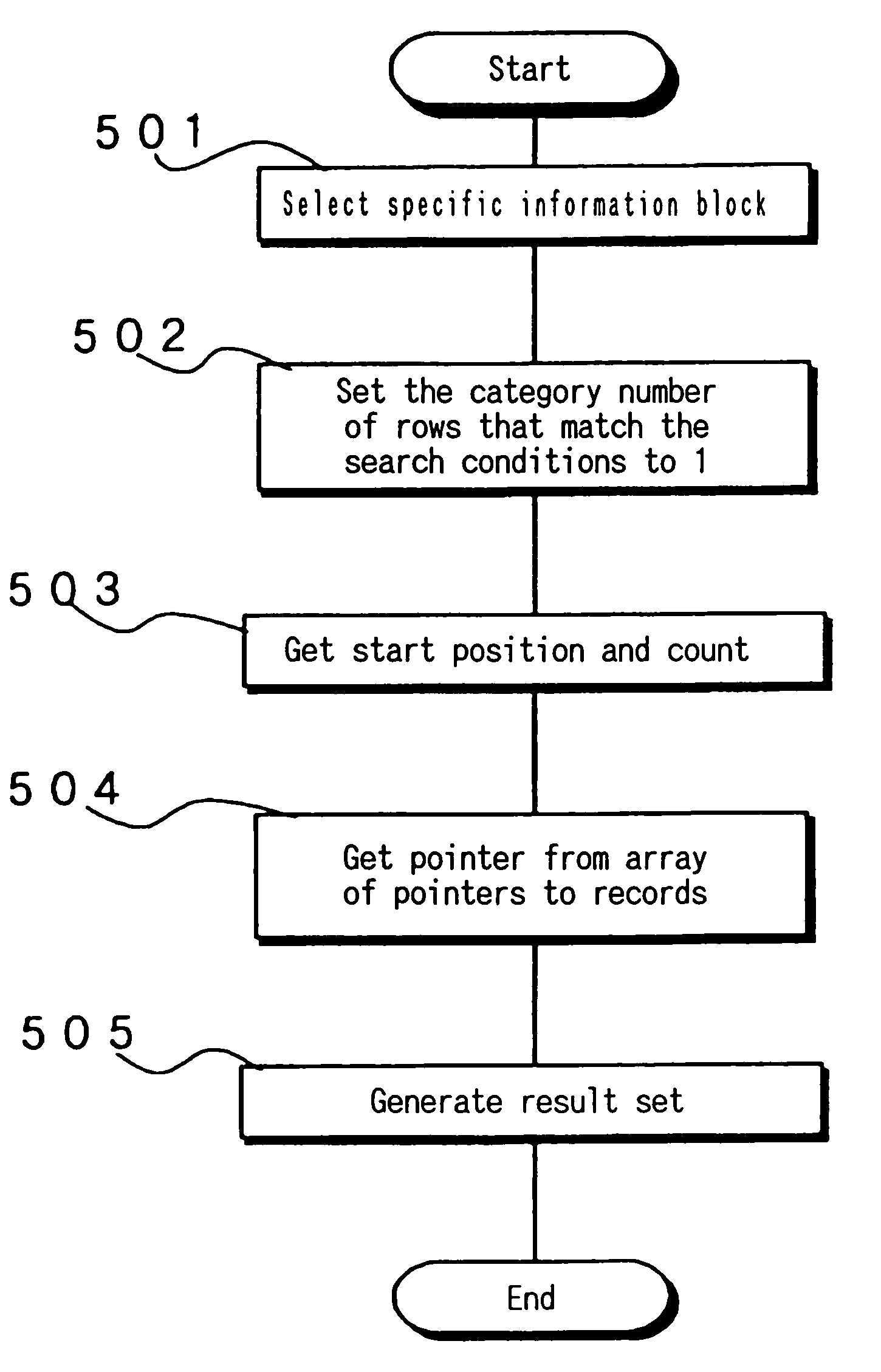
Table format data presenting method, inserting method, deleting method, and updating method
a table format and data presenting technology, applied in the field of data processing methods and data processing apparatuses, can solve the problems of not being able to create bitmaps for each value at all, not being able to adapt to the analysis of large-scale data (information-based work) from a structural standpoint, and not being able to solve the problem of not being able to sort the data, etc., and achieve the effect of substantial deletion of data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
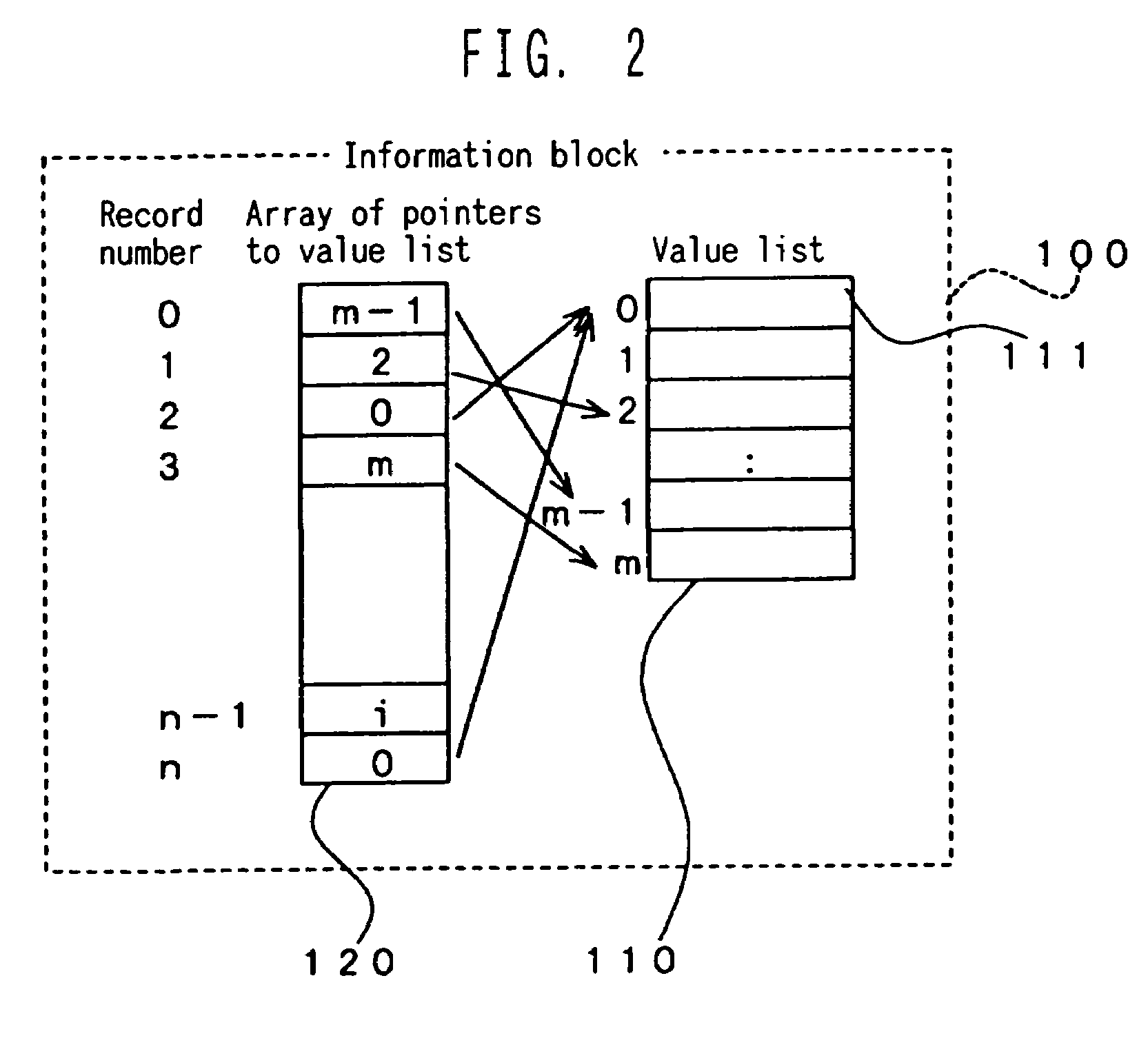
[0142]First, we shall describe a subscript conversion array for the insertion of elements, etc. which is used in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Considering the information block shown in FIGS. 2–4, subscripts may include the record number for specifying elements of the array of pointers to the value list (pointer values), or pointer values within the pointer array for specifying field values of the value list. In addition, the arrays may include arrays of pointers to value lists, value lists, and arrays of pointers to record numbers or the like.
[0143]For example, as shown in FIG. 10A, consider the case of inserting the element “Y0” between the 0th row (subscript “0”) and the 1st row (subscript “1”). In this case, after the insertion of the element “Y0,” the subscripts and the elements within the array (stored values) have the logical relationship shown in FIG. 10B.
[0144]In order to maintain the logical relationship shown in FIG. 10B while minimize the load arising from inser...
embodiment 4
[0171]Here follows a description of a value conversion array of the present invention. Regarding the array, it is necessary to perform the aforementioned insertion and deletion of elements and also change (update) the elements (stored values) of the array themselves. In this embodiment, the value conversion array described below is used for the updating of elements of the array.
[0172]For example, as shown in FIG. 23A, consider the case in which it is necessary to increment those records within a certain array (record number list) that have a value of 1 or greater. With the conventional technique, it is necessary to perform the process of determining whether or not the elements (stored values) within an array are 1 or greater, and incrementing the element (stored value) it is 1 or greater, for every element in the array. In contrast, Embodiment 4 of the present invention uses a technique whereby a value conversion array is placed in the last stage (downstream side) of the array, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com