Method for forming a medium having data storage and communication capabilities
a technology of data storage and communication capabilities, applied in the field of mediums, can solve the problems of defeating the purpose of joining the rfid tag to the item, increasing the cost of the combined rfid tag and the item, and separating the rfid tag from the item
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039]The present invention will be directed in particular to elements forming part of, or in cooperation more directly with the methods and mediums of the present invention. It is to be understood that elements not specifically shown or described may take various forms well known to those skilled in the art.
Substrate Formation
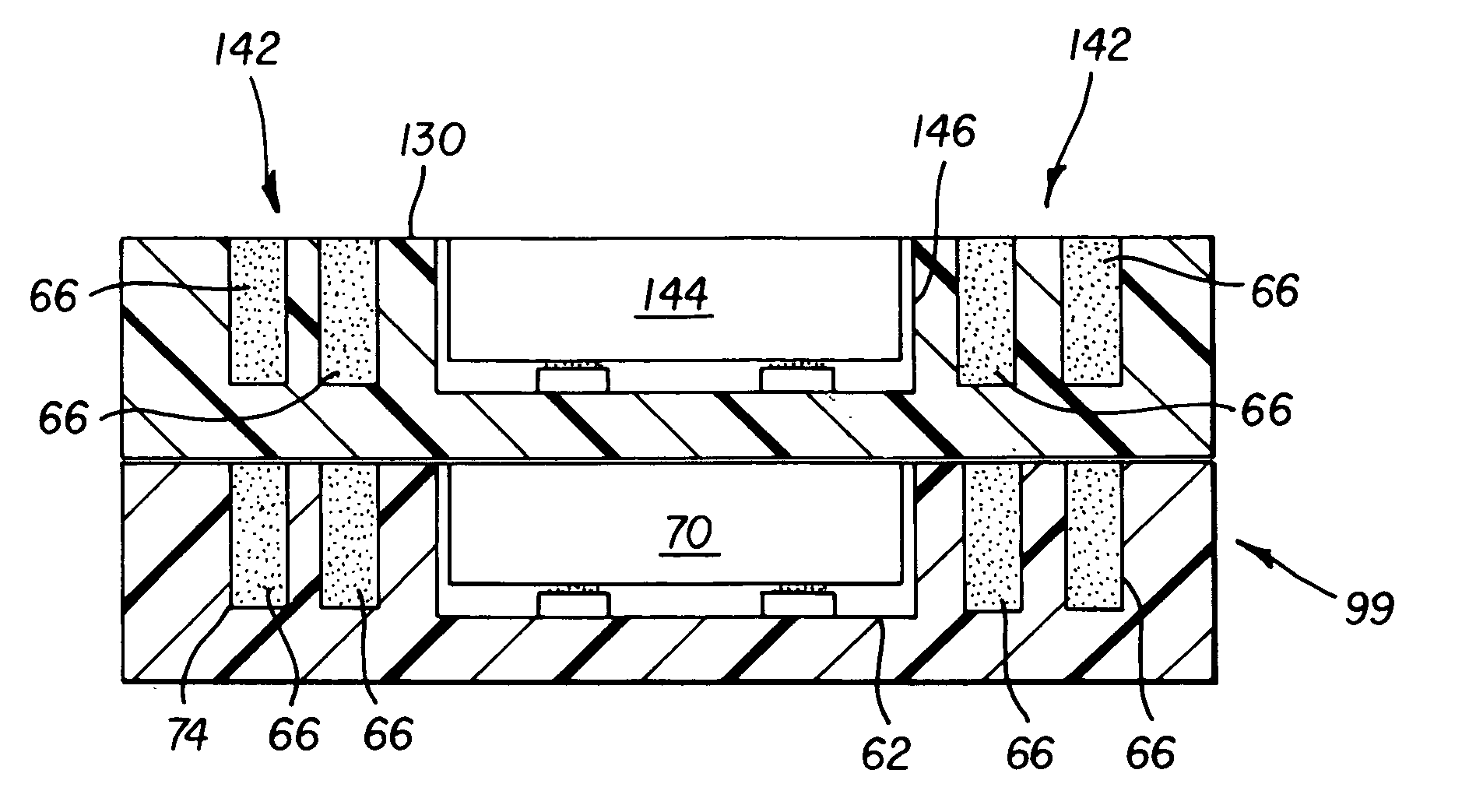
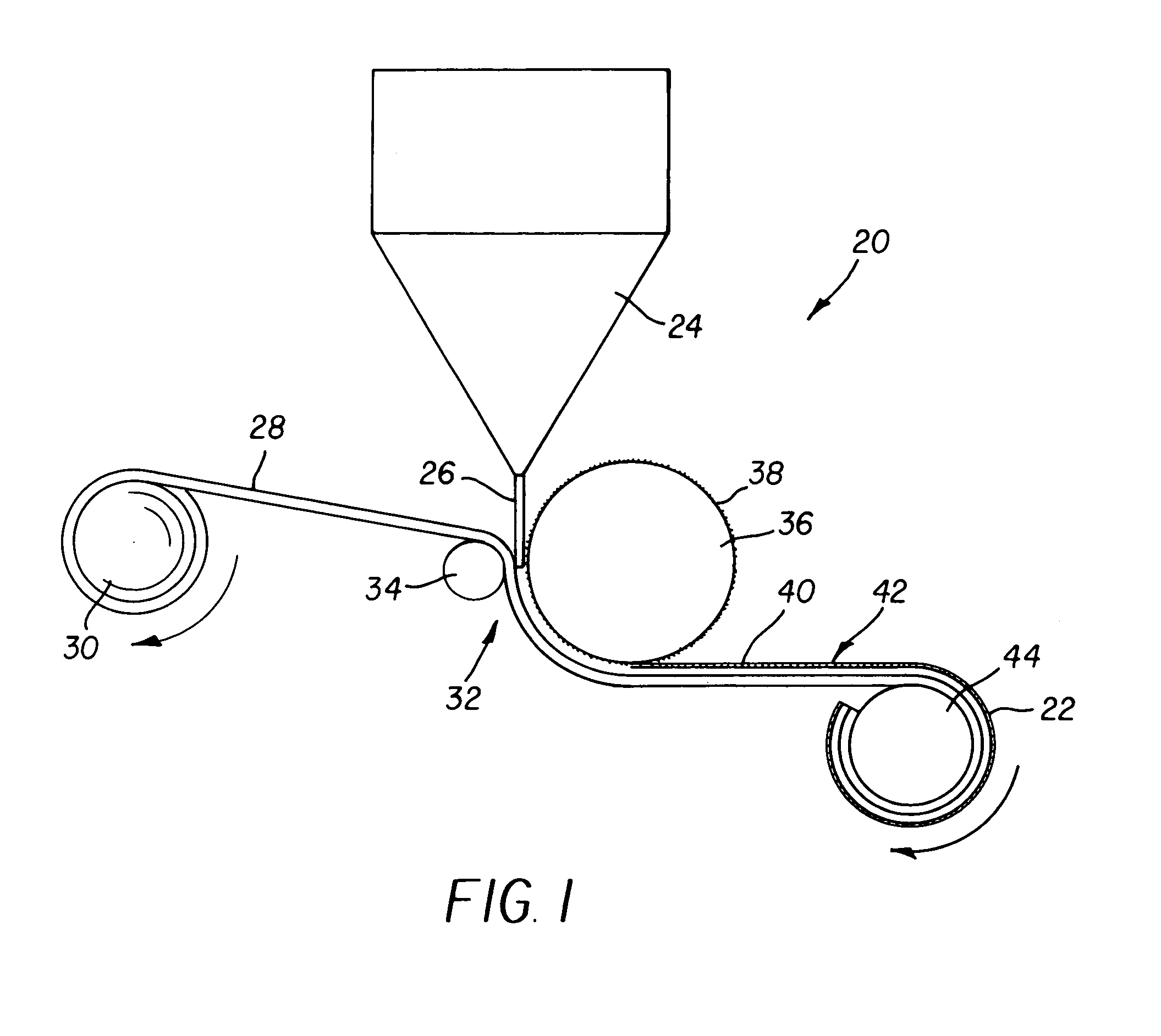
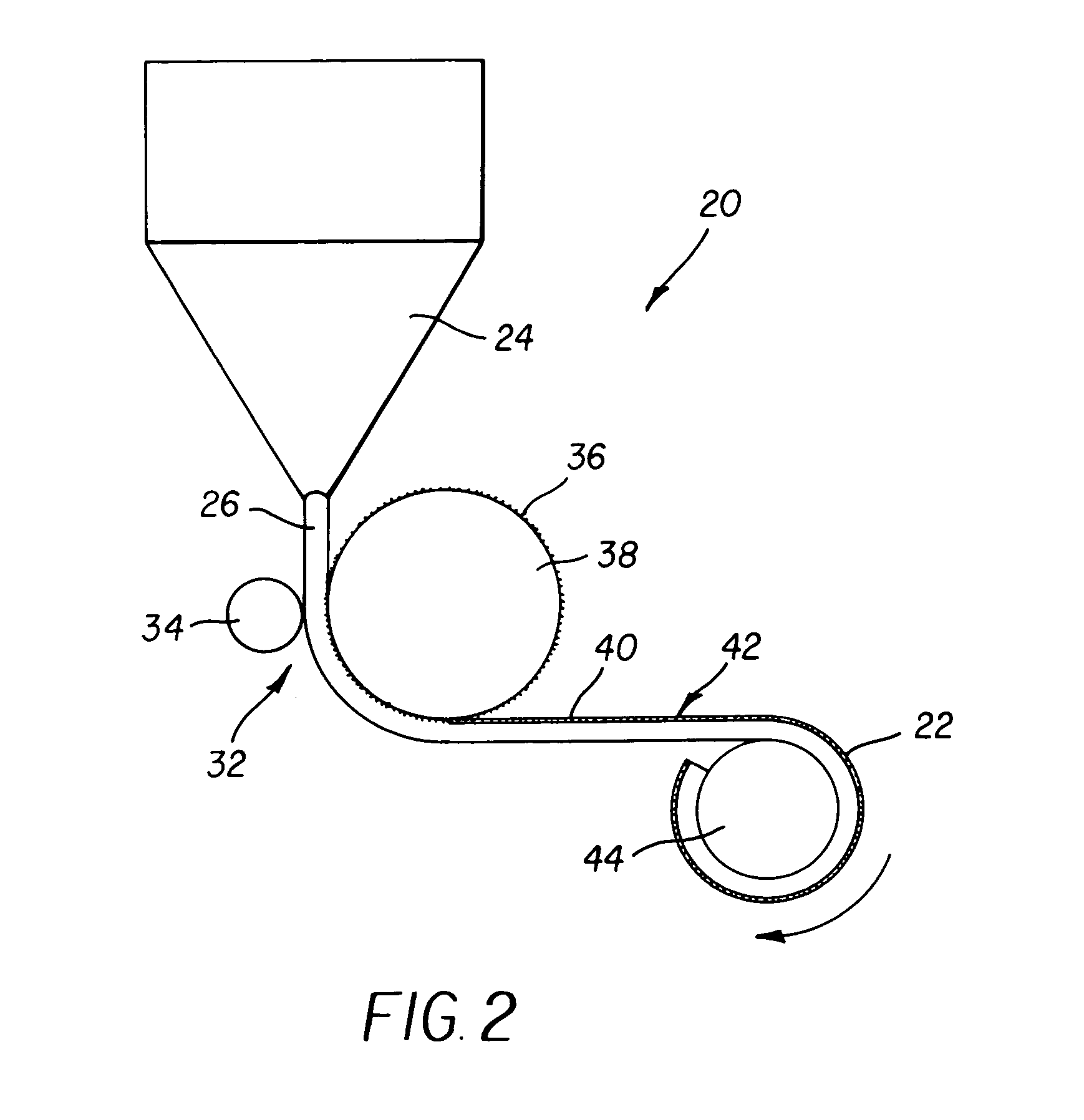
[0040]The medium of the present invention is formed using a substrate having a pattern of raised areas and channels. FIGS. 1 and 2 show alternative embodiments for the formation of such a substrate.
[0041]FIG. 1 shows a schematic illustration of an overall arrangement of one embodiment of an extrusion roll molding apparatus 20 for fabricating a substrate 22. In this embodiment, an extruder 24 provides a thermoplastic material 26, such as a polymer, onto a base 28 that can be formed from the same material as thermoplastic material 26 or that can be formed from different materials such as papers, films, fabrics or other useful base materials. Base 28 is fed from ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com