Golf club head with customizable center of gravity
a golf club head and center of gravity technology, applied in the field of customizable golf club head and golf club, can solve the problems of increased energy transfer problem, increased deformation of golf balls, energy loss,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
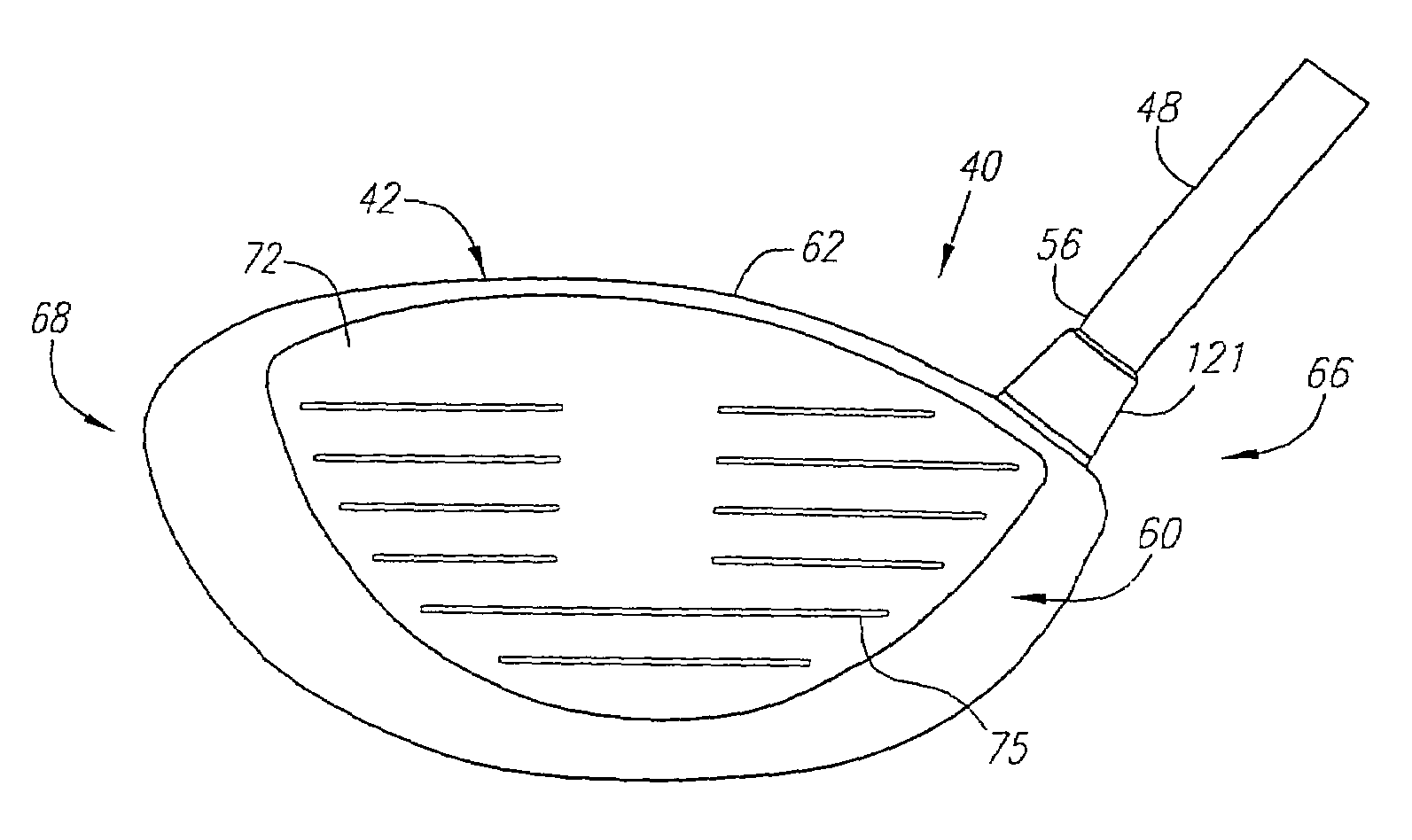
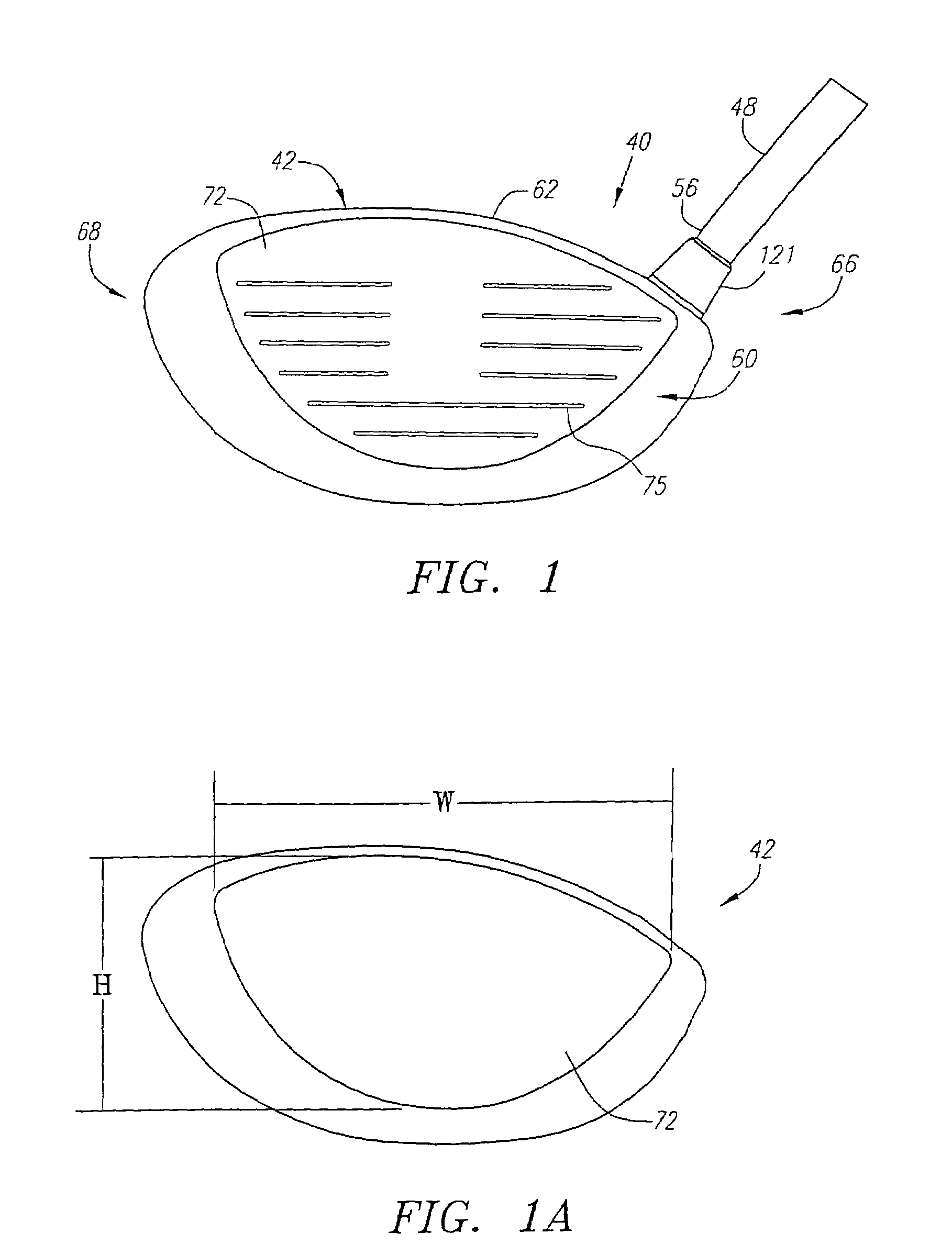
[0100]As shown in FIGS. 1–6A, a golf club is generally designated 40. The golf club 40 has a golf club head 42 with a hollow interior, not shown. Engaging the club head 42 is a shaft 48 that has a grip 50, not shown, at a butt end 52 and is inserted into a hosel 54 at a tip end 56.
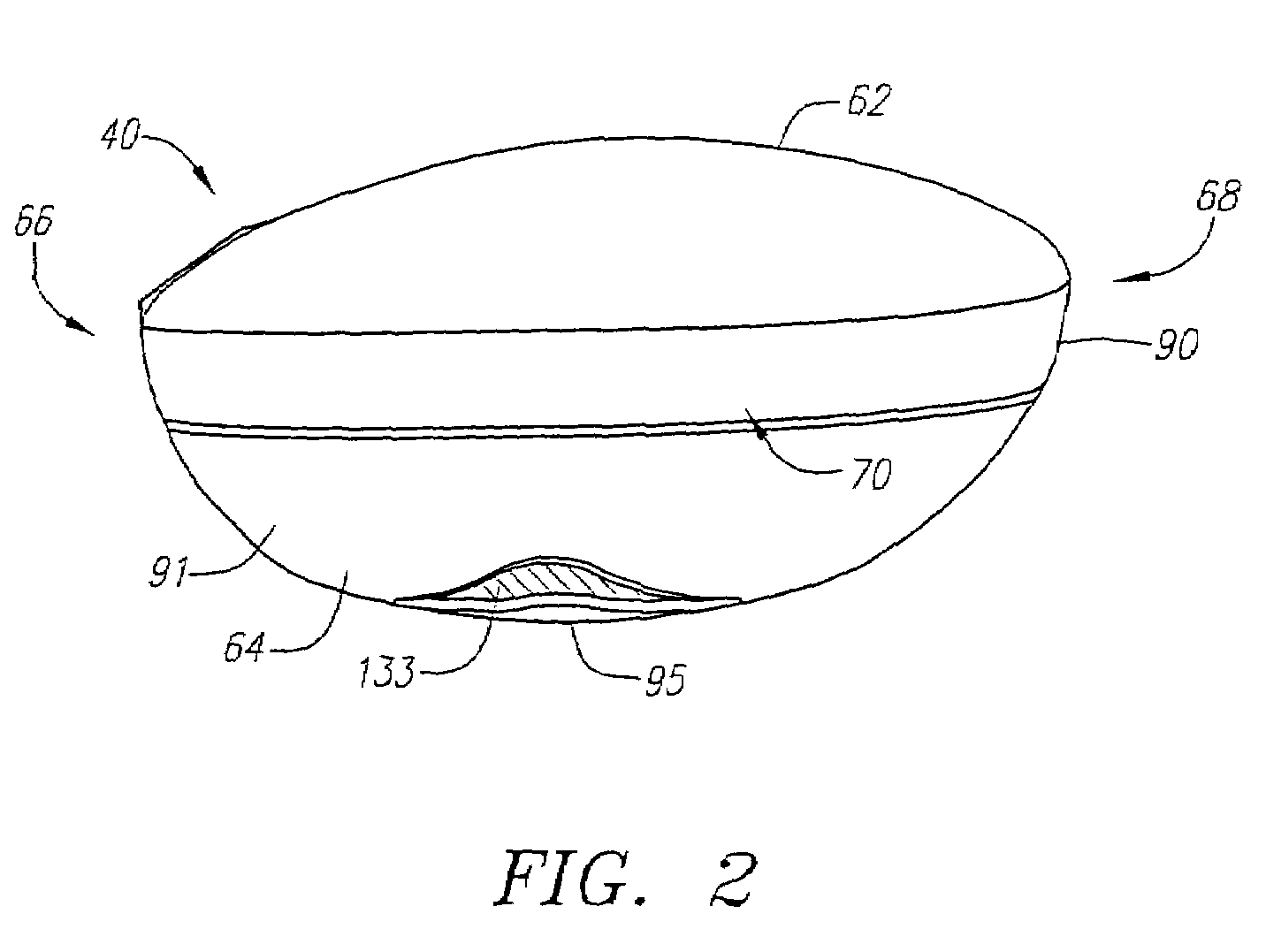
[0101]The club head 42 is generally composed of two components, a face component 60, and an aft-body 61. The aft-body 61 has a crown portion 62 and a sole portion 64. The club head 42 is preferably partitioned into a heel section 66 nearest the shaft 48, a toe section 68 opposite the heel section 66, and a rear section 70 opposite the face component 60. A sole weight member 133 is disposed within a sole undercut portion 133a of the sole portion. The sole weighing member has a mass ranging from 0.5 grams to 15 grams.
[0102]The face component 60 is generally composed of a single piece of metal, and is preferably composed of a forged metal material. More preferably, the forged metal material is a forged titani...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com