Method and apparatus to reduce interference in a communication device
a communication device and interference reduction technology, applied in electrical equipment, transmission monitoring, substation equipment, etc., can solve the problems of communication device actually interfering with itself, interfering between intermediate frequencies or baseband frequencies, and being particularly susceptible to the latter problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
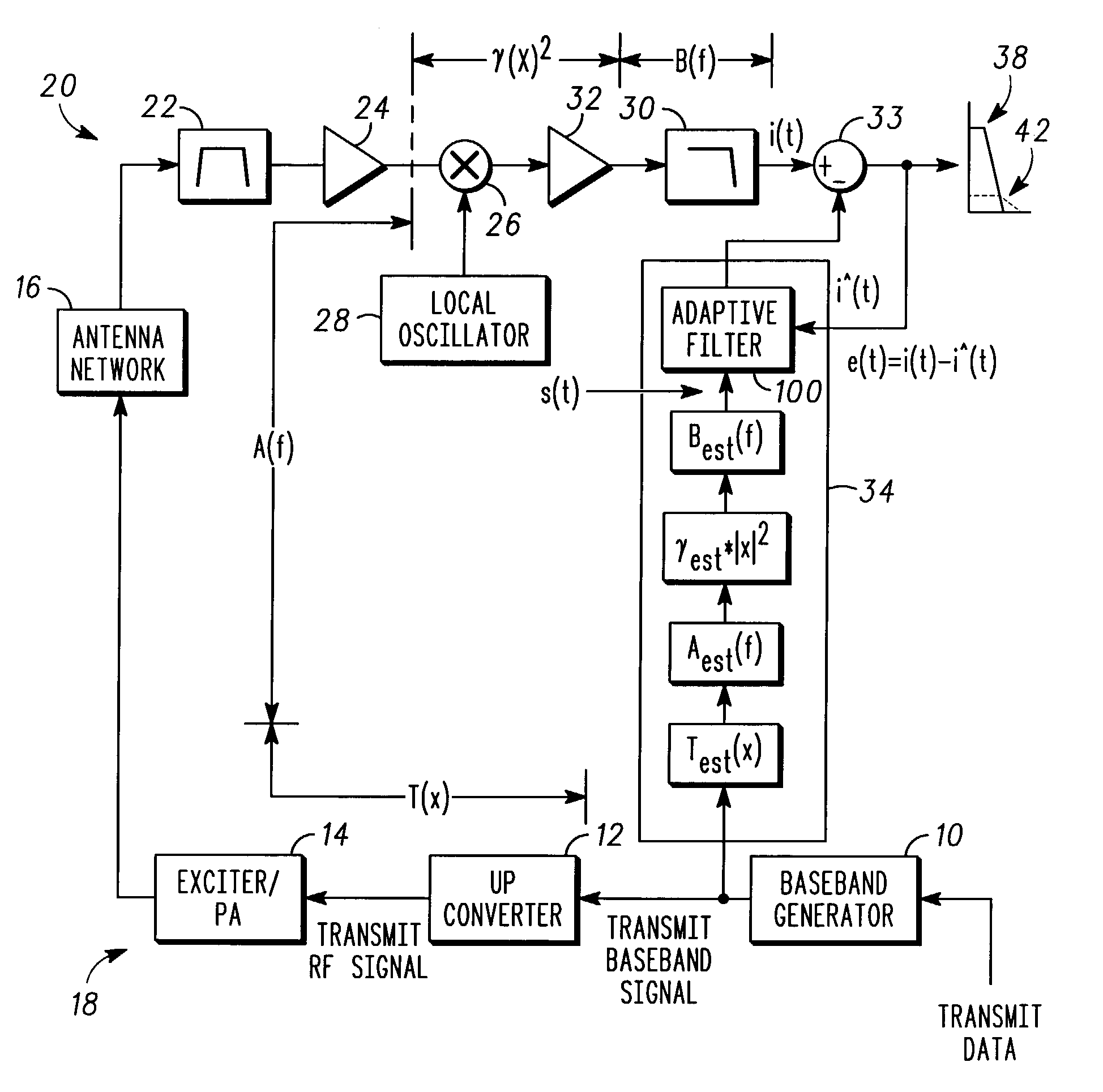
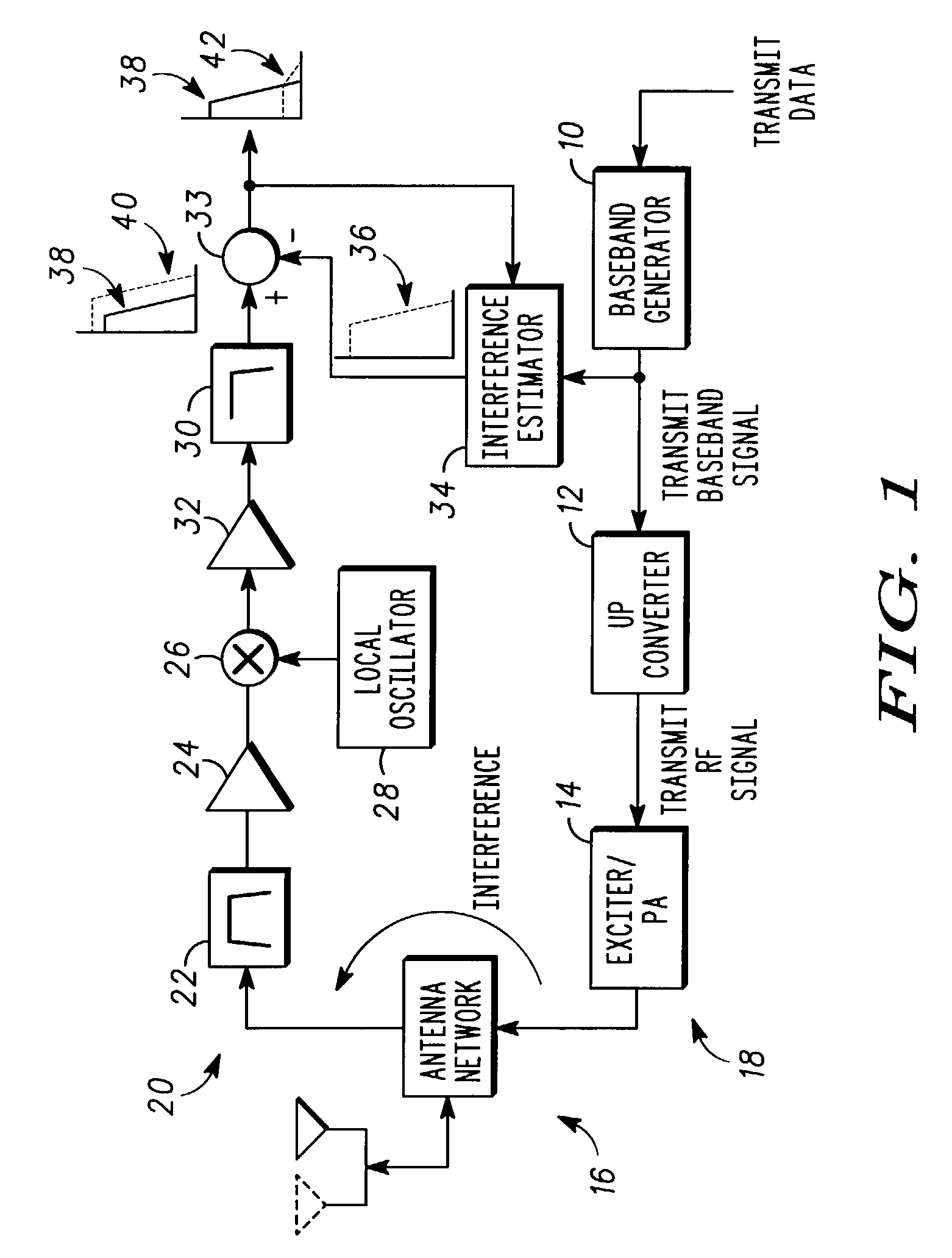
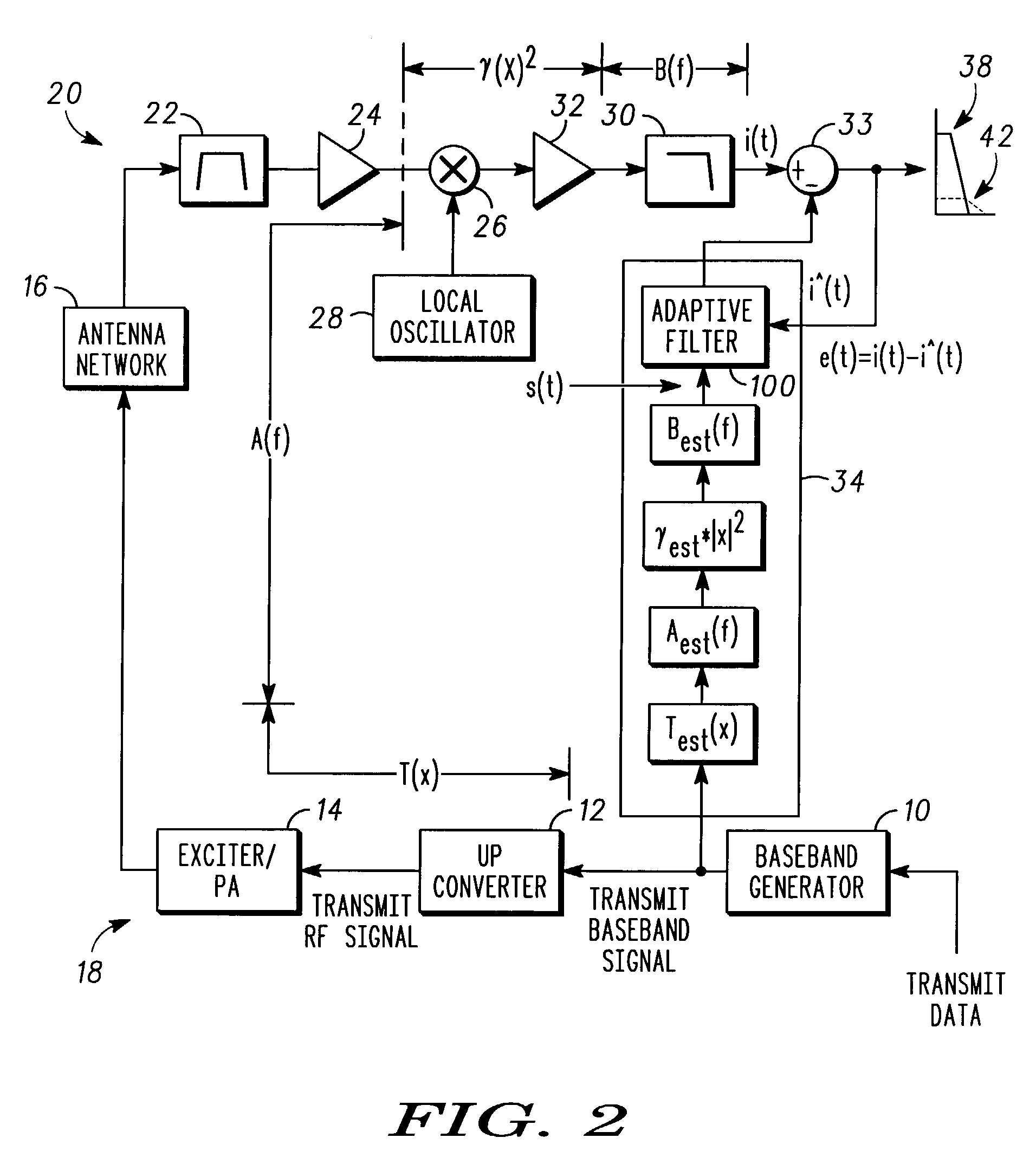
[0015]The present invention provides an improved method and apparatus to reduce second order transmit signal interference in a direct conversion, LIF or VLIF receiver. This is accomplished by estimation and compensation of the second order interference products and characterization of the radio circuitry architecture. As a result, the present invention can provide this improvement without concern for the radio architecture circuitry layout or a requirement for component improvements. The present invention advantageously utilizes existing circuitry in combination with simple software and hardware additions for the interference compensation of a receive signal in a communication device.
[0016]The present invention is equally applicable to analog or digital signals. As described herein, signals may be in digital or analog form and in some cases can be real or complex (i.e. separate signal components representing the real and imaginary parts). The digital, analog or complex nature of a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com