Determining and applying a voltage to a piezoelectric actuator
a piezoelectric actuator and voltage technology, applied in the field of piezoelectric actuators, can solve the problems of time and power consumption, difficult implementation, hysteresis and piezo creep, etc., and achieve the effect of small power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
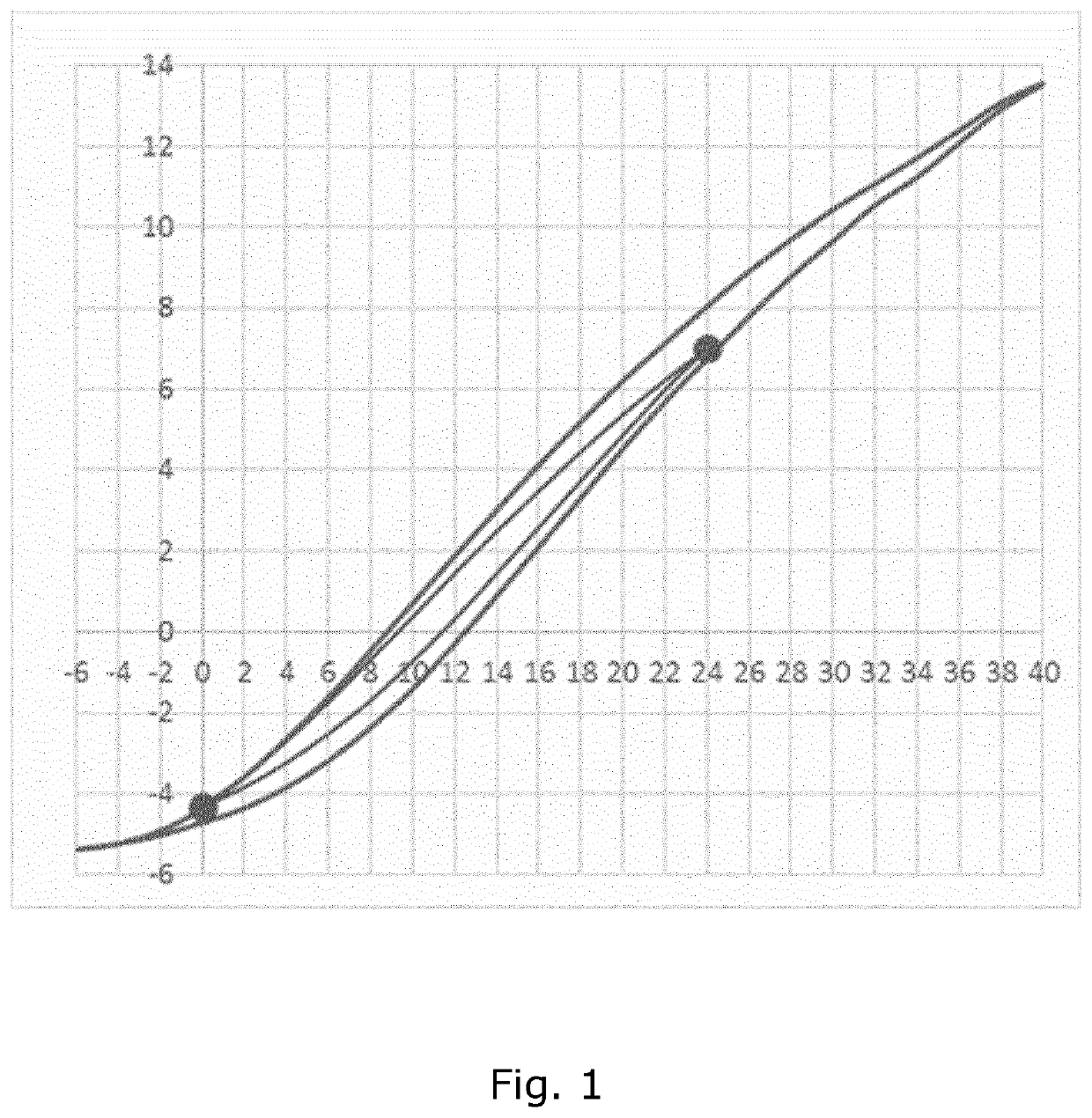
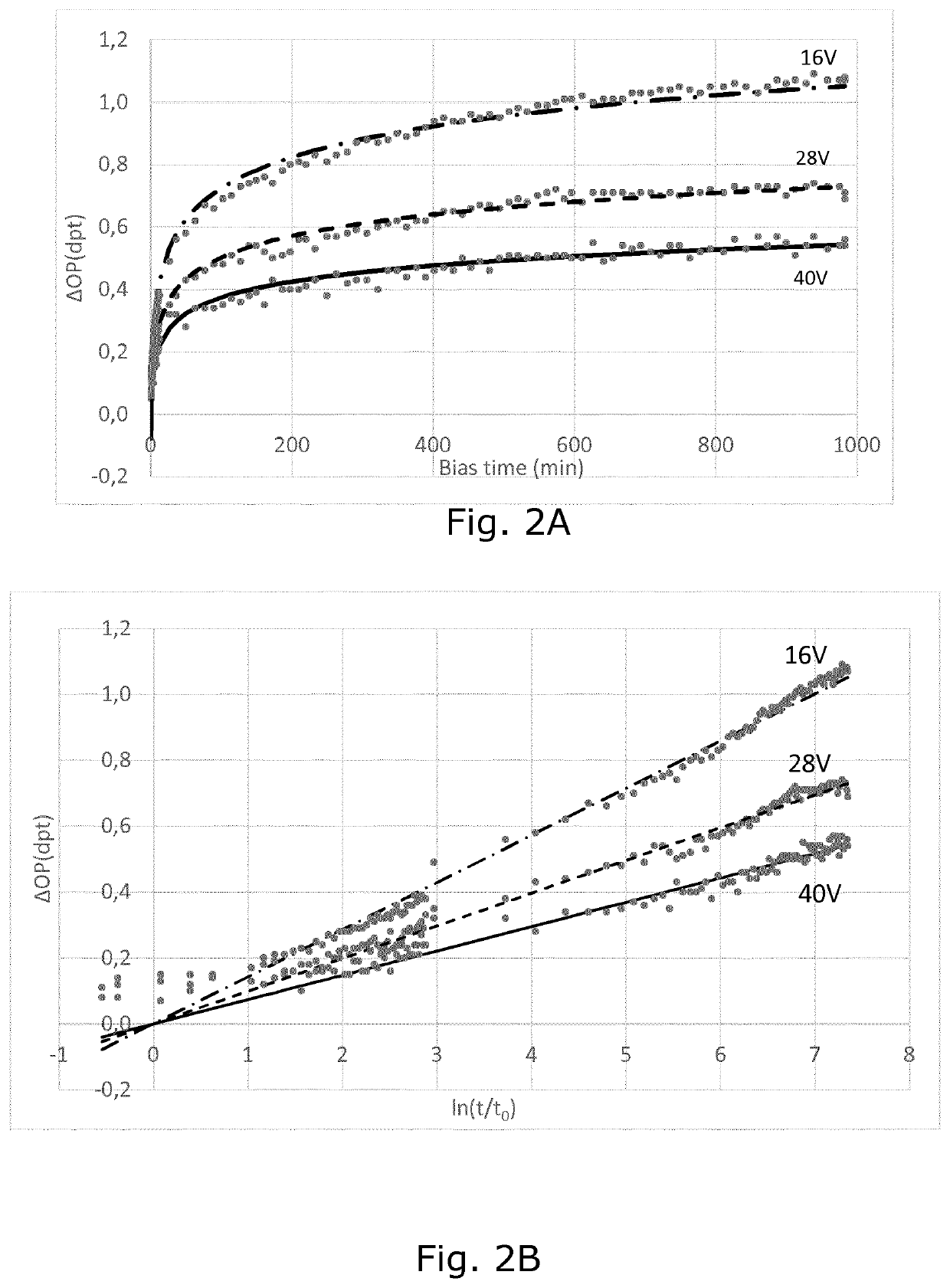
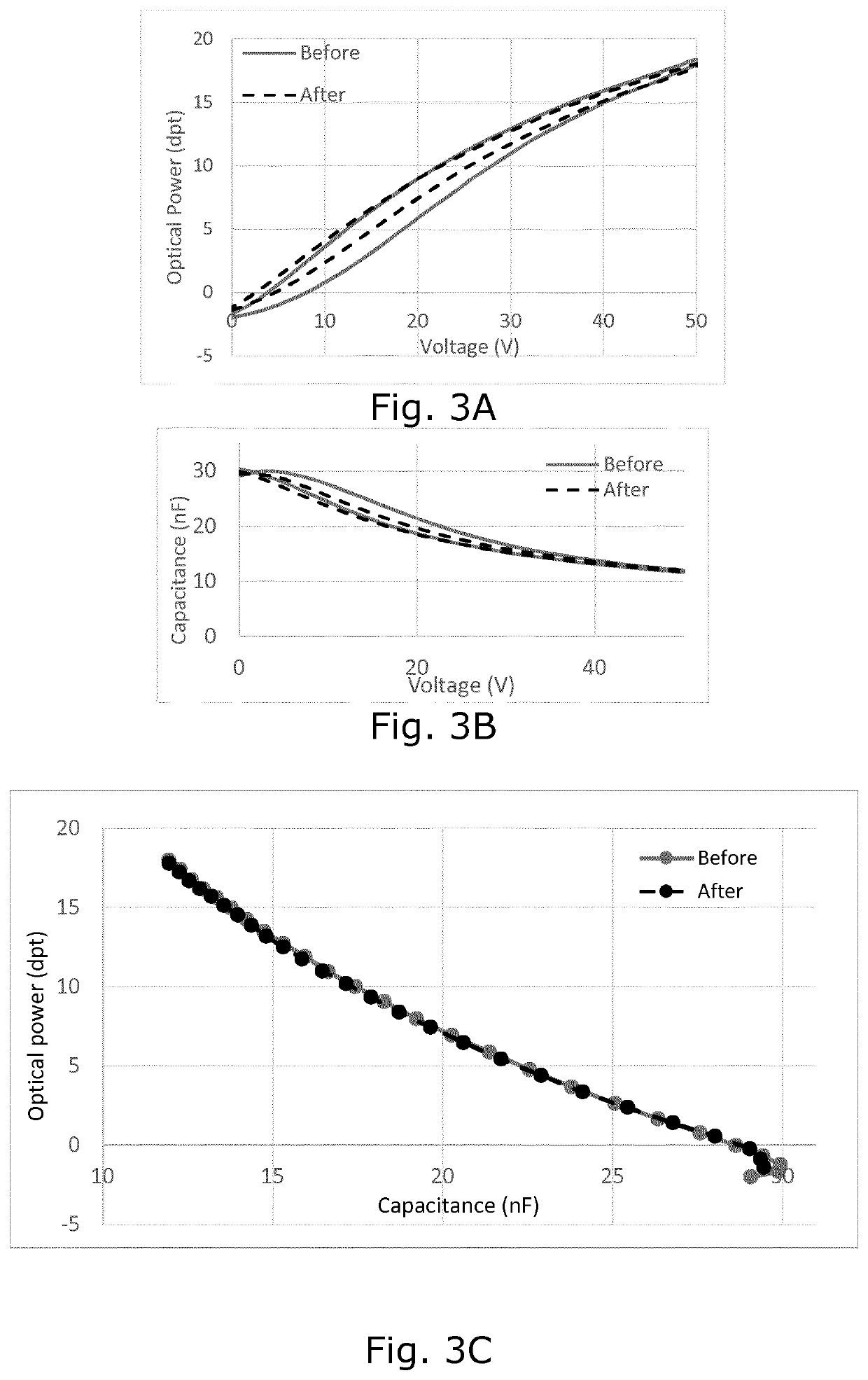
[0058]In the following, various aspects and embodiments of the invention are described in relation to a PEA forming part of an adjustable focus lens assembly in a camera module.
[0059]The adjustable focus lens assembly can for example be a deformable, non-fluid lens body sandwiched between an optical support and a transparent, flexible membrane to form a lens, with a PEA in the form of a film arranged on the flexible membrane to deform the flexible membrane to change the focus of the lens. The PEA of the lens assembly can then be connected to a piezo driver involving a processing unit connected to the piezo driver and holding software for controlling the piezo driver. Such adjustable lens assembly is described in e.g. WO 2008 / 035983. The various measurements described and shown are obtained from a setup on a laboratory bench, and in this setup the displacement measure is optical power measured in dioptre. Measurement of optical power, however, is not practical in normal use of the in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com