Francis turbine
a turbine and blade technology, applied in vessel construction, renewable energy generation, greenhouse gas reduction, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the efficiency of hydraulic machines, promoting wear and tear, and reducing the mass of machines, etc., to achieve the effect of too high cost price and too large mass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
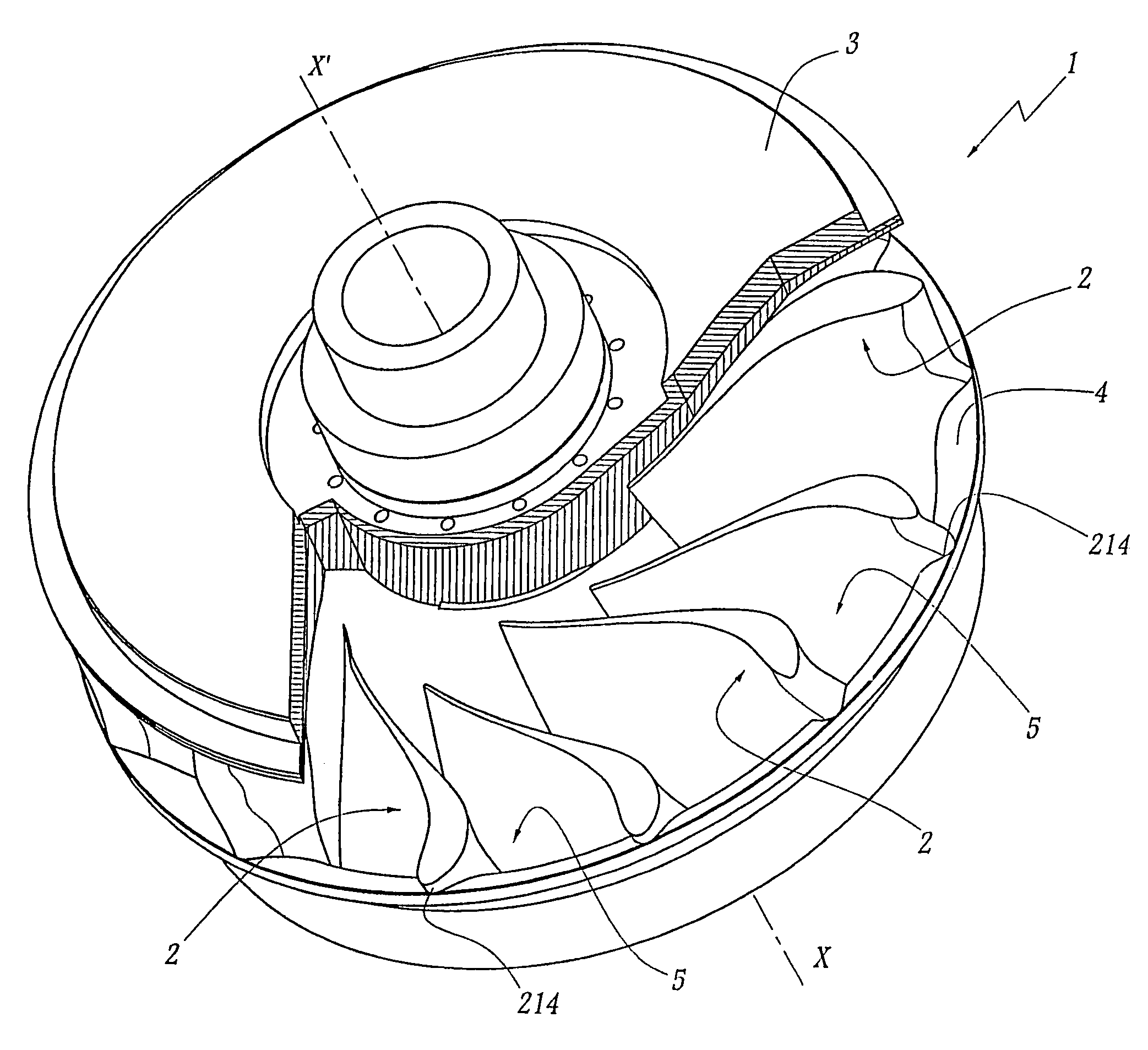
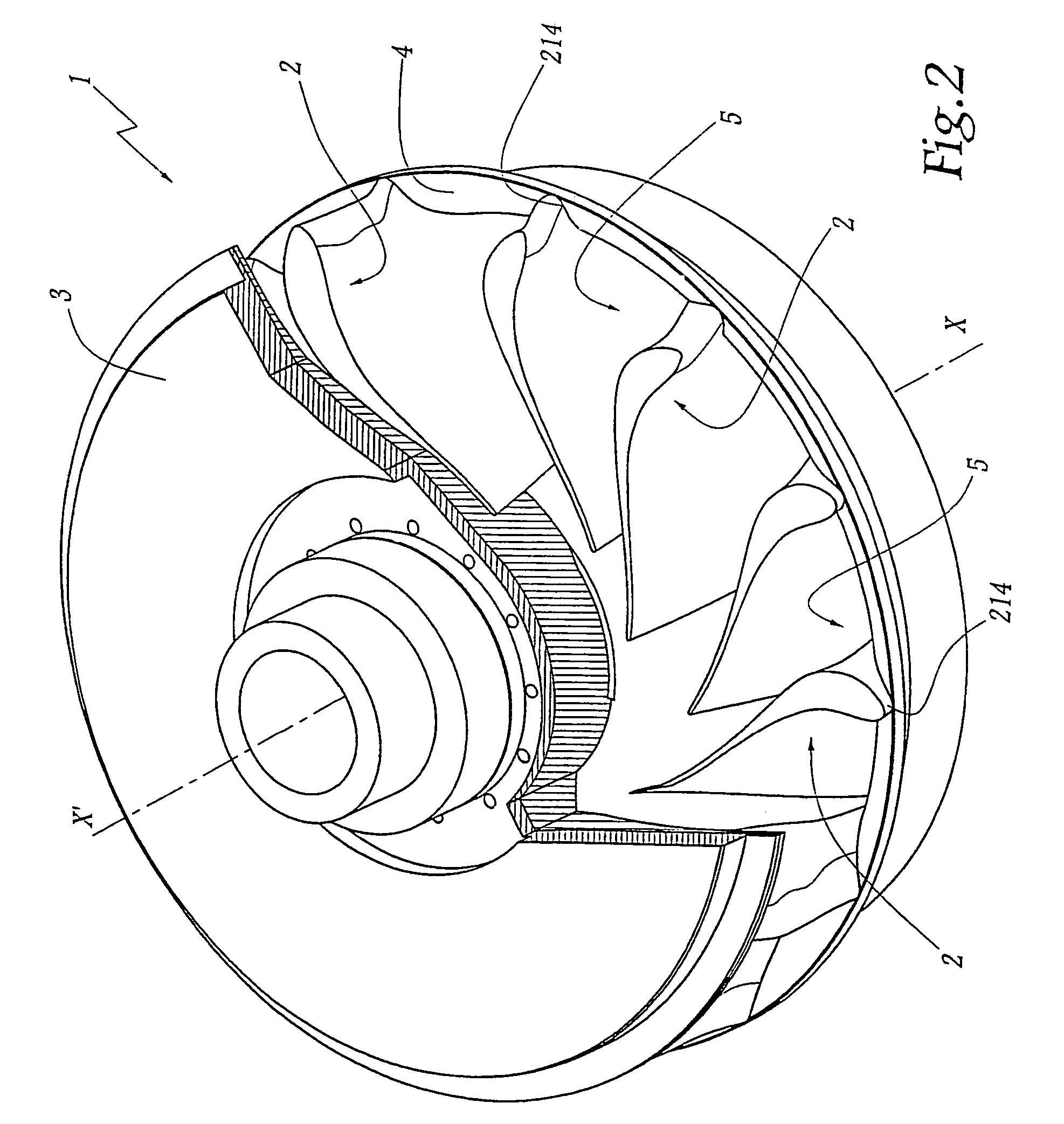
[0022]The runner 1 shown in FIGS. 2 to 4 comprises identical blades 2 distributed about a central axis X–X′ of rotation of the runner 1. A crown 3 is provided in the upper part of the runner 1, while a band 4 borders the lower, radial and external part of the blades 2. A flow channel 5 is thus defined between each pair of two adjacent blades 2, this channel being bordered by the crown 3 and the band 4.
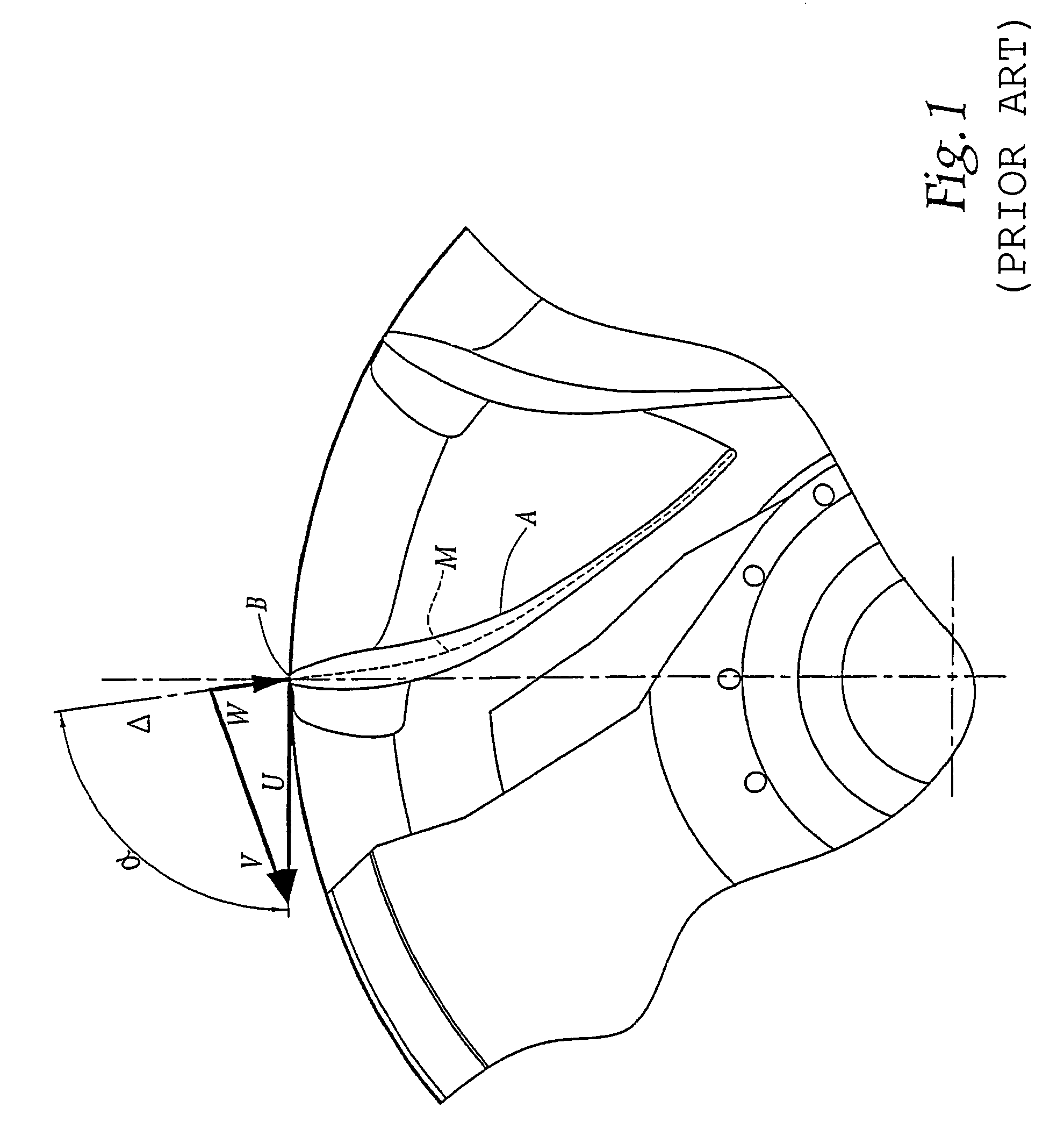
[0023]21 denotes the leading edge of a blade 2.22 denotes its trailing edge. The average fibre 23 of the blade 2 is defined as being, in each transverse plane of this blade, a curve located at equal distance from the pressure side surface 24 and from the suction side surface 25 of the blade 2.
[0024]L denotes the average length of this fibre 23, this average being taken as equal to the half-sum of the length of the average fibre of a blade 2 at the level is of the crown 3 and at the level of the band 4.
[0025]e denotes the maximum thickness of the blade 2.
[0026]The geometry of the blade ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com