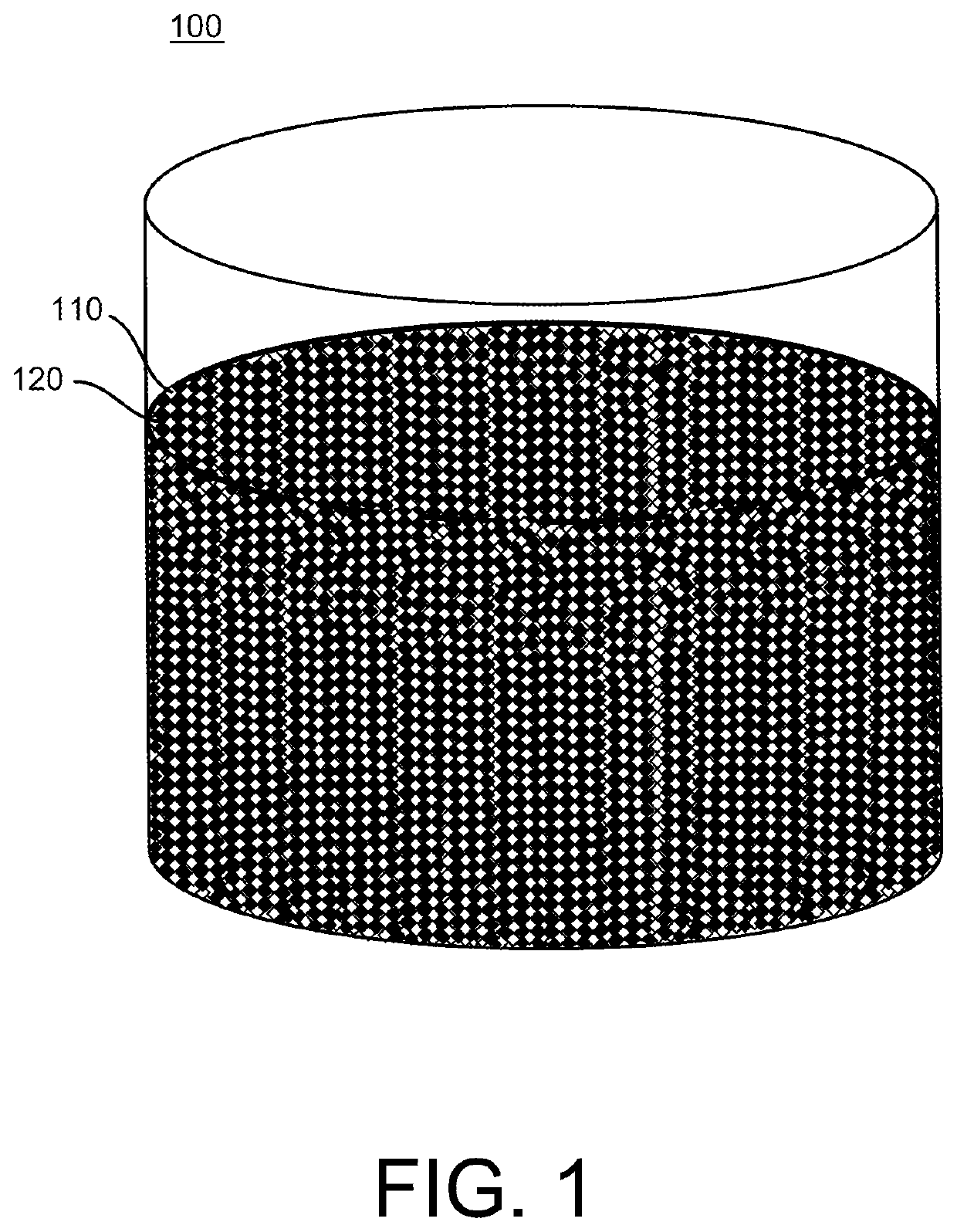
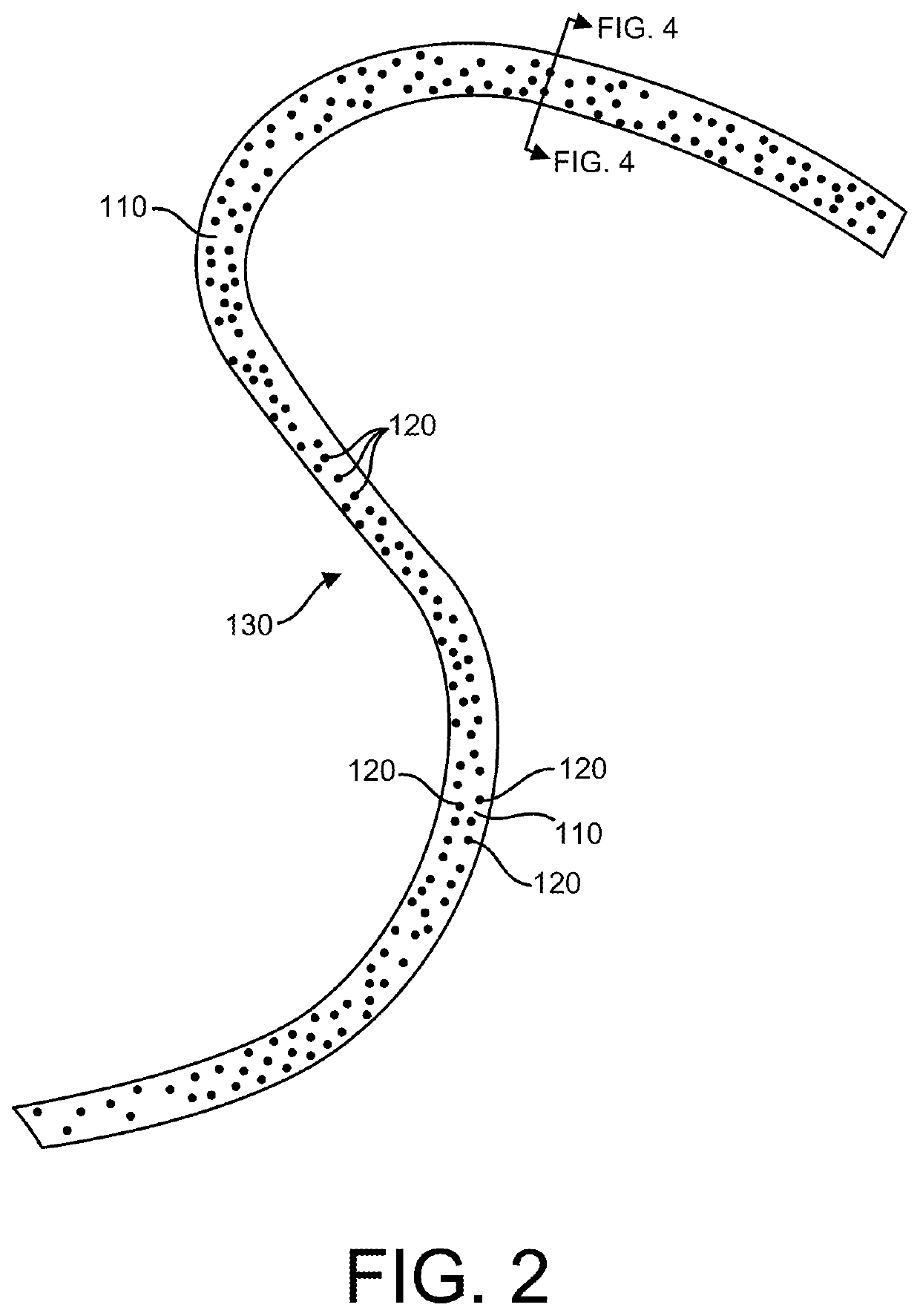
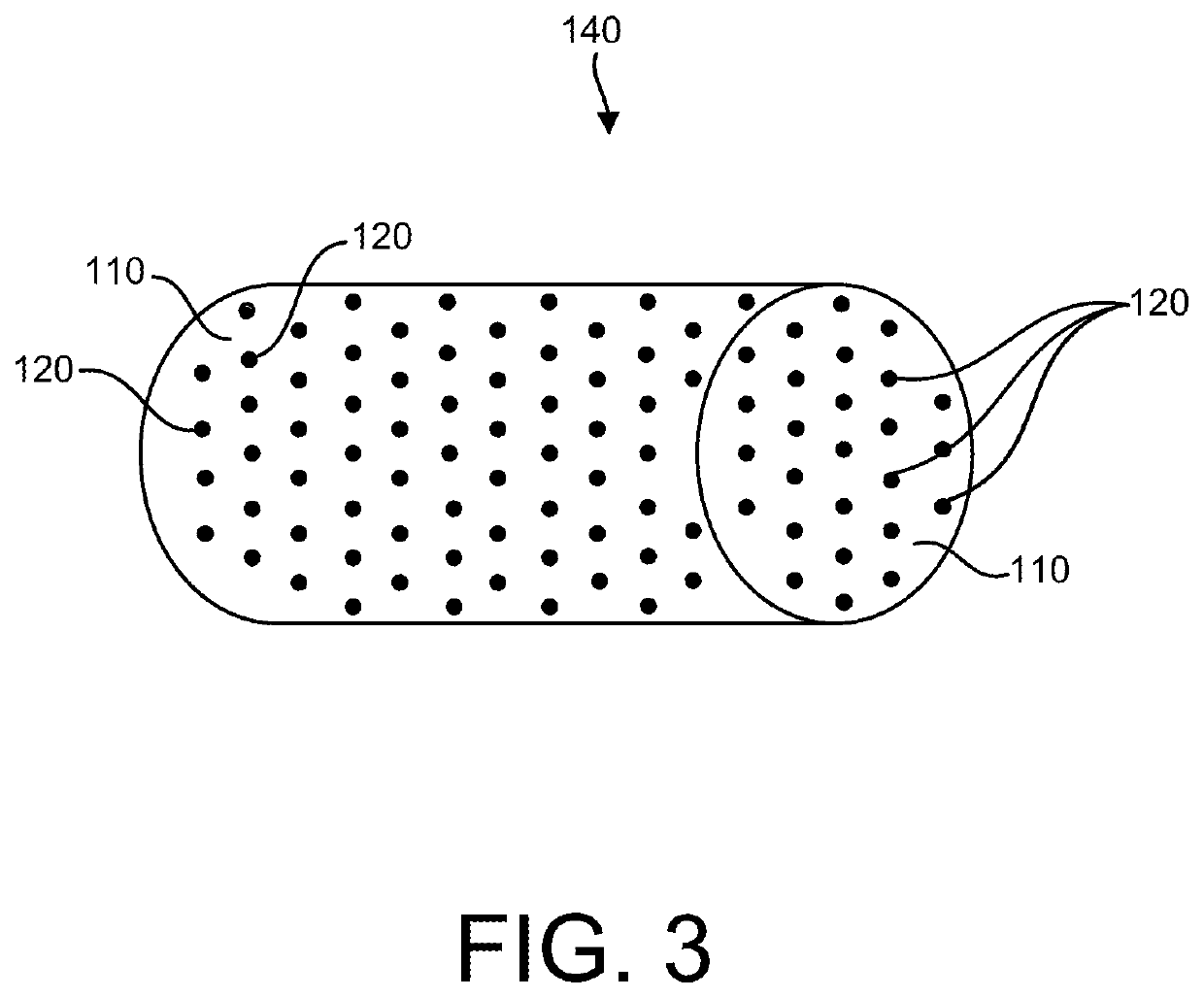
Biodegradation-enhanced synthetic fiber and methods of making the same
a synthetic fiber and biodegradation technology, applied in the chemical characteristics of fibres, monocomponent polyester artificial filaments, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of environmental littering and destruction, polymer family, and may eventually degrade, and achieve the effects of improving biodegradation, reducing and reducing the strength and/or insulative qualities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
,” one will understand how the features of the various embodiments disclosed herein provide a number of advantages over the current state of the art. For example, in some embodiments, the synthetic biodegradation-enhanced fiber provides improved biodegradation properties, thereby lending itself toward “environmentally friendly” fibers, monofilaments, fill, yarn, woven and nonwoven materials (e.g., insulation materials), articles (e.g., apparel, footwear, bedding, fabrics, mechanical belts and industrial products) and / or textiles. Embodiments of the synthetic biodegradation-enhanced fiber may be micro-denier or macro-denier synthetic (e.g., polyester) fiber with improved biodegradation properties, that may maintain, inter alia, a silky hand feel and heightened water repellency during normal use (e.g., before being discarded in a microbial biodegradation environment, such as in a landfill or seawater).
[0015]These and other features and advantages of this invention will become apparent...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com