Non-human primate Fc receptors and methods of use
a technology of human primate fc and receptor, which is applied in the field of nonhuman primate fc receptor, can solve the problems of missing information regarding the interaction of human antibodies with primate fc, and achieve the effects of facilitating oligomerization of protein, facilitating purification of fusion protein, and enhancing stability of fusion protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Molecular Cloning of Cynomolgus and Chimp Fc Receptor DNA and .beta.-2 Microglobulins
[0154] Materials and Methods:
Cloning of Cynomolgus Monkey Fc.gamma.R
[0155] Since cynomolgus monkey DNA shares approximately 90% homology to human DNA, a series of PCR primers for each Fc.gamma.R was designed based on the sequence of the corresponding human receptor. Each sense primer starts at a site immediately 5' of the coding region or at the start of the coding region. The antisense primers were designed in the same way, i.e. immediately 3' of the C terminal stop codon or at the C terminal stop codon. Primers incorporated endonuclease restriction sites used to subclone PCR product into a pRK vector (Eaton et al.). The sequences of the primers are shown in Table 1.
2TABLE 1 Restriction sites are underlined. Receptor Cyno Fc.gamma.RI Full-Length Forward CAGGTCAATCTCTAGACTCCCACCAGCTTGGAG Primer (SEQ ID NO: 31) Reverse GGTCAACTATAAGCTTGGACGGTCCAGATCGAT Primer (SEQ ID NO: 32) Restriction XbaI / HindIII ...
example 2
Alignment of Nucleotide and Amino Acid Sequences of Cynomolgus, Chimp and Human Fc.gamma.R
[0160] Nucleotide and amino acid sequences for FcR polypeptides from human, cynomolgus and chimps were aligned and % sequence identity calculated.
[0161] Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of primate and human proteins were aligned manually and differences in nucleotide or protein sequence noted. Percent identity was calculated as [number of identical residues] / [number of total residues]. When the sequences differed in the total number of residues, two values for percent identity are provided, using the two different numbers for total residues. Nucleotide sequences begin at the coding sequence for the signal sequence.
[0162] The alignment of nucleic acid sequences for human (SEQ ID NO: 2) and cynomolgus Fc.gamma.RI .alpha.-chain (SEQ ID NO: 1) as shown in Table 3 below. The dots indicate locations of nucleotide sequence differences. An analysis of the % sequence identity shows that the human and...
example 3
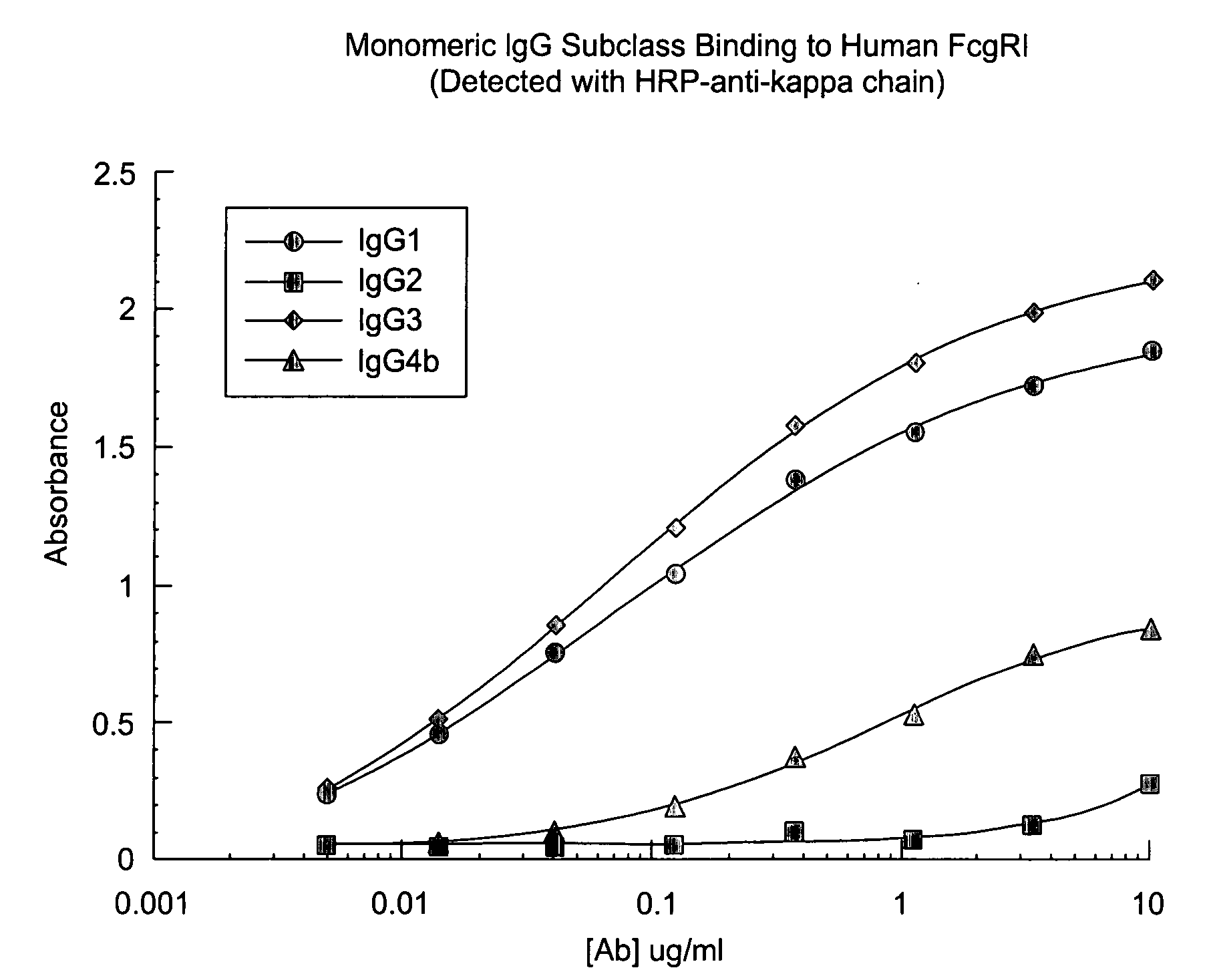
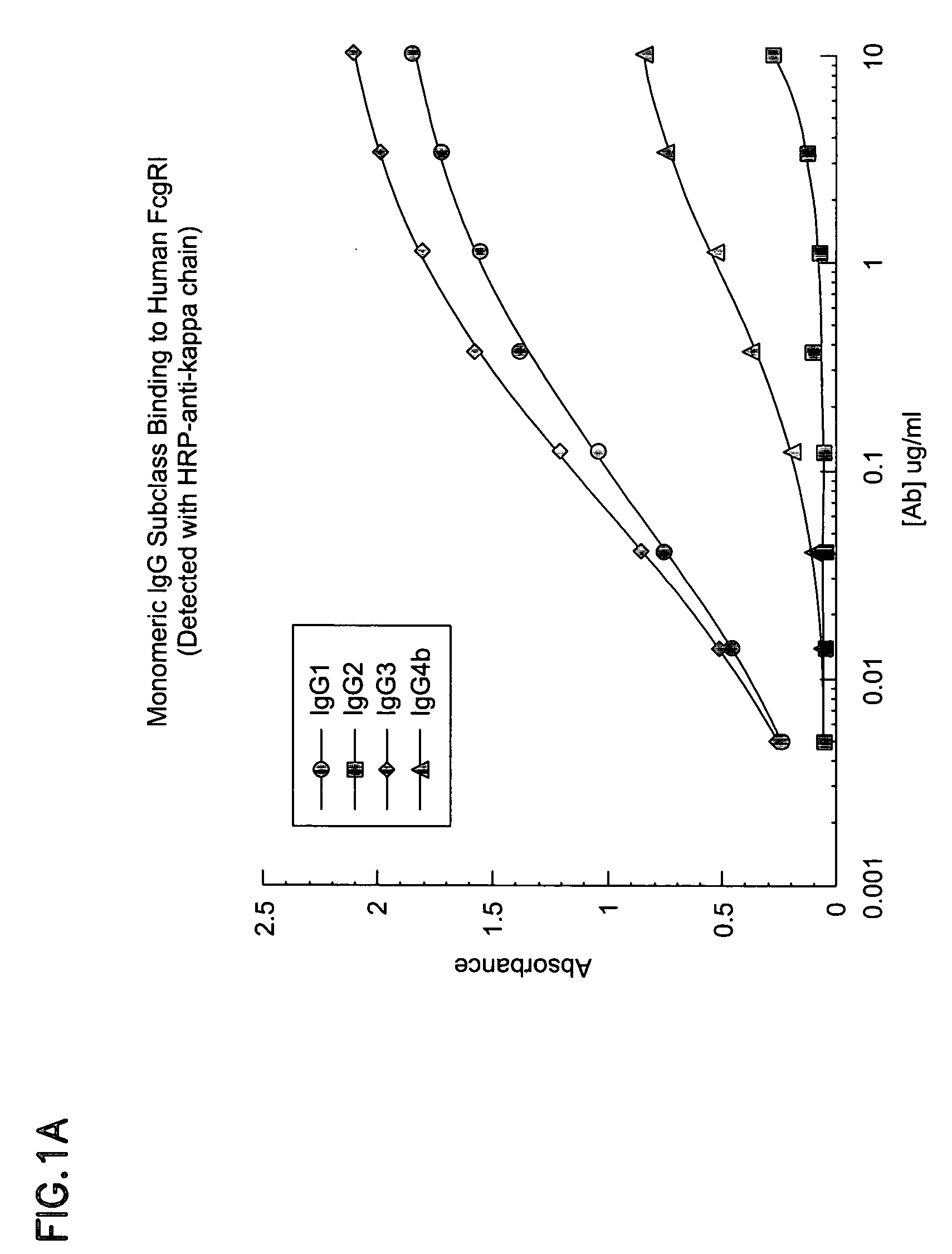
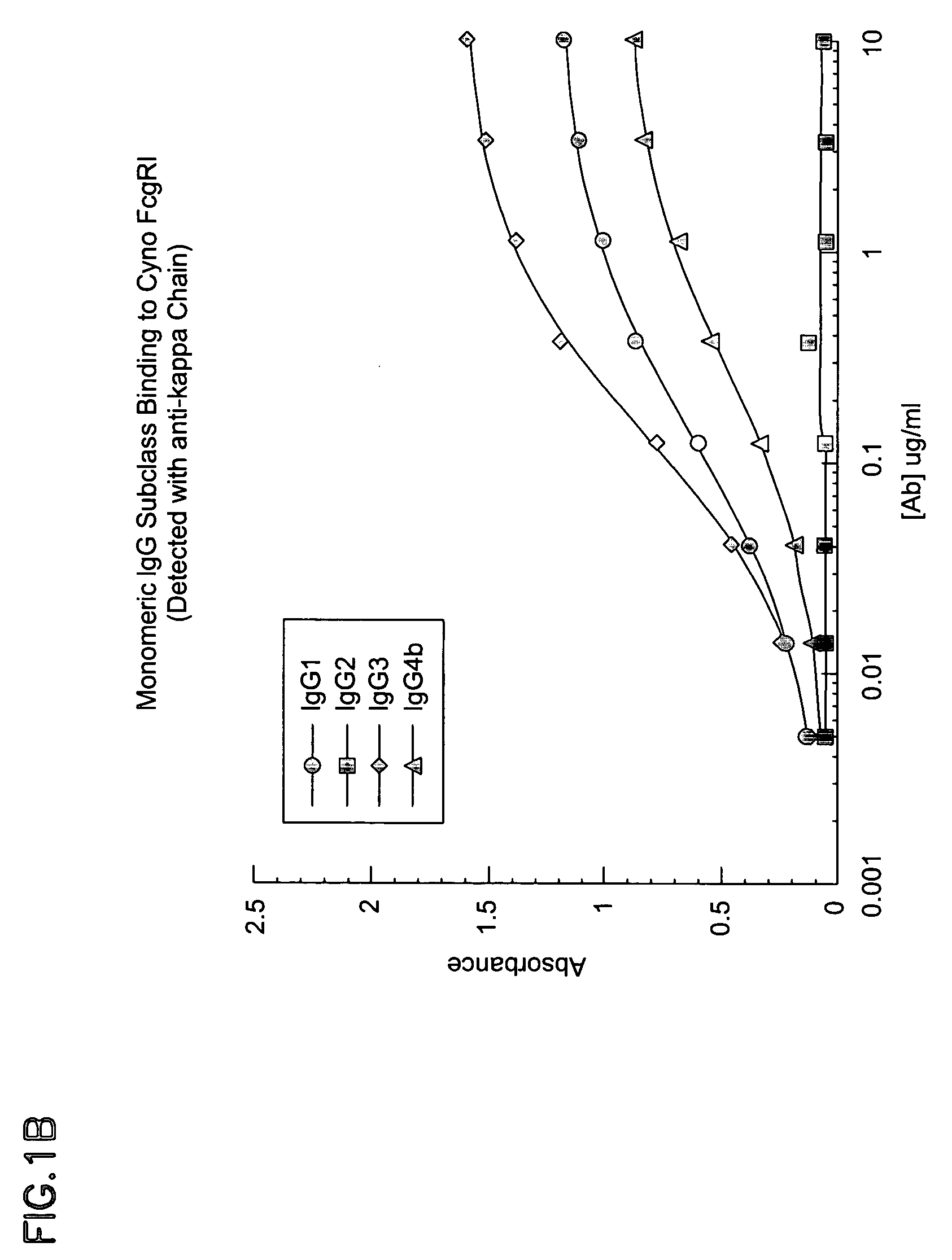
Cynomolgus Fe.gamma.RI And Human Fc.gamma.RI Bind Human IgG Subclasses Equivalently
[0213] Materials and Methods:
[0214] Human IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 isotypes of E27 (IgG 1) were constructed by subcloning the appropriate heavy chain Fc cDNA from a human spleen cDNA library into a pRK vector containing the E27 variable heavy domain. All IgG subclasses and variants were expressed using the same E27 .kappa. light chain as described in Shields, R. L., Namenuk, A. K., Hong, K., Meng, Y. G., Rae, J., Briggs, J., Xie, D., Lai, J., Stadlen, A., Li, B., Fox, J. A., and Presta, L. G. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:6591-6604 or U.S. Pat. No. 6,194,551.
[0215] Following cotransfection of heavy and light chain plasmids into 293 cells, IgG1, IgG2, IgG4 and variants were purified by protein A chromatography. IgG3 was purified using protein G chromatography. All protein preparations were analyzed using a combination of SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, ELISA, and spectroscopy.
[0216] The cDNA for Human ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| δ δ δ δ | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| δ δ δ δ | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| δ δ | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com