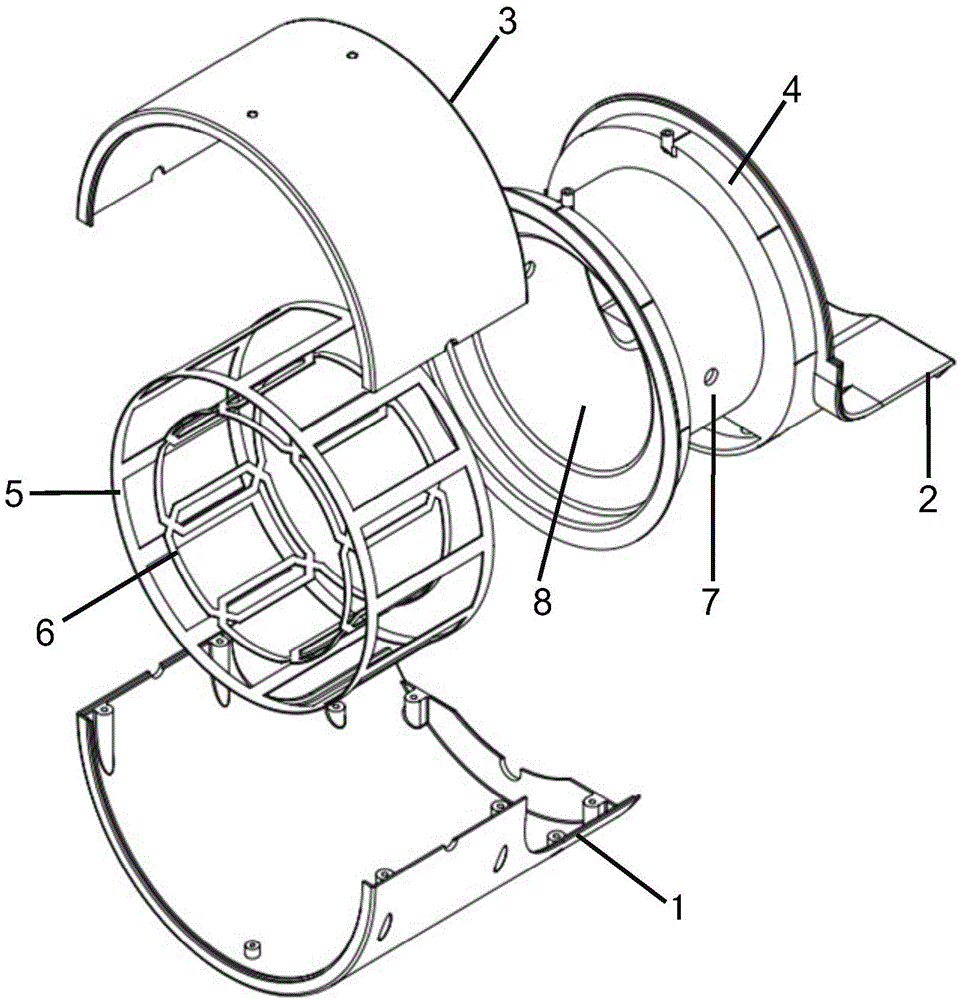
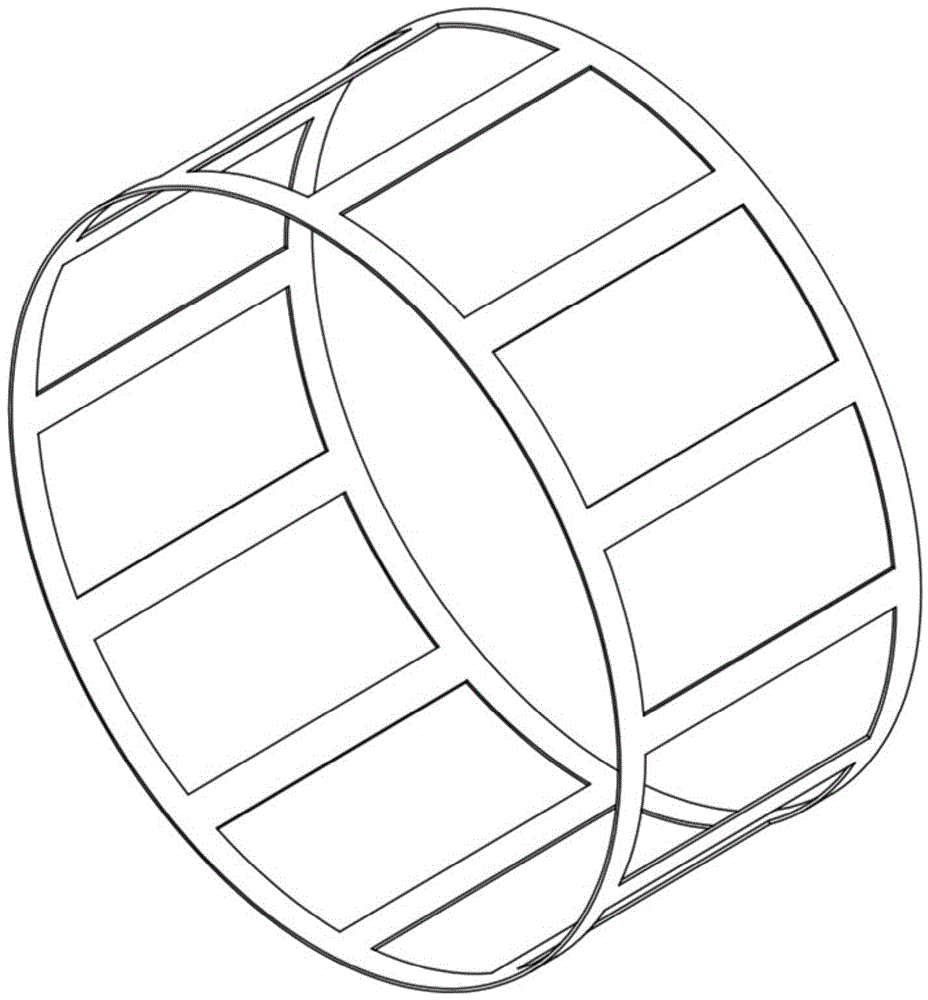
The invention discloses an integrated coil, special for non-human primates, in a magnetic resonance imaging system. According to the technical scheme, the integrated coil comprises a coil shell, a radio-frequency emission unit, a signal receiving unit, a pre-amplification unit, a cable connector connected and communicated with the magnetic resonance imaging system and a three-dimensional positioning device matched with the coil. The integrated coil has the advantages that the radio-frequency emission unit uses a birdcage type coil, provides a stable and even radio-frequency field, and is high in emission efficiency and low in SAR value; the signal receiving unit uses an eight-channel phased array coil, fits the head of a primate, detects deep tissue signals, acquires images with high signal-to-noise ratio and high spatial resolution and is cooperated with the parallel imaging technology to increase magnetic resonance imaging speed, shorten echo time and evidently improve EPI image signal-to-noise ratio and geometric distortion; the head fixing component of the three-dimensional positioning device is fixed with the coil through ear rods on two sides, and the head of the primate can be stably fixed in the optimal imaging area of the coil for magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
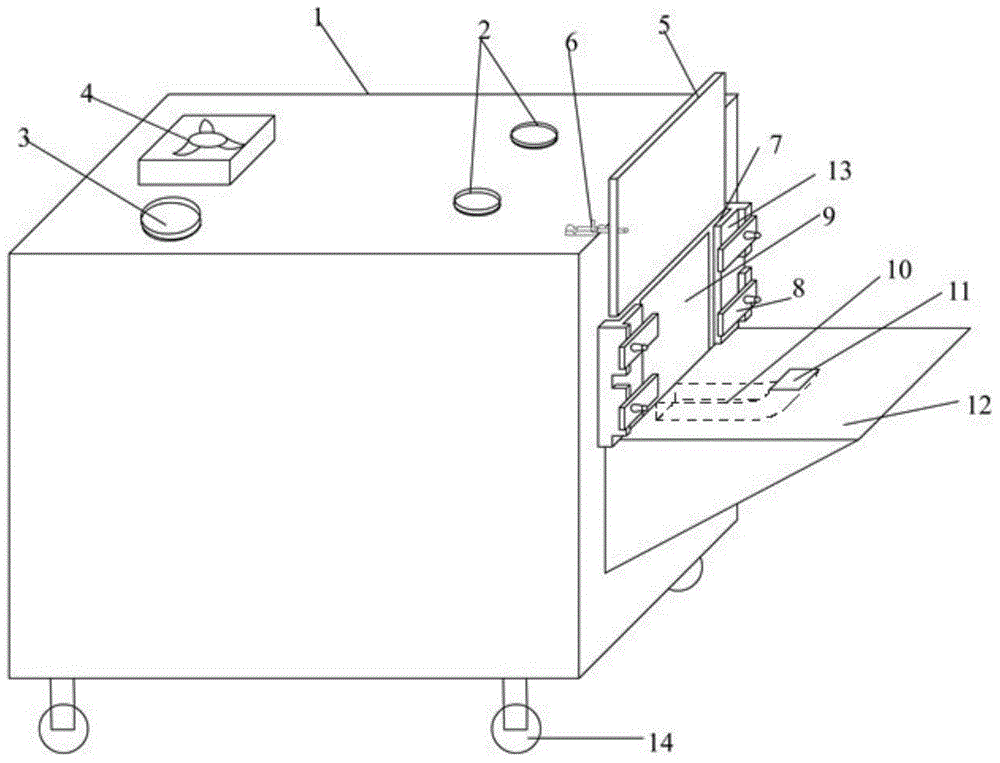
Non-human primate test animal medium and long-term weightlessness simulation model device
The invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace medicine and in particular relates to a device for performing a physiological test by simulating microgravity. The technical scheme is that the non-human primate test animal medium and long-term weightlessness simulation model device comprises a device main frame (100), a horizontal body position positioning device, a trunk side inclined angle positioning device, a feeding device (600), a water intake device (700) and a metabolin collecting disc (500), wherein a bed surface outer ring (401) of the horizontal body position positioning device is connected to the device main frame (100) through a connecting shaft (201) and is fixed by a locking handle (203); a bed surface inner ring (402) of the trunk side inclined angle positioning device is connected to the bed surface outer ring (401) through a positioning shaft (303) and is fixed by a locking device; and the metabolin collecting disc (500) is arranged below the device main frame (100). According to the invention, head low-position inclined angle and trunk side inclined angle can be positioned precisely by positioning and locking devices, and various zero-gravity environments can be simulated.
Owner:63919 TROOPS PLA
Methods to identify polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences which may be associated with physiological and medical conditions
InactiveUS7247425B2Reduce resistanceImprove developmentCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPolynucleotideICAM-1
The present invention provides methods for identifying evolutionarily significant polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences in human and / or non-human primates which may be associated with a physiological condition, such as enhanced resistance to AIDS infection. The invention also provides methods for identifying evolutionarily significant polynucleotides with mutations that are correlated with susceptibility to diseases, such as ICAM 1. The methods employ comparison of human and non-human primate sequences using statistical methods. Sequences thus identified may be useful as host therapeutic targets and / or in screening assays.
Owner:EVOLUTIONARY GENOMICS LLC
Non-human primate animal self-drug delivery system operation box
InactiveCN105393926AAvoid scratchesAvoid damageAnimal housingOther apparatusInterior spaceComputer module
The invention relates to a non-human primate animal self-drug delivery system operation box comprising an operation box main body, a separation plate, a signal stimulating module, a reaction recording module and a rewarding module. A separation plate is disposed in the operation box main body; the internal space of the operation box main body is divided into a front area and a back area; a non-human primate animal is placed in the front area; the signal stimulating module is placed in the back area to stimulate the animal; the reaction recording module is arranged in the back area or outside the operation box to record operations to the animal; and the rewarding module is arranged in the back area or outside the operation box to give relative reward to the animal according to the operation data recorded by the reaction recording module. With the separation plate, the internal space of the operation box is divided into the front area and the back area, so the animal and testing equipment can be separated via the separation plate and rational layout is achieved; damage to the testing equipment by the animal can be avoided; relative connection lines can be prevented from being pulled break; and the test can be normally conducted.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
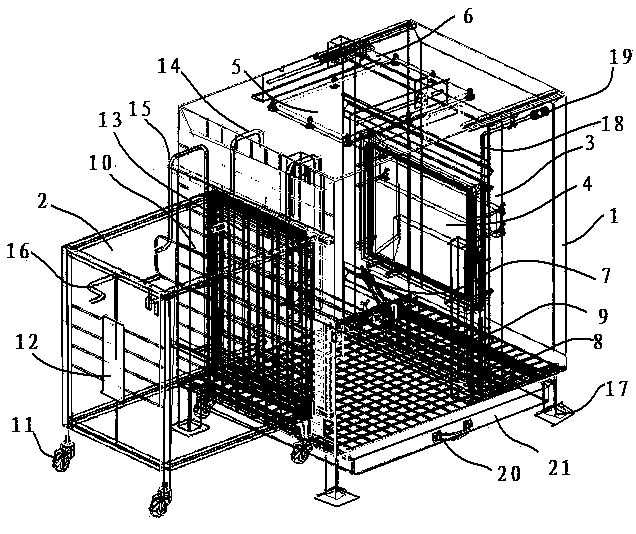
Touch-screen multifunctional non-human primate animal cognitive-function testing cage
The invention discloses a touch-screen multifunctional non-human primate animal cognitive-function testing cage and belongs to the technical field of animal experiment devices. The touch-screen multifunctional non-human primate animal cognitive-function testing cage comprises a testing cage and a transfer cage. An infrared-induction touch screen connected with a computer is fastened on the rear vertical face of the testing cage capable of moving back and forth, an observation window and a movable camera are arranged on the top face, a water supply nozzle is located at the rear locking-fixing position capable of moving vertically in front of the touch face of the touch screen, a feces receiving plate which can be pushed into or pulled out of the lateral vertical face of the testing cage is arranged under a grid-shaped base, and a testing cage door which can be pushed into or pulled out of the side face of the testing cage is arranged on a grid-shaped front vertical face. The transfer cage is provided with truckles and an observation window, and the front vertical face is a push-pull type transfer cage door which can be in butt joint with the testing cage door after being opened. The touch-screen multifunctional non-human primate animal cognitive-function testing cage can be used for flexibly, conveniently, intelligently, efficiently and accurately performing non-human primate animal training and testing based on a modern computer technology, does not need an additionally-equipped corresponding cage, has multiple practical functions and is low in purchase cost and usage cost.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Materials and Methods for the Delivery of a Nanocarrier to the Brain
Materials and methods for magnetically guided delivery of nanoparticles across the blood brain barrier (BBB) in the central nervous system (CNS) are provided. The method can comprise injecting a subject with an aqueous solution comprising magneto-electro nanoparticles and applying a static magnetic field directed toward the subject brain, thereby inducing a stimulus response of the nanoparticles in a controlled manner. Materials and methods provided herein are effective in delivering the nanoparticles across the BBB in the brains of animal subjects including mice and non-human primate such as baboon.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Identification of genes involved in fertility, ovarian function and/or fetal/newborn viability
InactiveUS20070054289A1Enhance their pregnancy competencyGood curative effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseHormone function
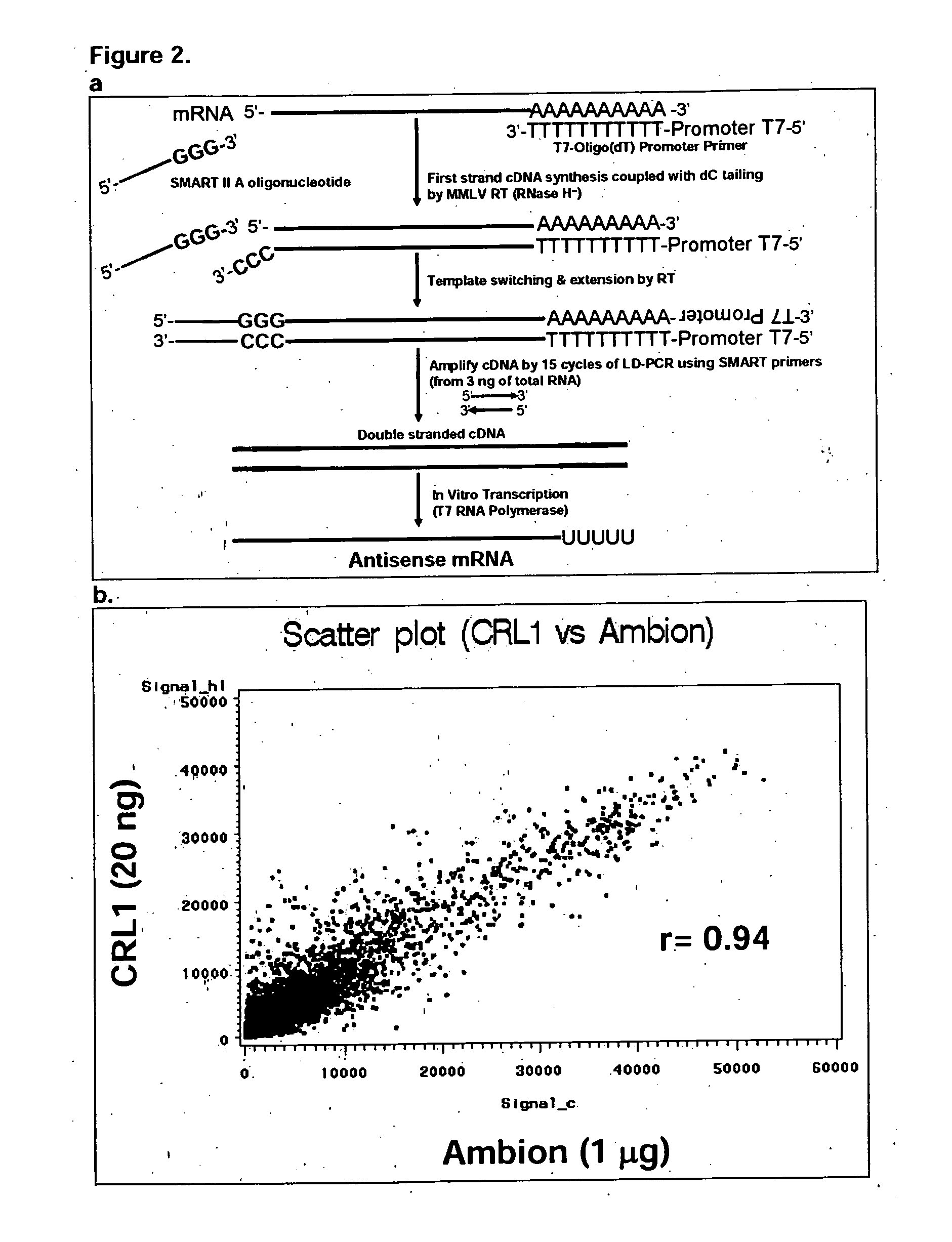
A genetic means of determining whether a female subject produces "pregnancy competent" oocytes is provided. The means comprises detecting the level of expression of one or more genes that are expressed at characteristic levels (upregulated or downregulated) in cumulus cells derived from pregnancy competent oocytes. This characteristic gene expression level, or pattern referred to herein as the "pregnancy signature", also can be used to identify subjects with underlying conditions that impair or prevent the development of a viable pregnancy, e.g., pre-menopausal condition, other hormonal dysfunction, ovarian dysfunction, ovarian cyst, cancer or other cell proliferation disorder, autoimmune disease and the like. Microarrays containing "pregnancy signature" genes or corresponding polypeptides provide another preferred aspect of the invention. Still further, the subject invention can be used to derive animal models, e.g., non-human primate animal models, for the evaluation of the efficacy of putative female fertility treatments. Additionally, an improved RNA amplification protocol is provided herein referred to as the CRL amplification protocol which is suitable for reproducibly amplifying all the RNAs expressed by a cell sample, even when only a few cells are available.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Compositions and methods to mitigate or prevent an immune response to an immunogenic therapeutic molecule in non-human primates
ActiveUS20190022186A1Reduce probabilityReduce intensityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody fragmentsSignalling pathways
Owner:JOMOCO CORP
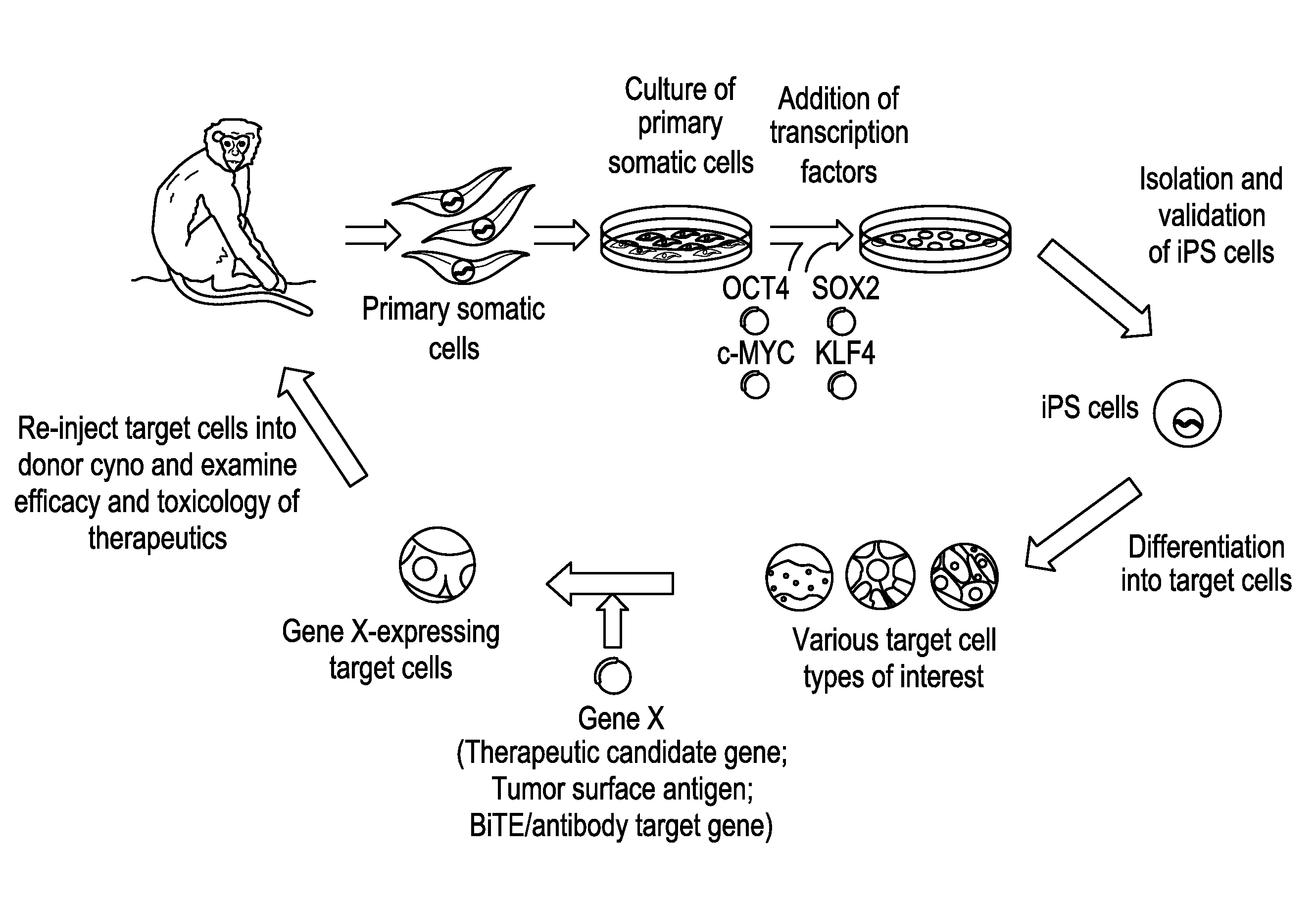
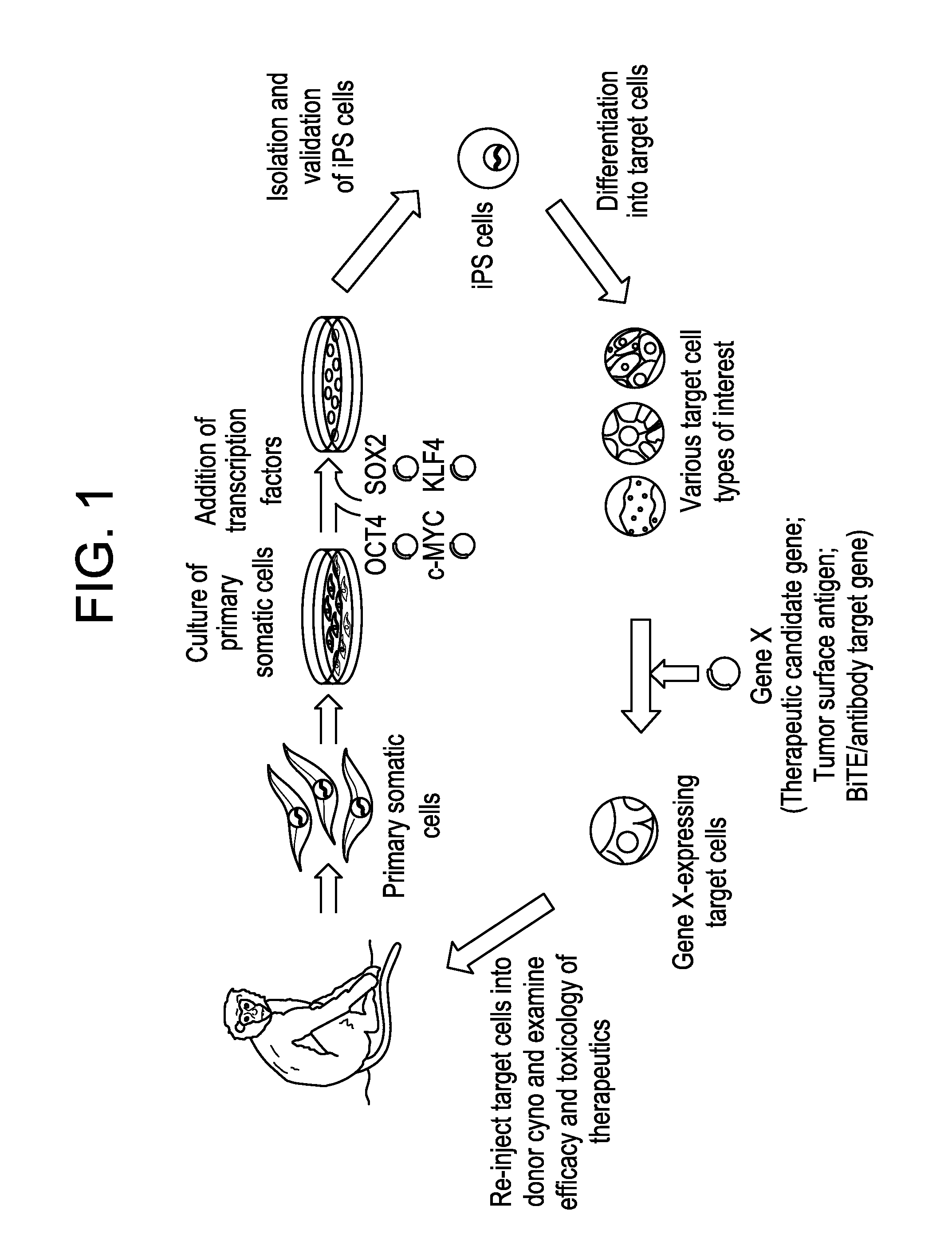
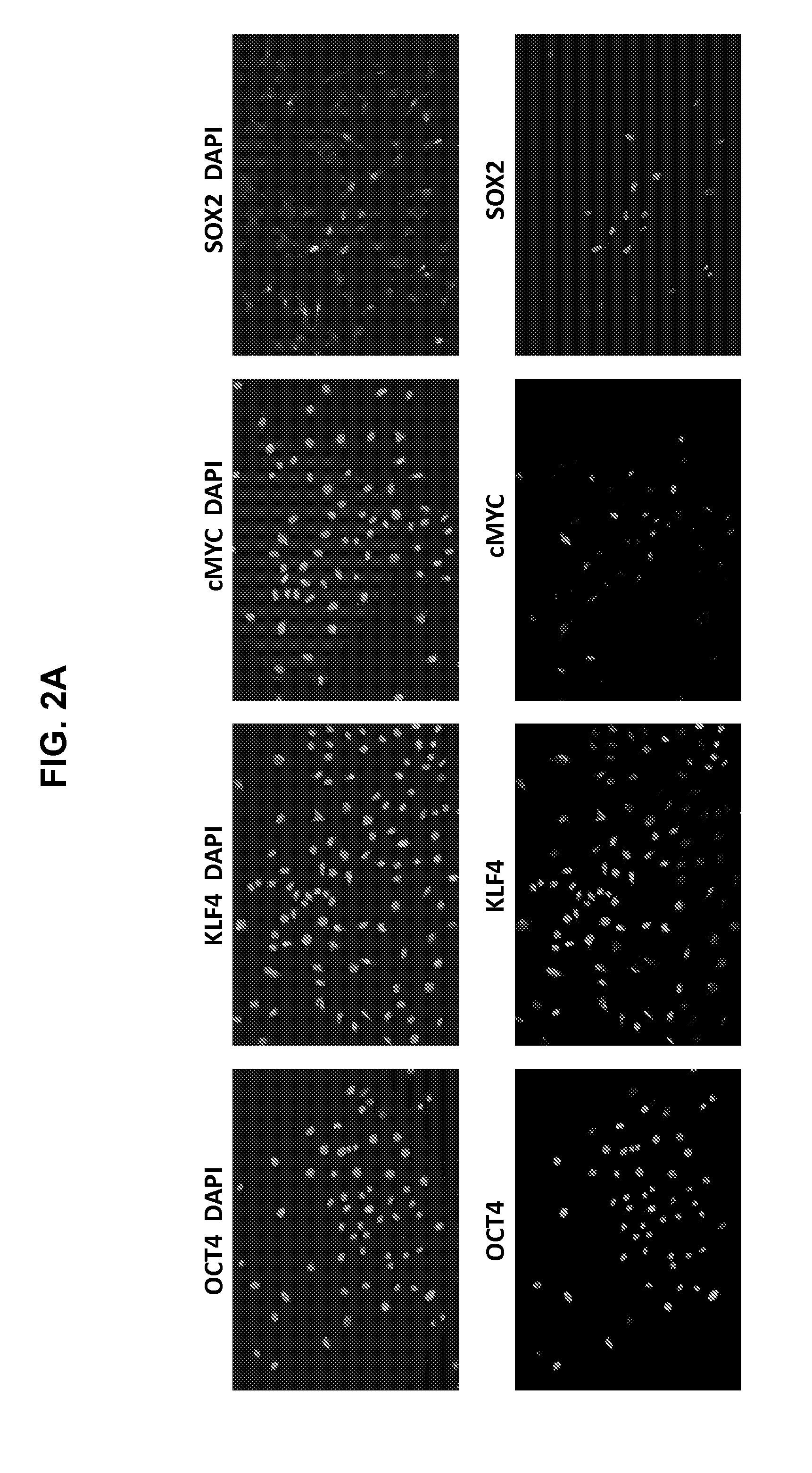
Autologous Mammalian Models Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Related Methods
InactiveUS20150201588A1Wide applicabilityEfficient and reliableGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementSOX2Reprogramming
Disclosed is an autologous non-human mammalian model system derived from induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. Also disclosed are methods of differentiating non-human primate iPS cells, which can result in populations of cells enriched for SOX2+ or PDX1+ foregut-like cells, for CDX2+ hindgut-like cells, for CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor-like cells, or epithelial-like cells. Also disclosed is a non-human primate containing an autologous cell type of interest, which is differentiated in vitro from an induced pluripotent stem cell reprogrammed from a primary somatic cell. Methods of monitoring exogenously introduced cells within a non-human mammal are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Method for building animal model of social position induced depression
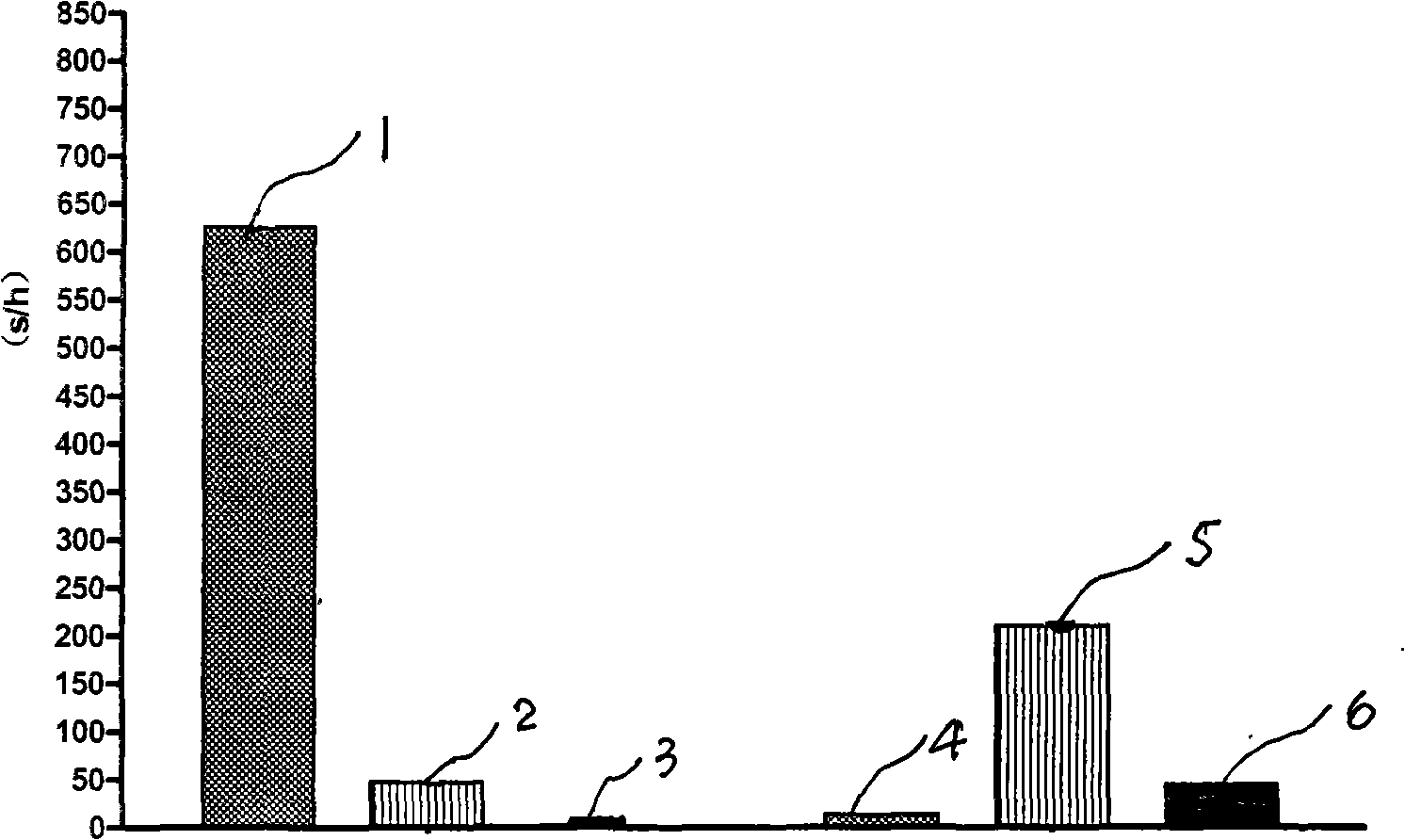
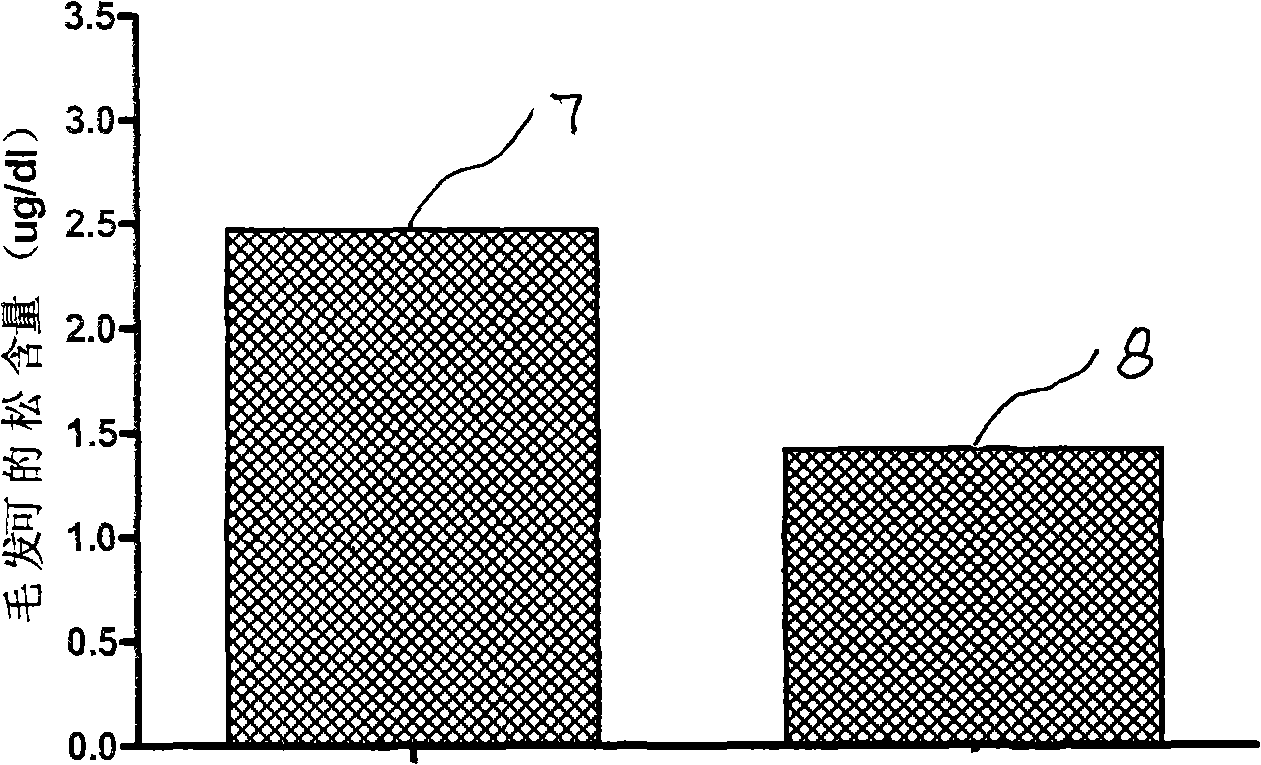
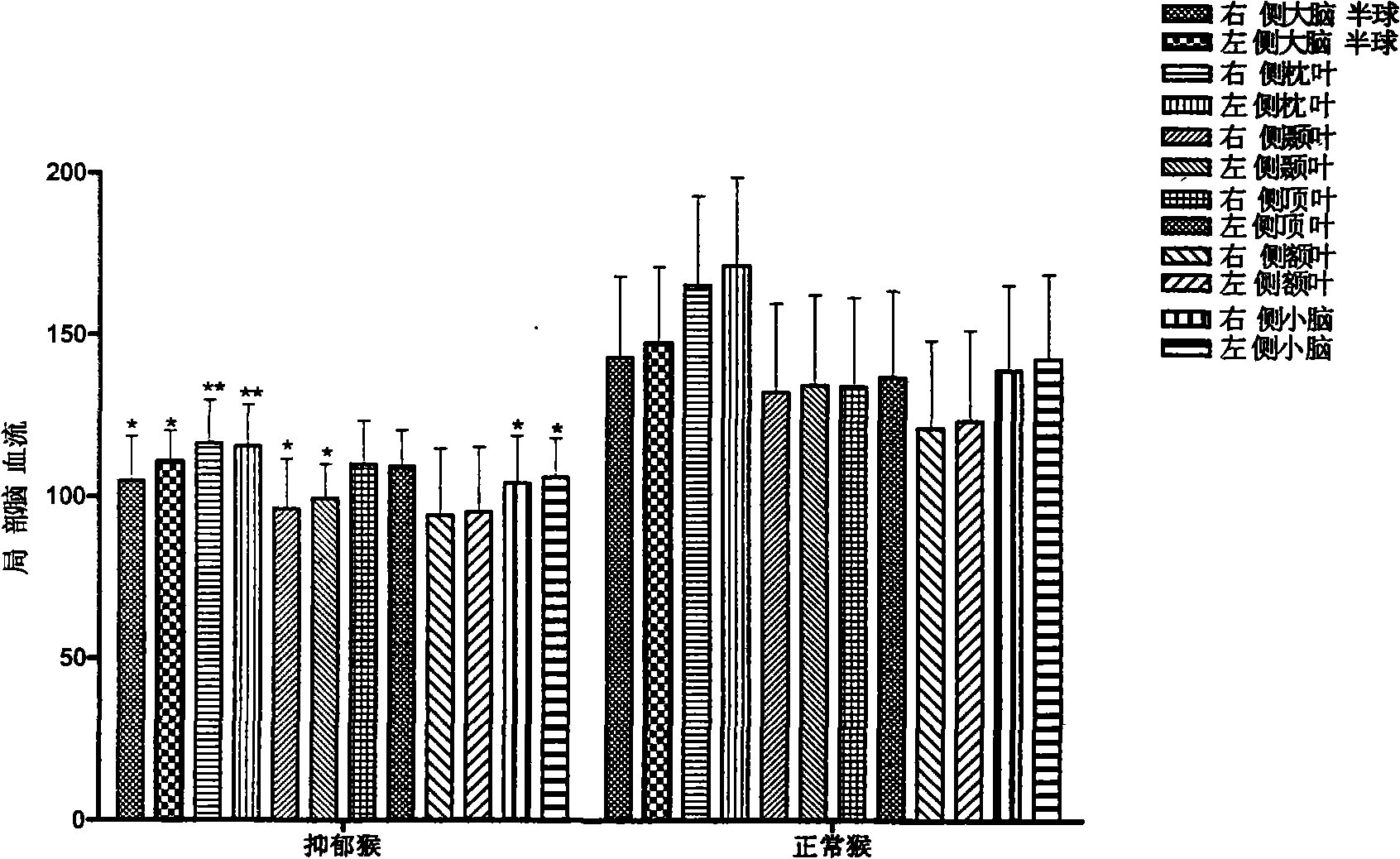
InactiveCN101773096AHigh pine contentDecreased cerebral blood flowAnimal husbandryCortisoneActivity time
The invention discloses a method for building an animal model of social position induced depression, which belongs to the technical field of life sciences. The method comprises the following steps of: in natural colonies of non-human primates, recording total curling time, total spontaneous activity time and total external stimuli reaction time of each individual; dividing the total curling time of each individual into four equal parts, wherein the individuals with the shortest curling time are abnormal and others are depressive; performing independent sample t experiments on the hourly average spontaneous activity time and the hourly average external stimuli reaction time of the individuals of the two groups, wherein if the spontaneous activity time and the reaction time of the individuals of the normal group are obviously longer than those of the individuals of the depressive group, the individuals of the depressive group meet behavior characteristic requirements; and measuring hair cortisone content and partial cerebral blood flow values of the individuals of the two groups to perform the independent sample t detection, wherein if the average cortisone content of the individuals of the normal group is obviously lower than that of the depressive group and the average partial cerebral blood flow value of the individuals of the normal group is obviously higher than that of the depressive group, the individuals of the depressive group meet biochemical criterion requirements. The individuals who simultaneously meet the two types of requirements are the built natural depressive models, so the method can completely simulate the evolution of human depression.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Automated training assisting device for training non-human primate animal to control mechanical arm to conduct stretching and grabbing
InactiveCN108849606AEnsure safetyImprove securityTaming and training devicesMicrocontrollerEvaluation result
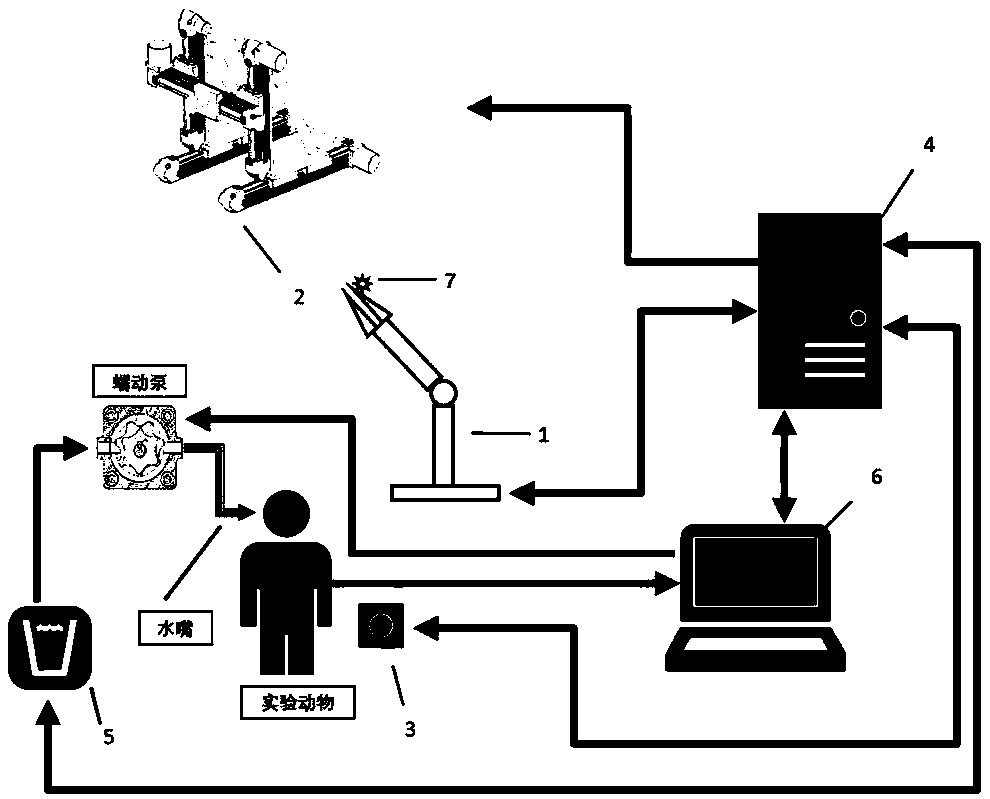
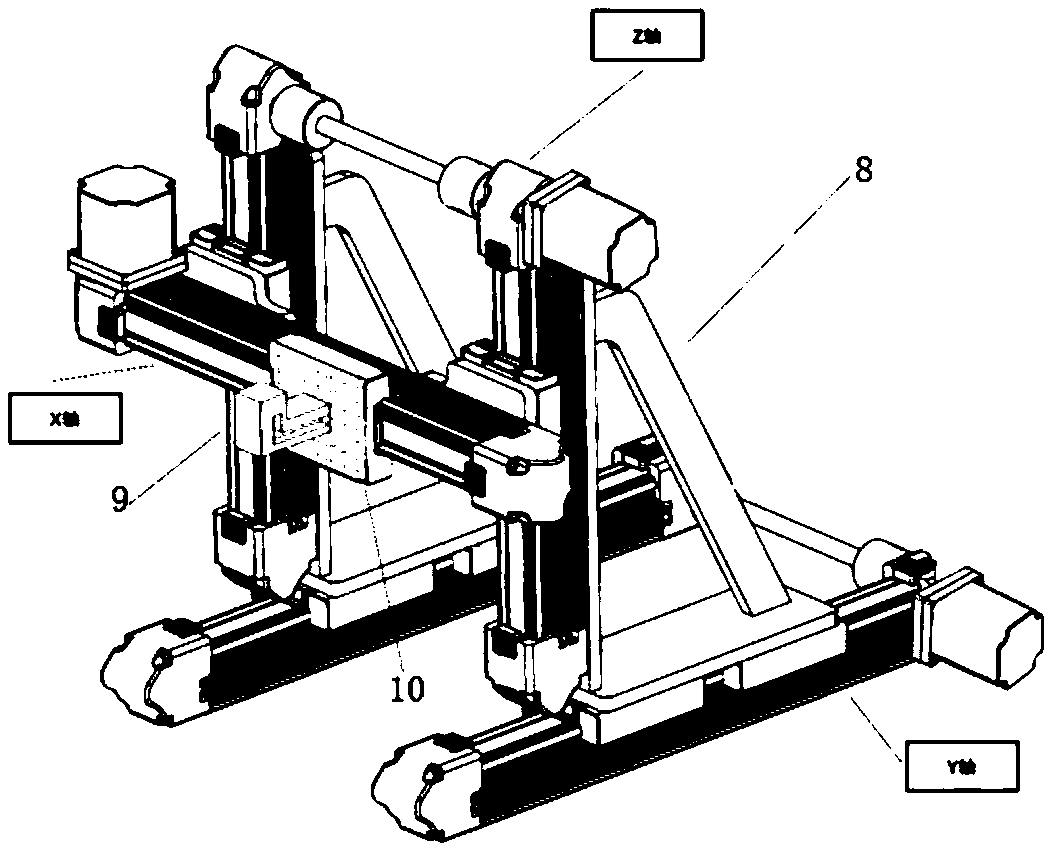
The invention provides an automated training assisting device for training a non-human primate animal to control a mechanical arm to conduct stretching and grabbing. The automated training assisting device comprises a mechanical arm, a three-dimensional storage platform, an animal control device, a microcontroller, a water feeding control system and a PC; the microcontroller is connected with themechanical arm, the three-dimensional storage platform, the animal control device, the water feeding system and the PC separately. The automated training assisting device is reasonable in design, easyto operate and high in training efficiency; the position of a grabbed object can be automatically changed in a three-dimensional space, the grabbing identification range of the mechanical arm, the movement speed, the illuminating range of an LED matrix and other training parameters can be quickly adjusted, stepwise learning training is achieved, the learning difficulty is reduced, the training process is adapted to, and switching can be achieved between the movement mode of the animal control device and the movement mode of the mechanical arm; through the combination of active learning, passive observing and other modes with learning training, reasonable evaluation is made, after training is completed, the evaluation result can be directly used for the next experiment, and it is achievedthat the non-human primate animal automatically controls the mechanical arm to conduct stretching and grabbing training.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
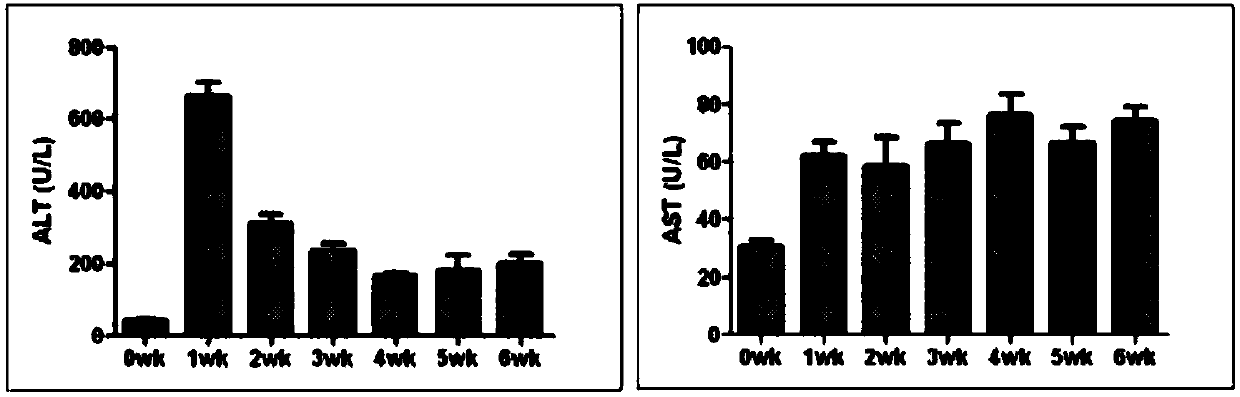
Chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis non-human primate model, method for building same and application of chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis non-human primate model
ActiveCN107912366AImprove stabilityReduce mortalityAnimal husbandryDiabetes mellitusHepatocellular carcinoma
The invention discloses a chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) non-human primate model, a method for building the same and application of the chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis non-human primate model. The chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis non-human primate model, the method and the application have the advantages that the chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis non-human primate model built by the aid of the method further can be accompanied by pathological characteristics of chronic hepatic fibrosis and hepatic cirrhosis, can be used for research and development of medicines forpreventing or treating chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, the chronic hepatic fibrosis and the hepatic cirrhosis and can be used as an animal model for research on chronic fatty livers, steatohepatitis, the hepatic fibrosis, the hepatic cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, metabolic diseases, diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications, and accordingly the chronic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis non-human primate model and the method have extremely high application values.
Owner:江苏珂玛麒生物科技有限公司
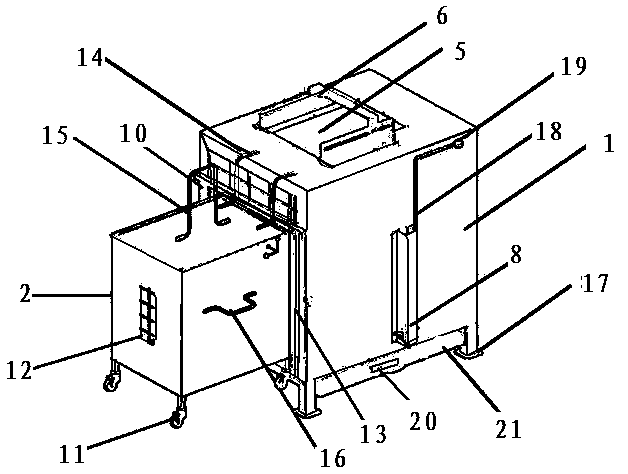
Touch screen multifunctional non-human primate cognitive function test cage
The invention discloses a touch-screen multifunctional non-human primate animal cognitive-function testing cage and belongs to the technical field of animal experiment devices. The touch-screen multifunctional non-human primate animal cognitive-function testing cage comprises a testing cage and a transfer cage. An infrared-induction touch screen connected with a computer is fastened on the rear vertical face of the testing cage capable of moving back and forth, an observation window and a movable camera are arranged on the top face, a water supply nozzle is located at the rear locking-fixing position capable of moving vertically in front of the touch face of the touch screen, a feces receiving plate which can be pushed into or pulled out of the lateral vertical face of the testing cage is arranged under a grid-shaped base, and a testing cage door which can be pushed into or pulled out of the side face of the testing cage is arranged on a grid-shaped front vertical face. The transfer cage is provided with truckles and an observation window, and the front vertical face is a push-pull type transfer cage door which can be in butt joint with the testing cage door after being opened. The touch-screen multifunctional non-human primate animal cognitive-function testing cage can be used for flexibly, conveniently, intelligently, efficiently and accurately performing non-human primate animal training and testing based on a modern computer technology, does not need an additionally-equipped corresponding cage, has multiple practical functions and is low in purchase cost and usage cost.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-human primate embryonic stem and germ cells: methods of use and methods of making same
The present invention provides a non-human primate (nhp) pluripotential embryonic stem (ES) cell, which can be used in several ways as described herein, including to generate chimeric primate embryos. The invention further provides methods to determine the differentiation status of an embryonic cell by comparing its transcriptional patterns with those of ES cells at particular stages of differentiation.The invention further provides a non-human primate embryonic germ (EG) cell which can also be used in several ways, including administering the differentiated EG cell line to a patient to treat a number of diseases.Also provided are methods of generating nhp ES cell+primate embryo chimeras, and methods of deriving EG cells.
Owner:MAGEE WOMENS RES INST & FOUND
Non-human primate animal protector
InactiveCN105533863ASo as not to damageHigh implementabilityCatheterProtective garmentBiologyBody surface
The invention relates to a non-human primate animal protector. The non-human primate animal protector comprises a protector body. A hole for exposing the back of an animal is formed in the back of the protector body so that a body surface indwelling tube can be conveniently arranged, and a protective box for containing the body surface indwelling tube is arranged on the outer side of the hole. According to the non-human primate animal protector, as the hole for exposing the back of the animal is formed in the back of the protector body so that the body surface indwelling tube can be arranged at the back of the animal, and the protective box for containing the body surface indwelling tube is arranged on the outer side of the hole, an animal can not touch the body surface indwelling tube located at the back; as the body surface indwelling tube is contained in the protective box, when the animal moves in a small degree, the body surface indwelling tube can not be damaged, and the implementation performance is good.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
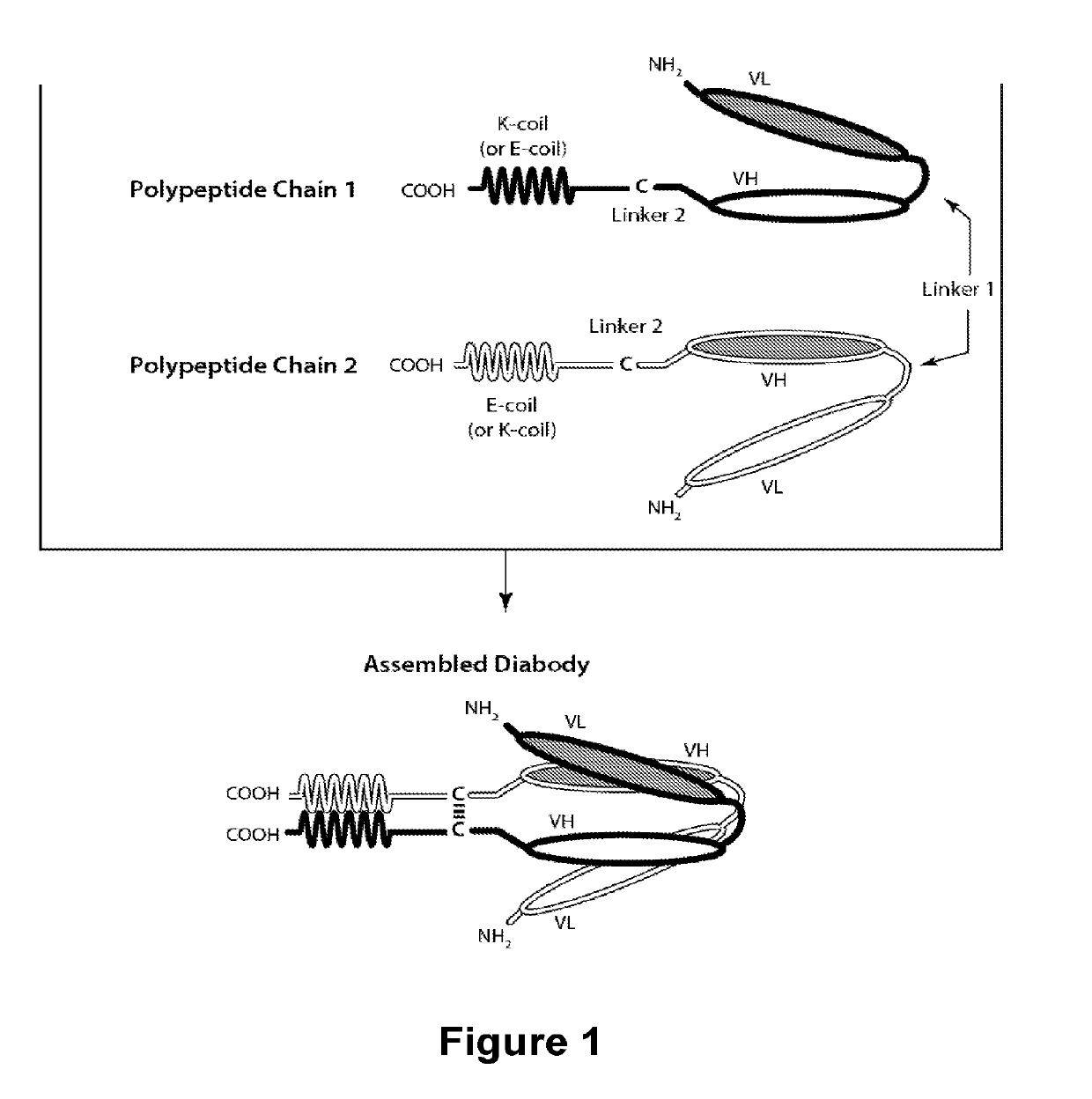
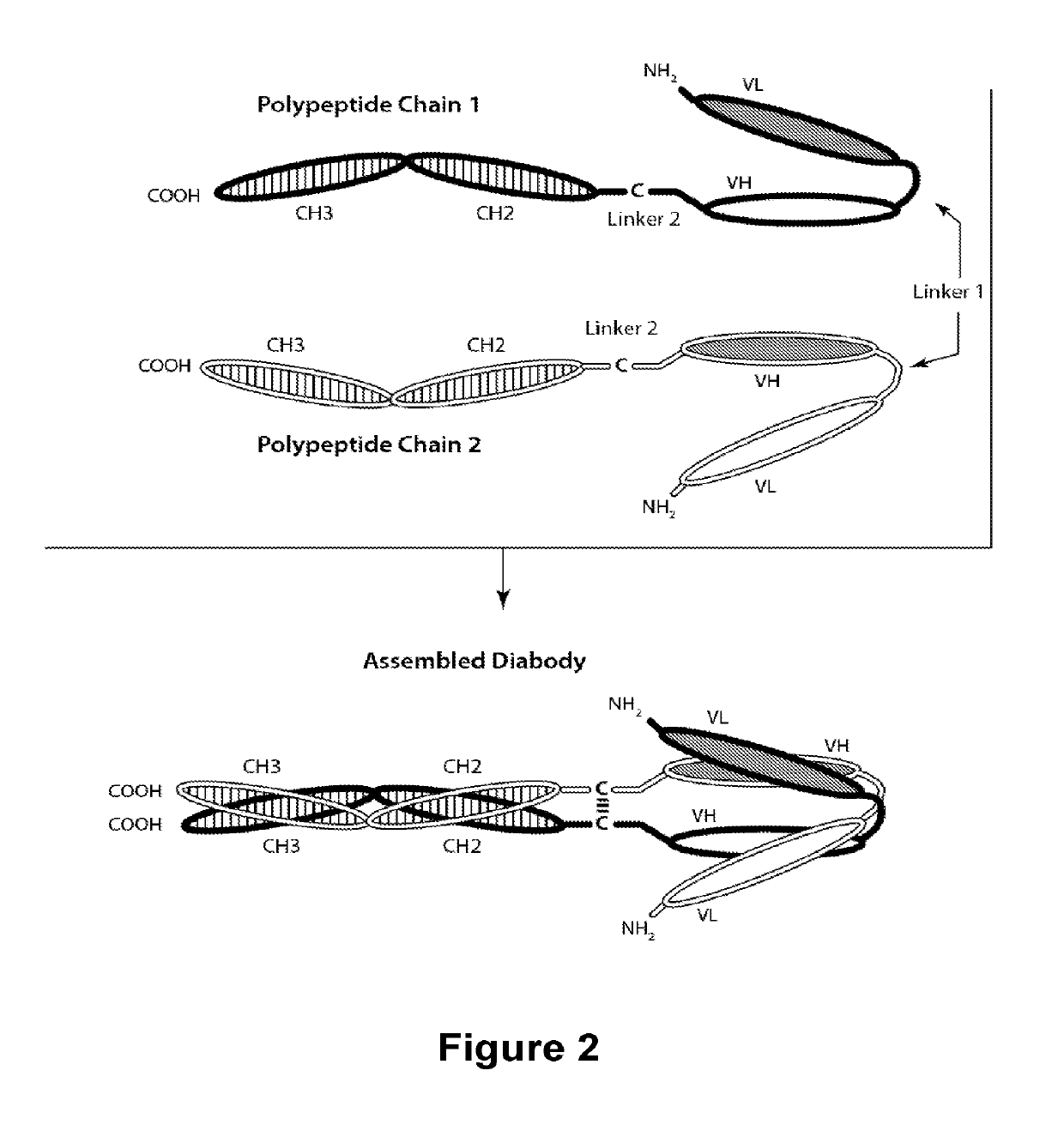
Novel b7-h3 binding molecules, antibody drug conjugates thereof and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20190127471A1Increased serum half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseAntibody conjugate
The present invention is directed to novel B7-H3-binding molecules capable of binding to human and non-human B7-H3, and in particular to such molecules that are cross-reactive with B7-H3 of a non-human primate (e.g., a cynomolgus monkey). The invention additionally pertains to B7-H3-binding molecules that comprise Variable Light Chain and / or Variable Heavy Chain (VH) Domains that have been humanized and / or deimmunized so as to exhibit a reduced immunogenicity upon administration to recipient subjects. The invention particularly pertains to bispecific, trispecific or multispecific B7-H3-binding molecules, including bispecific diabodies, BiTEs, bispecific antibodies, trivalent binding molecules, etc. that comprise: (i) such B7-H3-binding Variable Domains and (ii) a domain capable of binding to an epitope of a molecule present on the surface of an effector cell. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions that contain any of such B7-H3-binding molecules, and to methods involving the use of any of such B7-H3-binding molecules in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and conditions. The invention also particularly pertains to a molecule that comprises the human B7-H3 binding domain of a humanized anti-human B7-H3 antibody conjugated to at least one drug moiety (a “B7-H3-ADC”). The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions that contain such B7-H3-ADCs, and to methods involving the use of any of such B7-H3-ADCs in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and conditions.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
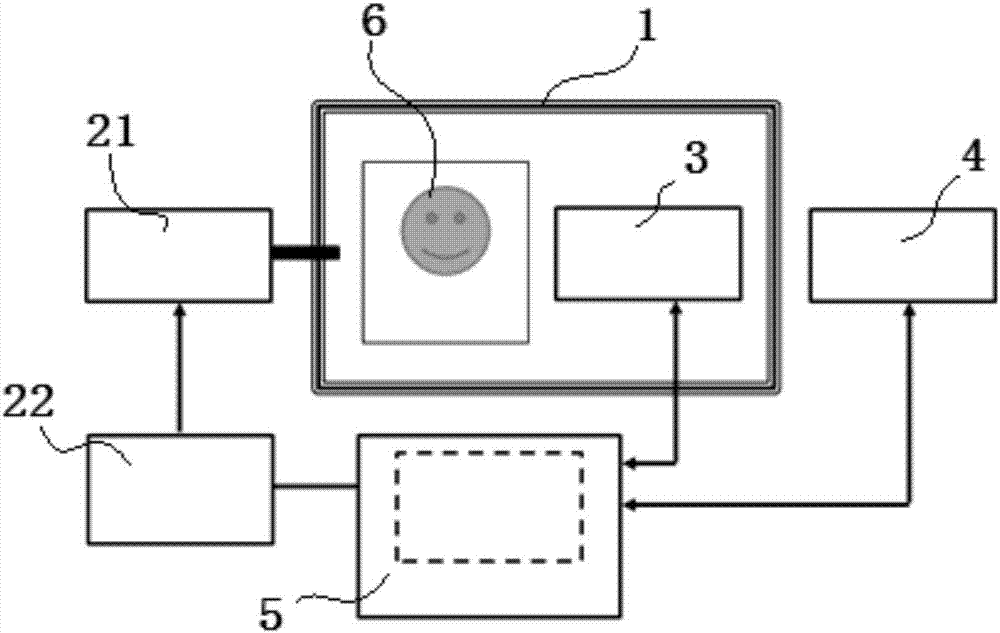
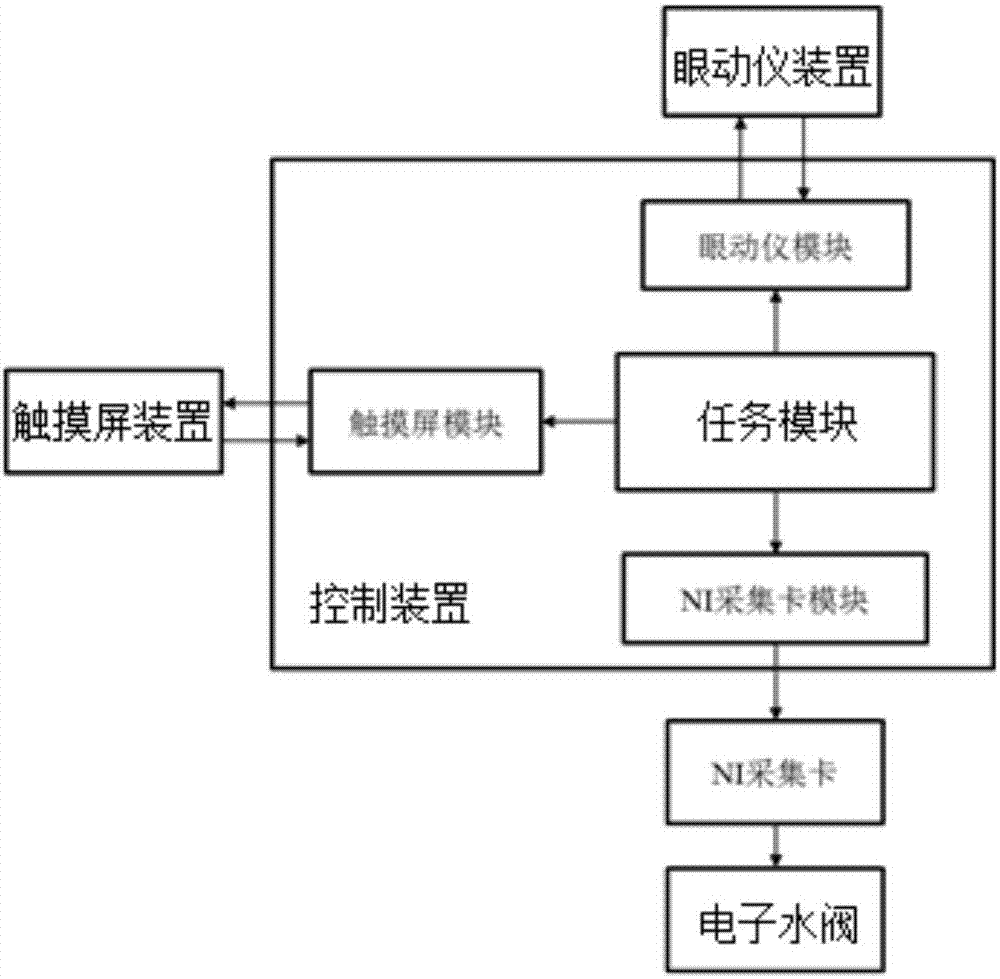
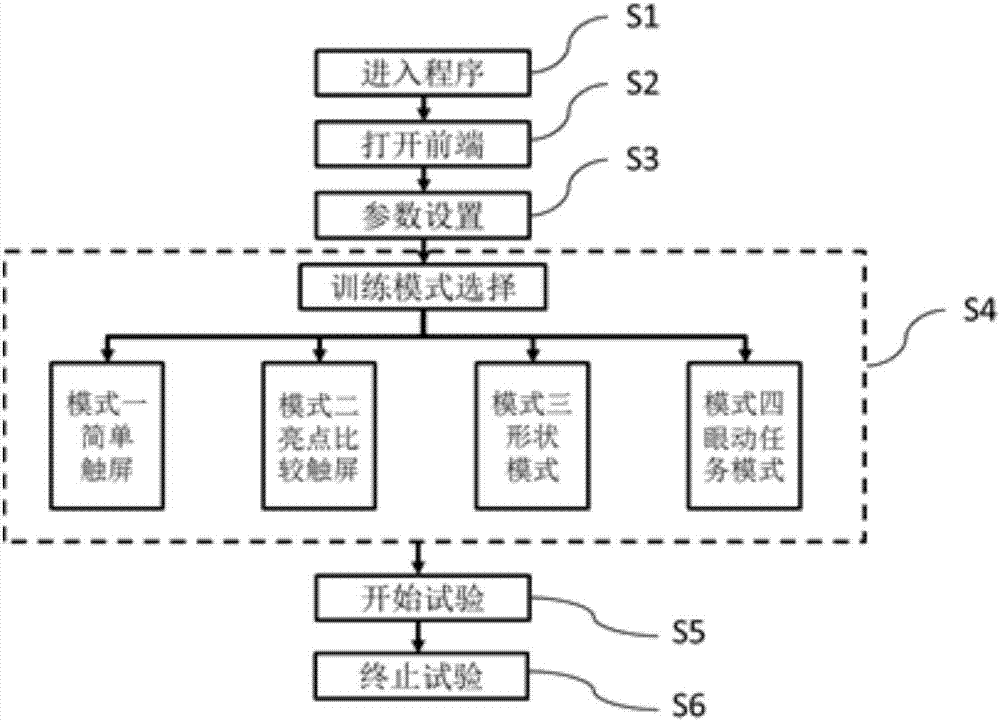
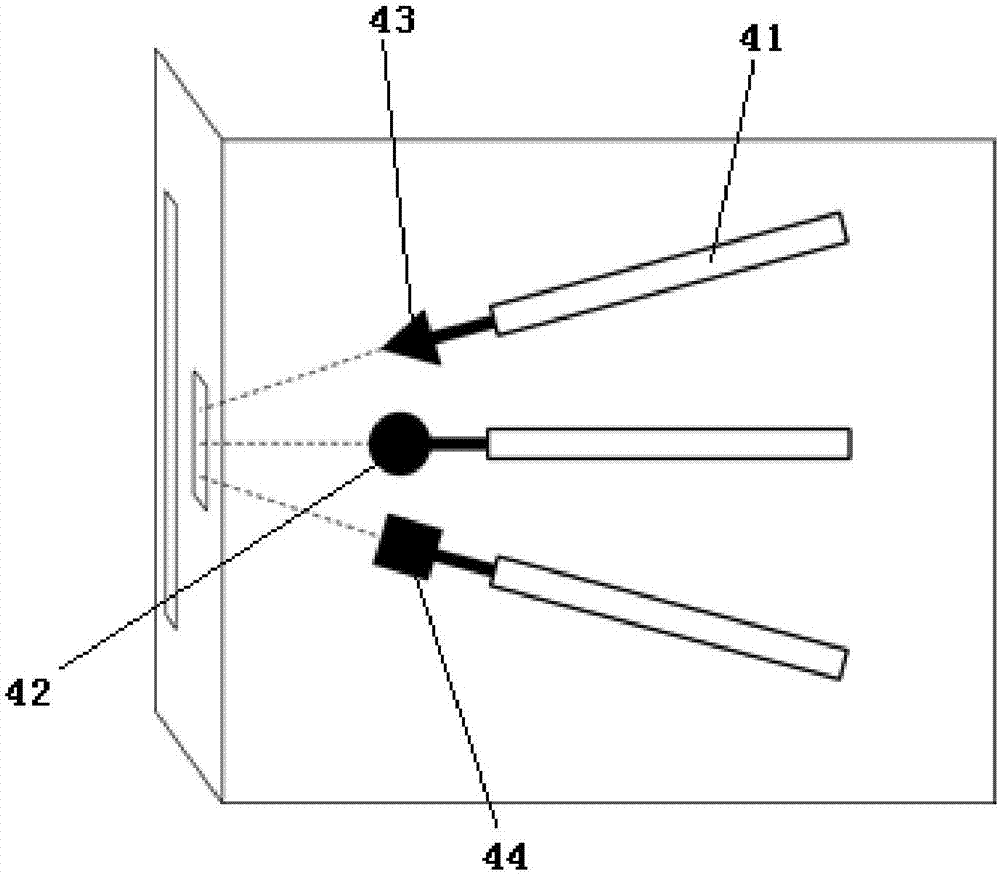
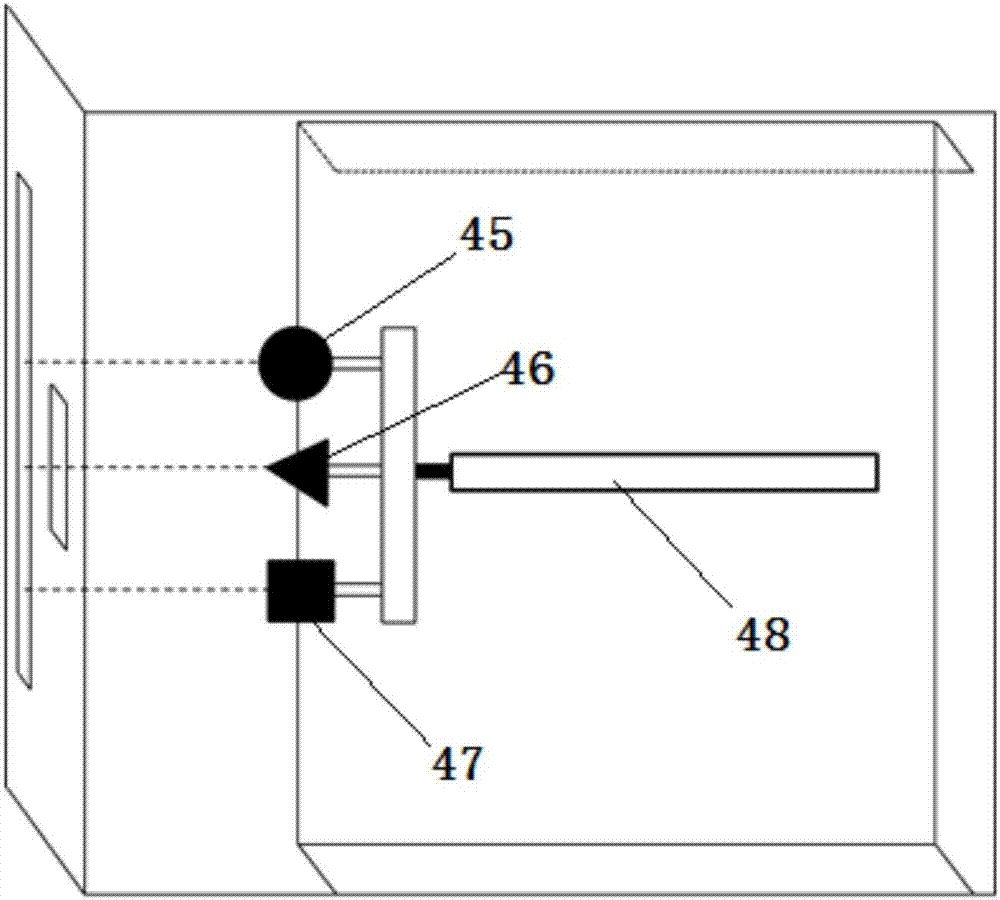
Non-human primate visual sense and cognition function research system
InactiveCN107041322APostural stabilityHigh interaction dimensionOther apparatusInfrared lampHuman–computer interaction
The invention discloses a non-human primate visual sense and cognition function research system comprising the following structures: a fixed seat including a seat, a lantern ring fixed system, a waist restrain plate, and a touch screen device portal frame; a water supply system including a water barrel, an electronic water valve and a NI acquisition card; a touch screen device having a visual sense stimulation touch screen capable of playing sounds for hearing stimulations and presenting images; an eye tracker including an infrared camera, an infrared lamp, an eye tracker body, and an interaction module; a controlling including an N1 acquisition card module, a touch screen module, an eye tracker module and a task module; the non-human primate visual sense and cognition function research system can obtain stable animal postures, thus further extracting animal eyeball motion direction characteristic vector and experiment animal cognition capability parameters; the system is high in interaction dimension, high in integration level, and high in experiment precision and efficiency.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Automatic training device of non-human primate touch sense research and training method of device
ActiveCN107347702AEasy to operateVarious training modesTaming and training devicesMicrocontrollerTouch Senses
The invention discloses an automatic training device of non-human primate touch sense research and a training method of the device. The automatic training device comprises a PC, a camera, a microcontroller, an animal seat and a multiple target selection grasping device, wherein the PC is provided with a display; the camera is connected with the PC; the microcontroller is connected with the PC by a serial port; the animal seat is used for fixing an experimental animal; the multiple target selection grasping device is located in front of the animal seat and divided into three layers, including a preparing button on the first layer, a grasping target object on the second layer and a judgement selection target object on the third layer; a prompt lamp is arranged on each layer, pressure sensors are fixed on the preparing button, the grasping target object and the judgement selection target object respectively, the grasping target object and the judgement selection target object are fixed on electric linear push rods which can move front and back, and the prompt lamps, the pressure sensors and the electric linear push rods are connected with the microcontroller respectively. According to the automatic training device, the training speed is greatly improved, and consumption of manpower resource can be saved.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Identification of genes or polypeptides the expression of which correlates to fertility, ovarian function and/or fetal/newborn viability
InactiveUS20060024693A1Microbiological testing/measurementTissue cultureAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
A genetic means of determining whether a female subject produces “pregnancy competent” oocytes is provided. The means comprises detecting the level of expression of one or more genes that are expressed at characteristic levels (upregulated or downregulated) in cumulus cells derived from pregnancy competent oocytes. This characteristic gene expression level, or pattern referred to herein as the “pregnancy signature”, also can be used to identify subjects with underlying conditions that impair or prevent the development of a viable pregnancy, e.g., pre-menopausal condition, other hormonal dysfunction, ovarian dysfunction, ovarian cyst, cancer or other cell proliferation disorder, autoimmune disease and the like. Microarrays containing “pregnancy signature” genes or corresponding polypeptides provide another preferred aspect of the invention. Still further, the subject invention can be used to derive animal models, e.g., non-human primate animal models, for the evaluation of the efficacy of putative female fertility treatments.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Non-human primate model of age-related macular degeneration and method for producing same
ActiveUS20180272009A1Accurate assessmentCompounds screening/testingAnimal husbandrySodium iodateVitreous humour
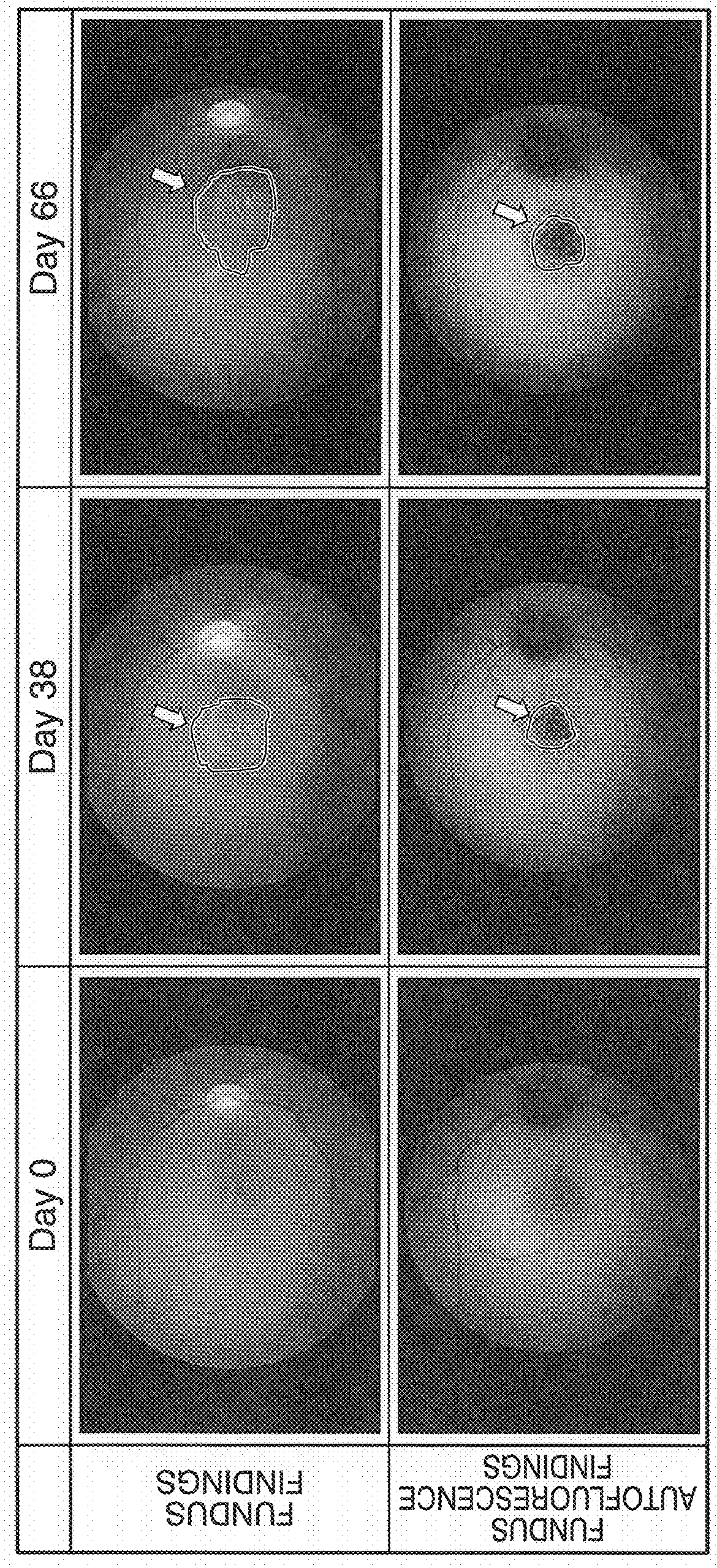
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a non-human primate model of AMD, a method for evaluating the efficacy of a test substance in the prevention or treatment of AMD using the AMD animal model produced according to this method, and a method for screening substances effective in the prevention or treatment of AMD using the aforementioned AMD animal model. The method for preparing the AMD animal model consists of administering sodium iodate into a vitreous body of a non-human primate, and the method for evaluating the efficacy of a test substance in the prevention or treatment of AMD consists of preparing a non-human primate model of AMD according to the aforementioned method for preparing an AMD animal model, and evaluating the efficacy of the test substance in the prevention or treatment of AMD using the resulting AMD animal model.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHARMA RES INC +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com