Method and apparatus for fabrication of lattice composite fuselage for commercial aircraft employing steered fiber lay up
a composite fuselage and steered fiber technology, applied in the direction of power plant exhaust arrangement, transportation and packaging, other domestic articles, etc., can solve the problems of non-recurring and recurring expenses, increased weight and cost, and less uniform lattice in aircraft structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019]The embodiments and methods described herein provide combined use of automated Steered Fiber Lay-up (SFL) and lattice design to fabricate integrally stiffened, stringerless sections of composite fuselage which incorporate windows, doors and other design features. The fuselage skin and stiffening lattice are fabricated as integral structure on the surface of a mold employing an automatic layup machine. This approach eliminates the need to separately produce skin, stringers and frames by different manufacturing equipment and a final assembly using co-curing, co-bonding, fastening. Use of automated SFL allows variation in lattice geometry and rib shape to accommodate local design features or disruptions. Unlike WFW no manual layup is required to support local reinforcement in areas of features or disruptions such as fuselage openings.
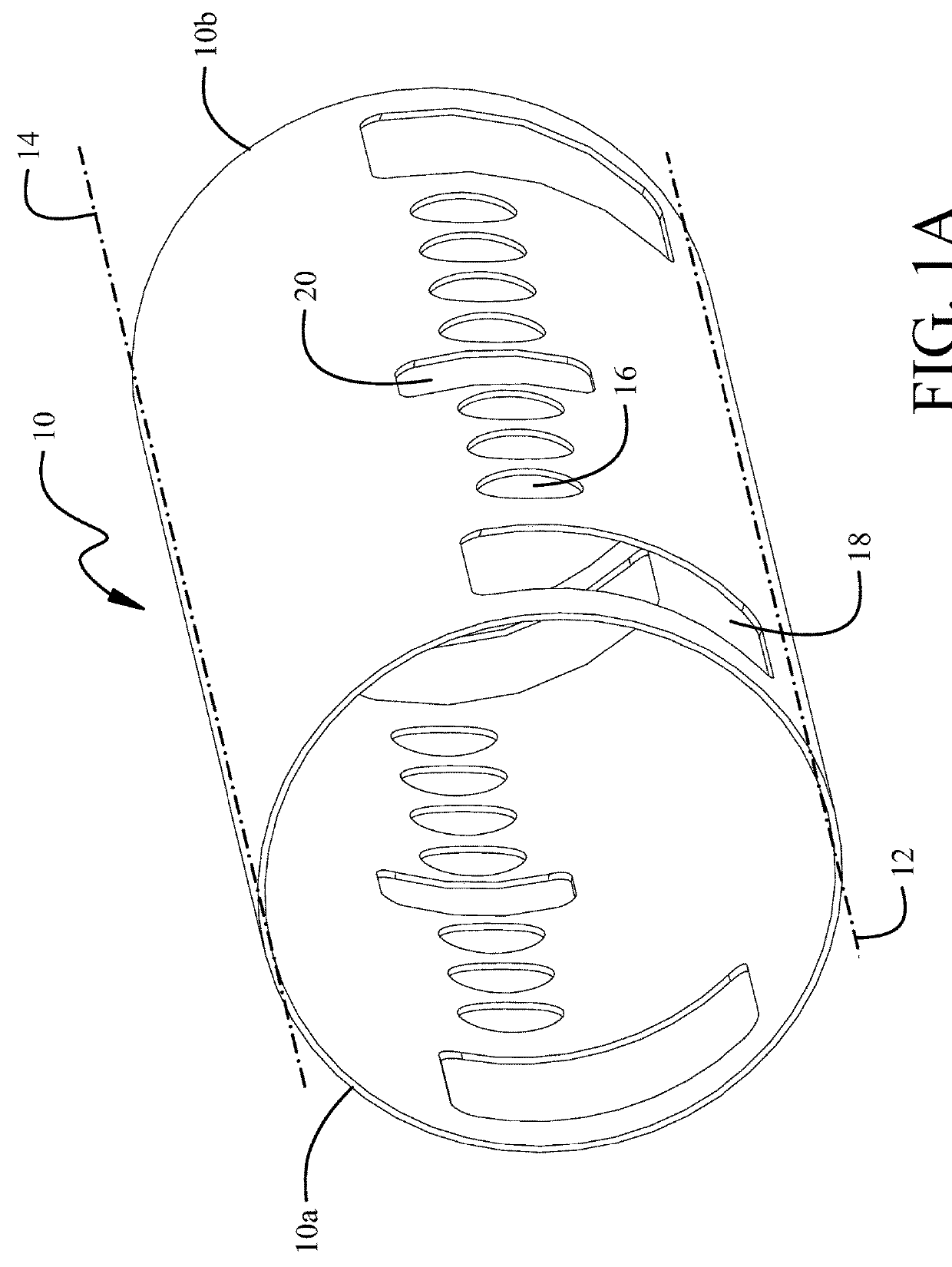
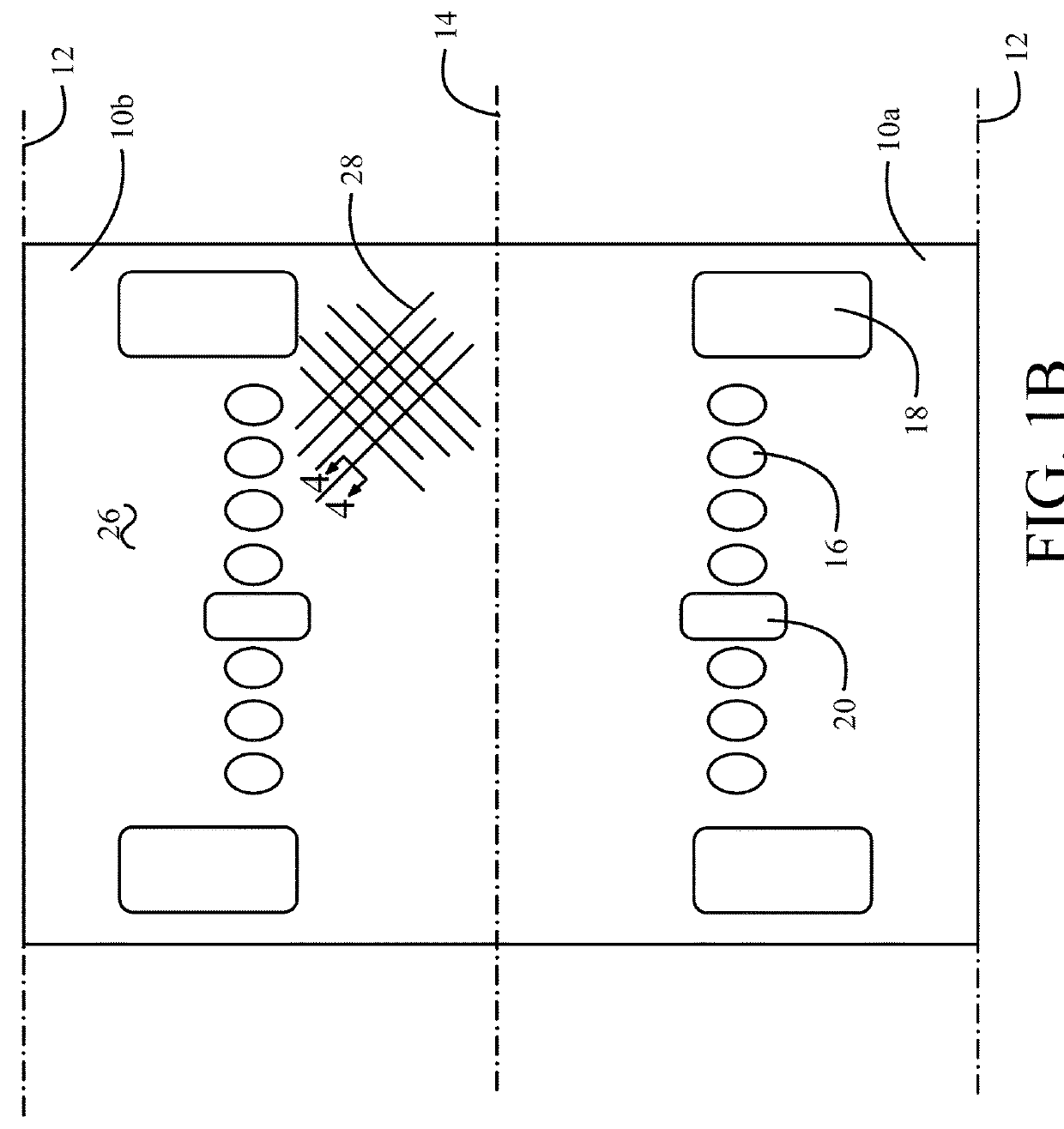
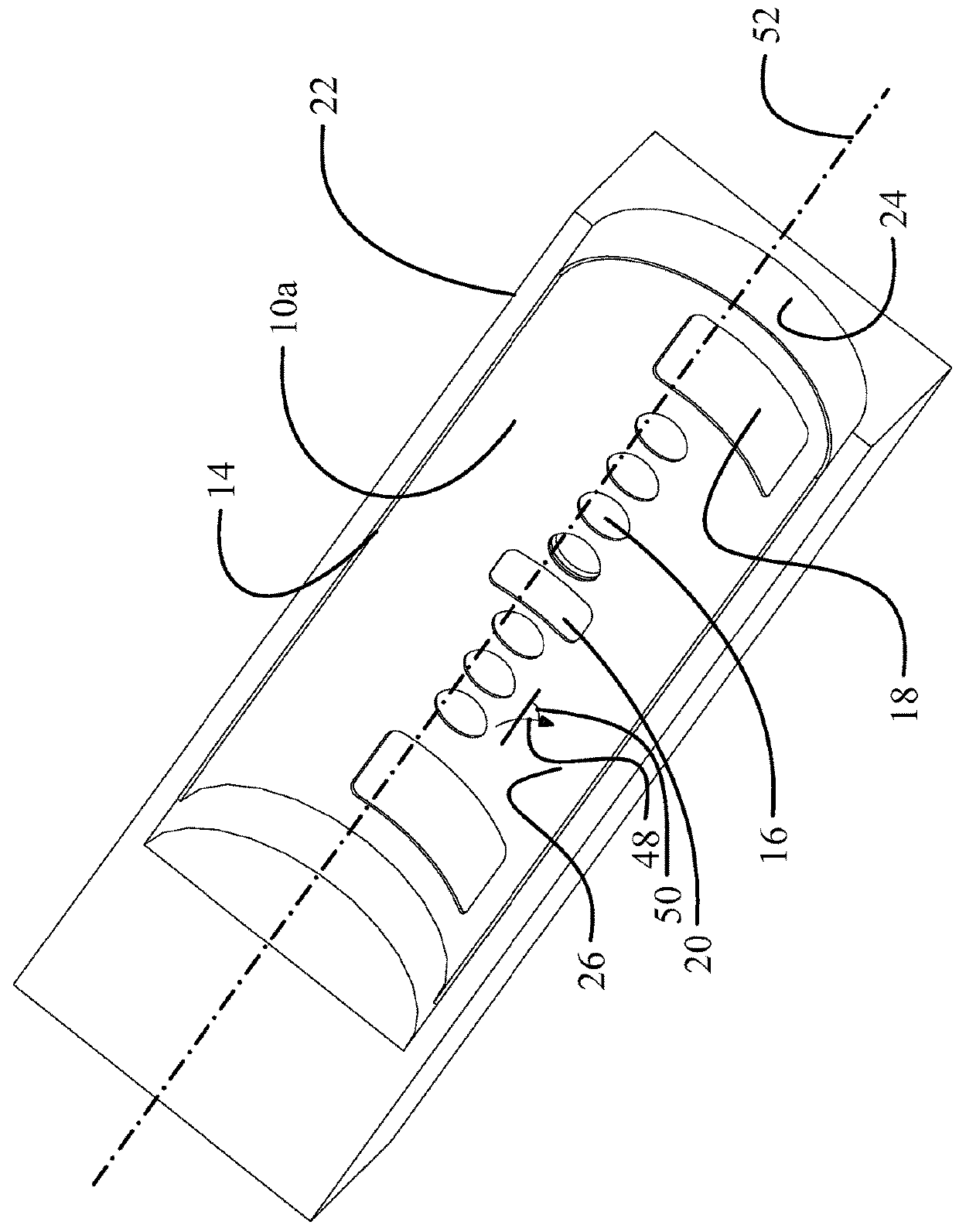
[0020]Referring to the drawings, FIG. 1A shows an exemplary fuselage section 10 for a commercial aircraft and FIG. 1B shows the fuselage depicted in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com