Rotary seal for directional drilling tools
a directional drilling and sealing technology, applied in the direction of turning apparatuses, engine components, valve arrangements, etc., can solve the problems of tool failure, valves have been known to stick, valve assembly actuation,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
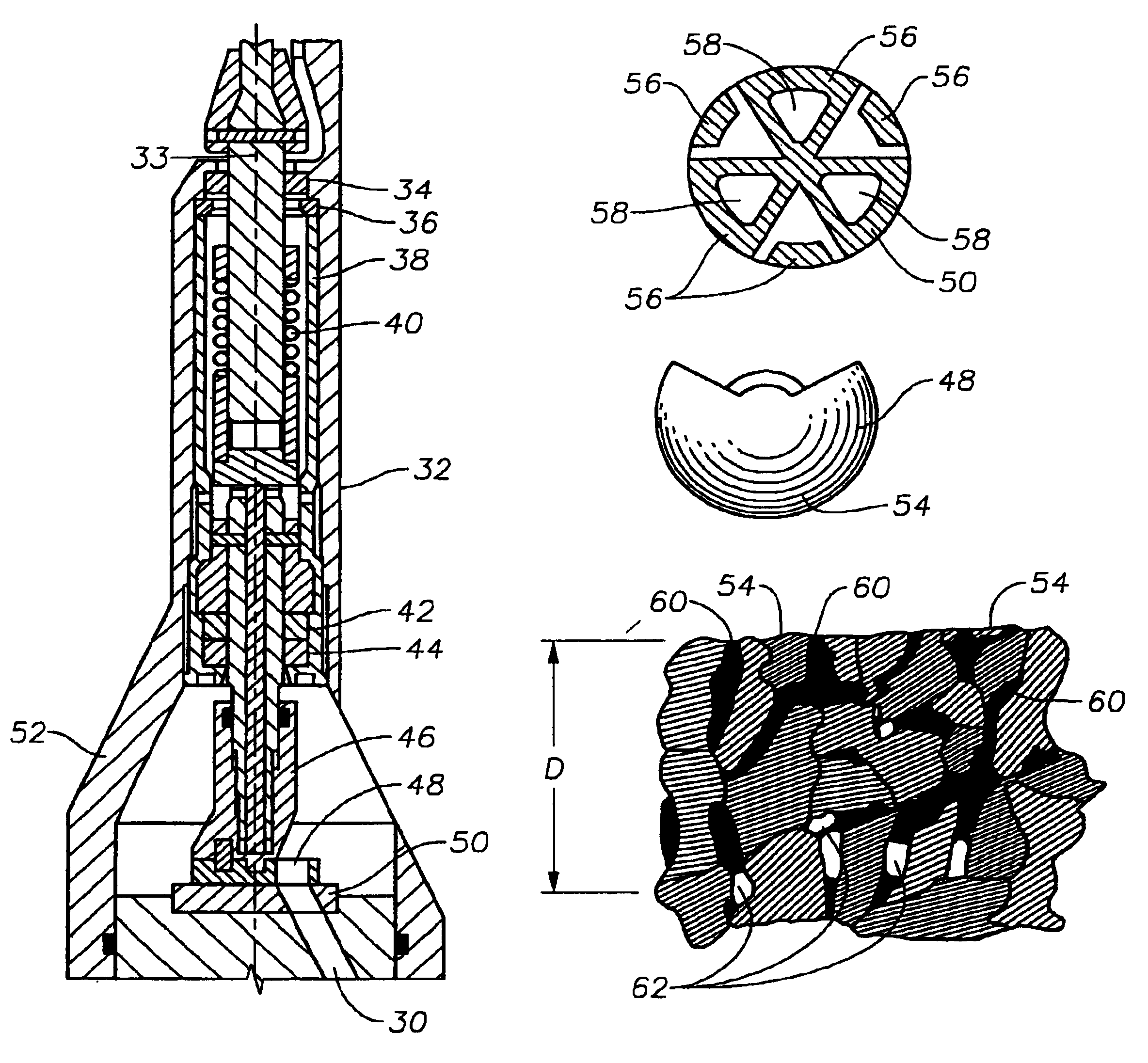
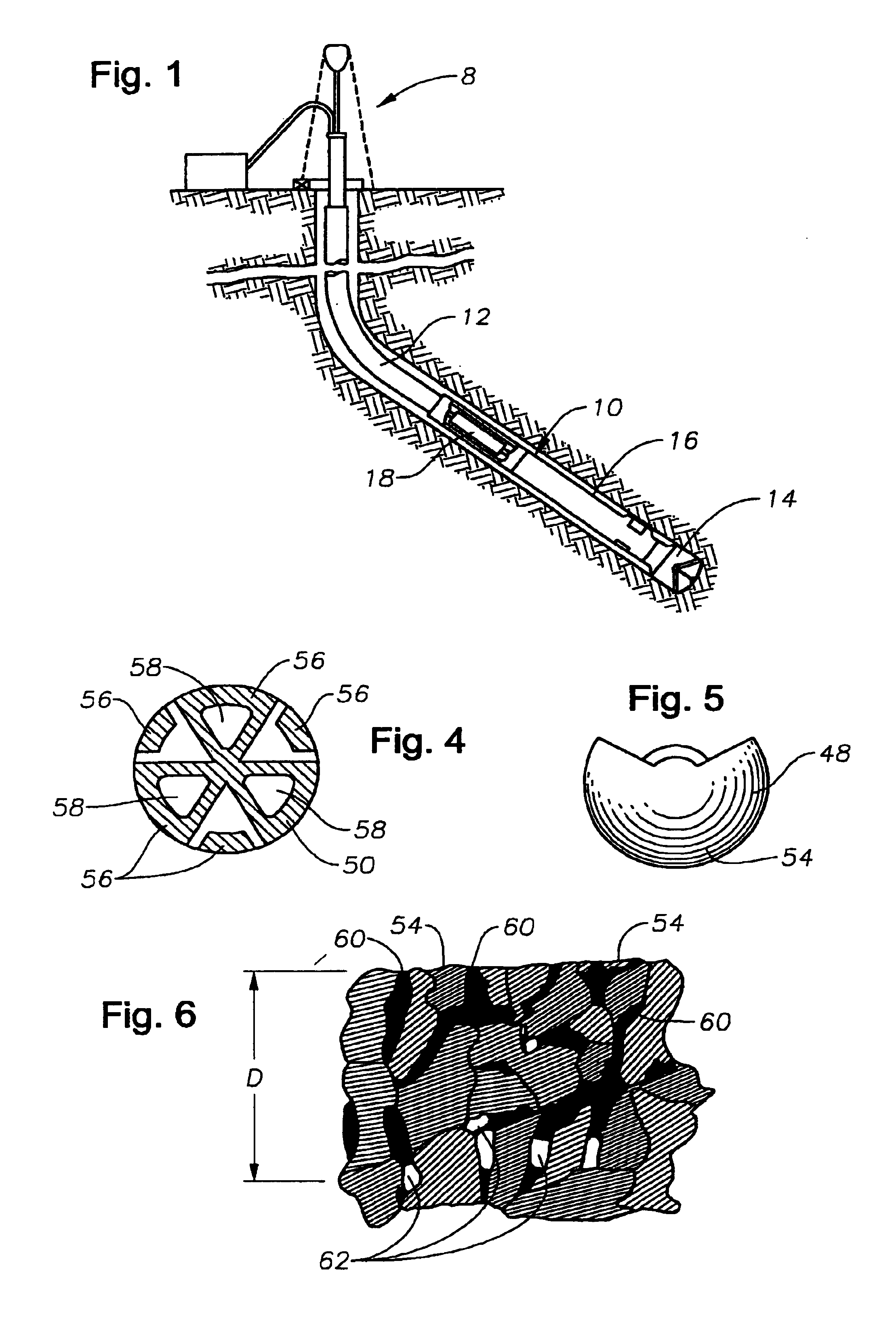
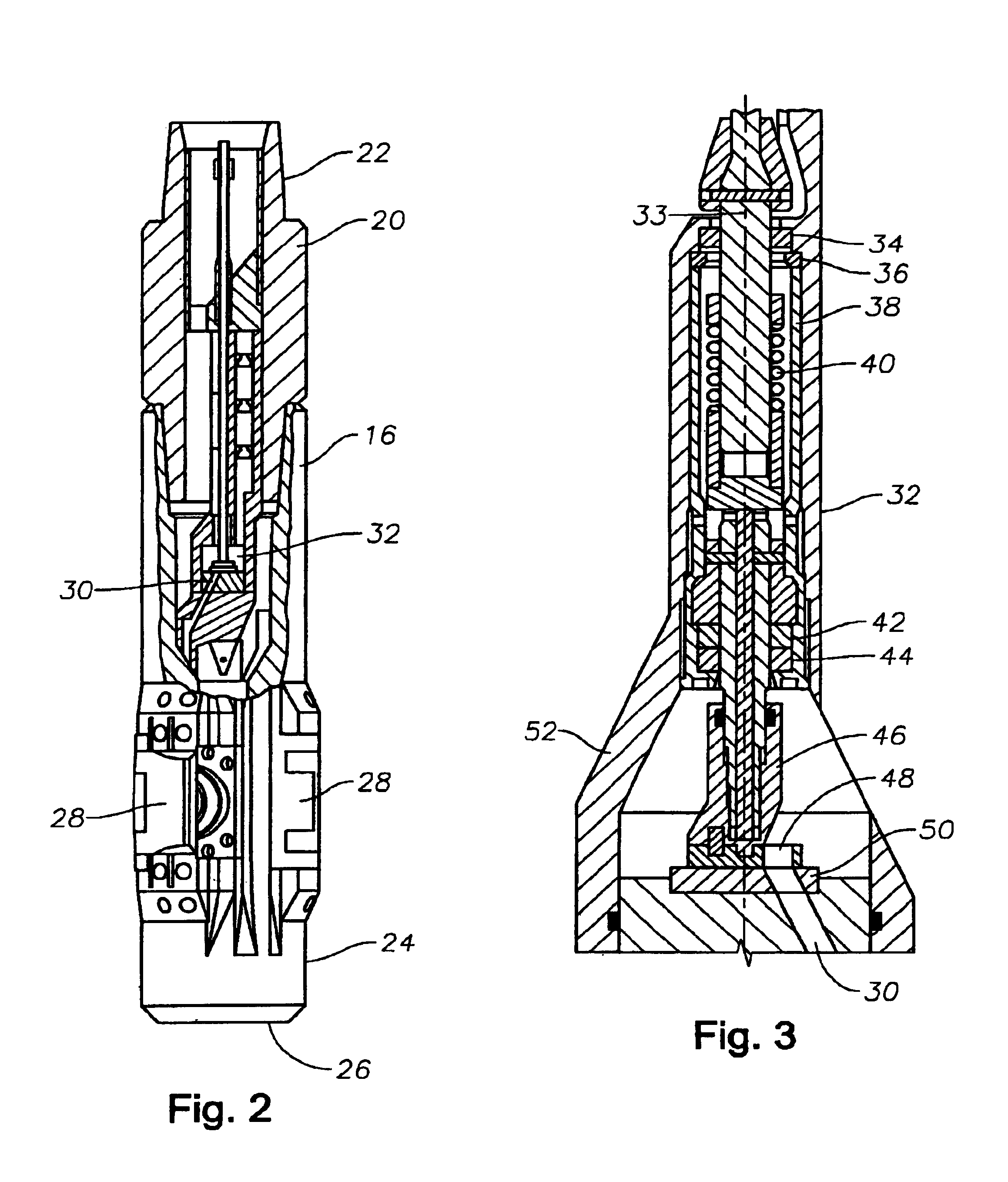
[0021]When drilling directional boreholes into earthen formations, it is common practice to use a bottom hole assembly as shown in FIG. 1. The bottom hole assembly, generally indicated as 10, is typically connected to the end of the tubular drill string 12 which is typically rotatably driven by a drilling rig 8 from the surface. In addition to providing motive force for rotating the drill string 12, the drilling rig 8 also supplies a drilling fluid under pressure through the tubular drill string 12 to the bottom hole assembly 10. The drilling fluid is typically laden with abrasive material, as it is repeatedly re-circulated through the borehole. In order to achieve directional control while drilling, components of the bottom hole assembly 10 include a drill bit 14, a modulated bias unit 16, and a roll stabilized control unit 18. The bias unit 16 is connected to and controlled by the roll stabilized control unit 18, which controls operation of the bias unit 16 in accordance with a pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com