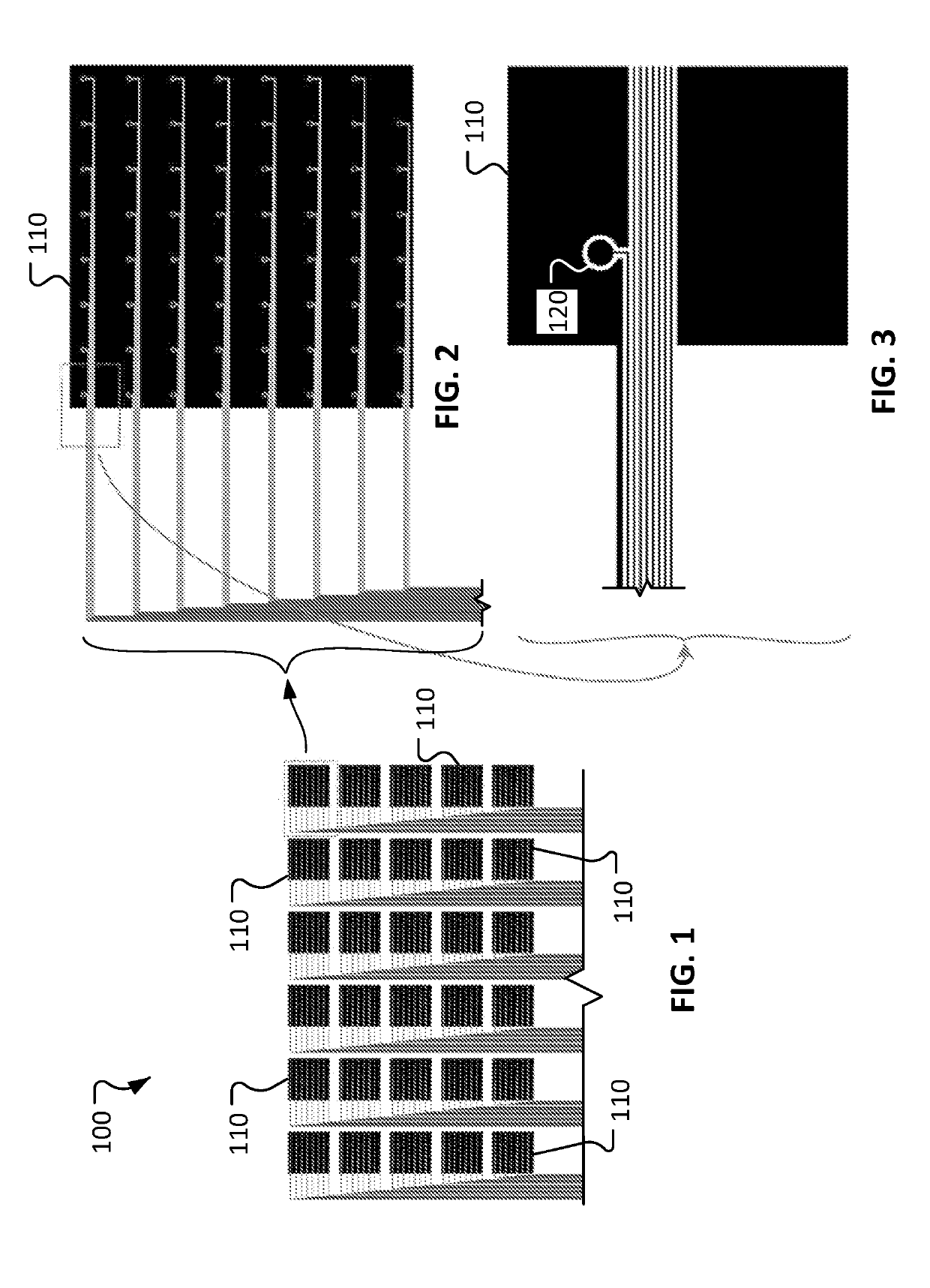
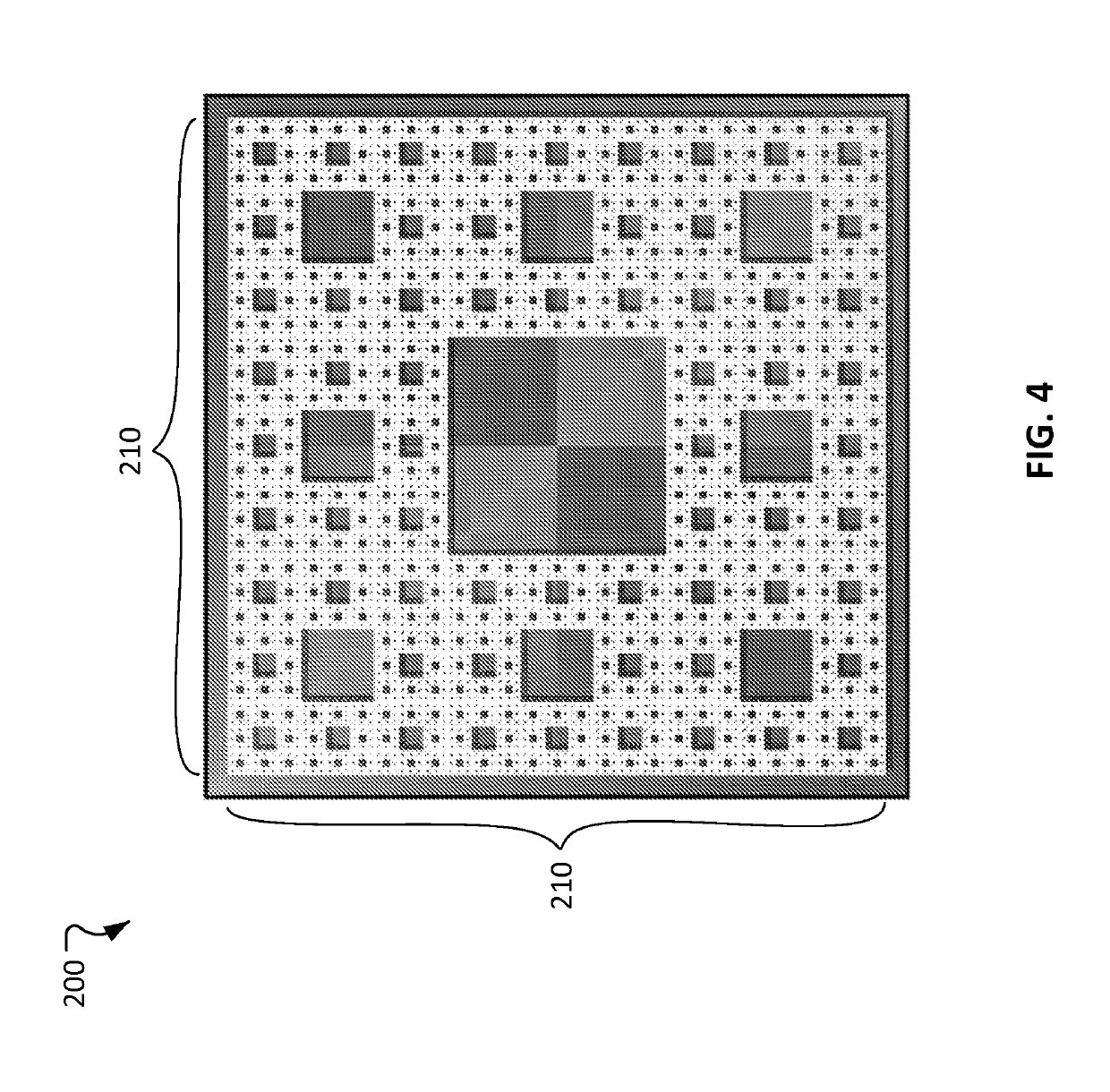
Multiscale brain electrode devices and methods for using the multiscale brain electrodes
a brain electrode and multi-scale technology, applied in the field of multi-scale electrodes, can solve the problems of significant challenge in recording and probing cortical gyri with optimal recording electrode, and achieve the effect of reducing seizure and saving tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working example # 1 (
Working Example #1 (Chronic Subthreshold Cortical Stimulation to Treat Focal Epilepsy)
[0063]Introduction:
[0064]Approximately one to three in 1,000 people have focal drug resistant epilepsy (DRE). Epilepsy surgery is the most effective treatment but may not be feasible when seizures originate from critical cortical areas, i.e. eloquent cortex. Despite evidence for efficacy, current approaches to focal brain stimulation rarely yield seizure free outcomes. In this working example, 13 patients were treated with continuous subthreshold electrical cortical stimulation, which led to suppression of interictal epileptiform discharges (IEDs) and improvement in clinical seizures.
[0065]Methods:
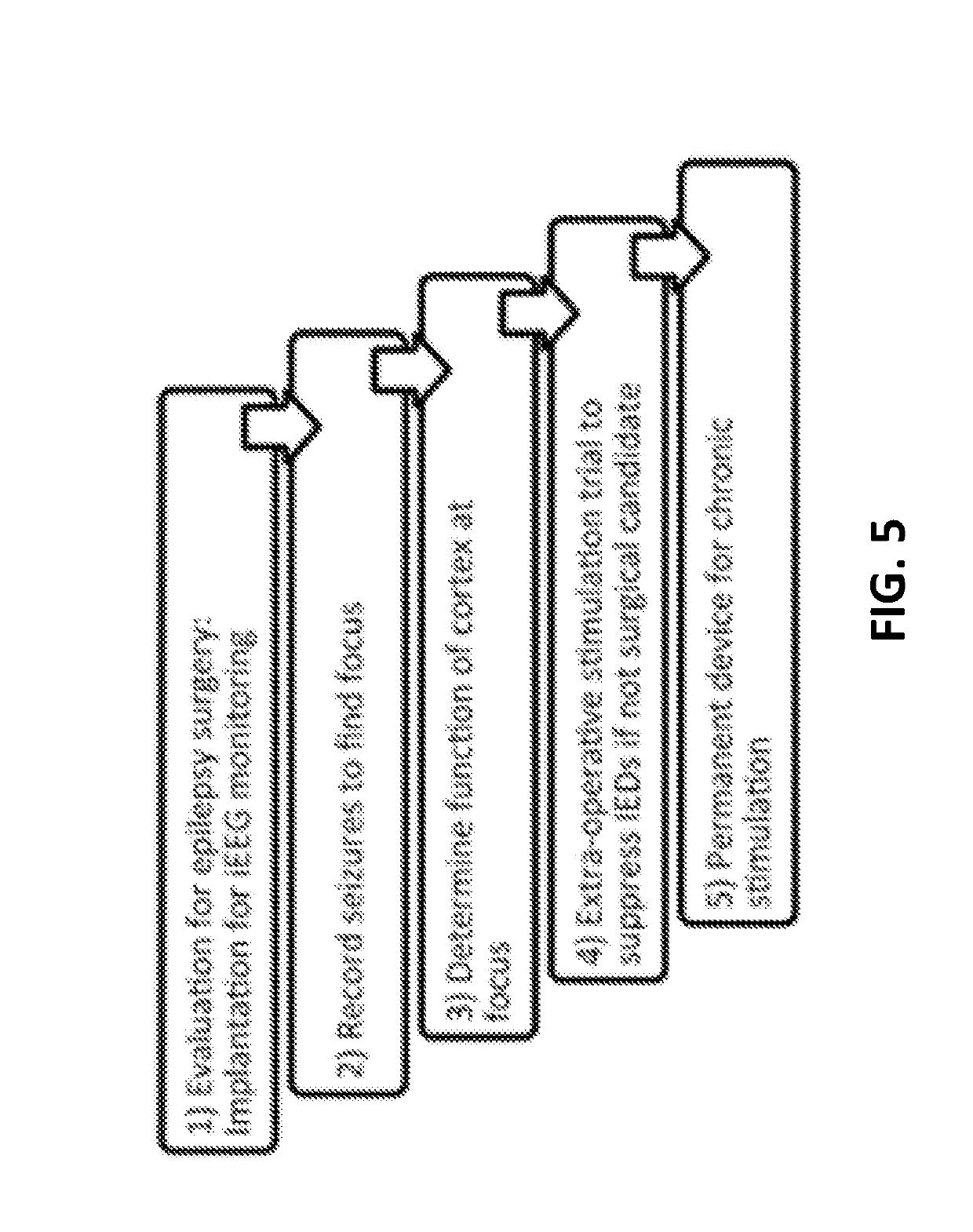
[0066]Thirteen patients with focal DRE were deemed unsuitable for resective surgery following intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG) monitoring with surgically implanted subdural grid and depth electrodes (see FIG. 5 showing steps of patient evaluation and treatment). Pre-stimulation monitoring was ty...
working example # 2 (
Working Example #2 (Multimodal Brain Mapping and Tracking)
[0071]Introduction:
[0072]Multimodal imaging of brain integrates complementary neurophysiological signals from multiple modalities at multiple scales to make classifications of tissue epileptogenicity. The modalities include, but are not limited to, SPECT, PET, MRI structure, and wide bandwidth multi-scale Electrophysiology. SPECT, PET, and multiscale continuous (days to week, from hundreds of channels, sampled at 32 kHz) local field potential (LFP) intracranial recordings from human subjects have been acquired using some embodiments of the multiscale brain electrodes described above.
[0073]This example in conjunction with the other disclosure provided herein encompasses at least the following innovative concepts:
[0074]1) A database of normal SPECT, PET, and LFP data from specific brain structures (Frontal, Temporal, sub-Temporal, medial temporal Parietal, Occipital) and specific functional regions (motor, sensory, language).
[0...
working example # 3 (
Working Example #3 (Microseizure Detection and HFO Detection)
[0113]Introduction:
[0114]This example includes methods for: 1) labeling microdomain epileptiform events called microseizures and HFO in large-scale EEG records, and 2) automated labeling brain tissue as epileptic and identifying the ictal onset zone (IOZ), i.e the brain regions generating spontaneous seizures, based on spatial maps of microseizure and HFO density.
[0115]High frequency oscillations (HFOs) are emerging as a promising biomarker of epileptogenic tissue. HFOs are spontaneous EEG transients with frequencies traditionally considered to range from 60 to 600 Hz with 4<=cycles <50 that stand out from the background as discrete electrographic events. HFOs are usually divided into subgroups of high γ (60-80 Hz), ripple (80-250) and fast ripple (250-600) bands (Bragin et al. 1999).
[0116]Video-EEG (v-EEG) monitoring has long been a cornerstone in the evaluation of patients with seizure disorders. Generally, the primary g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com