Method of thermally insulating coaxial pipes with a particulate insulating material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
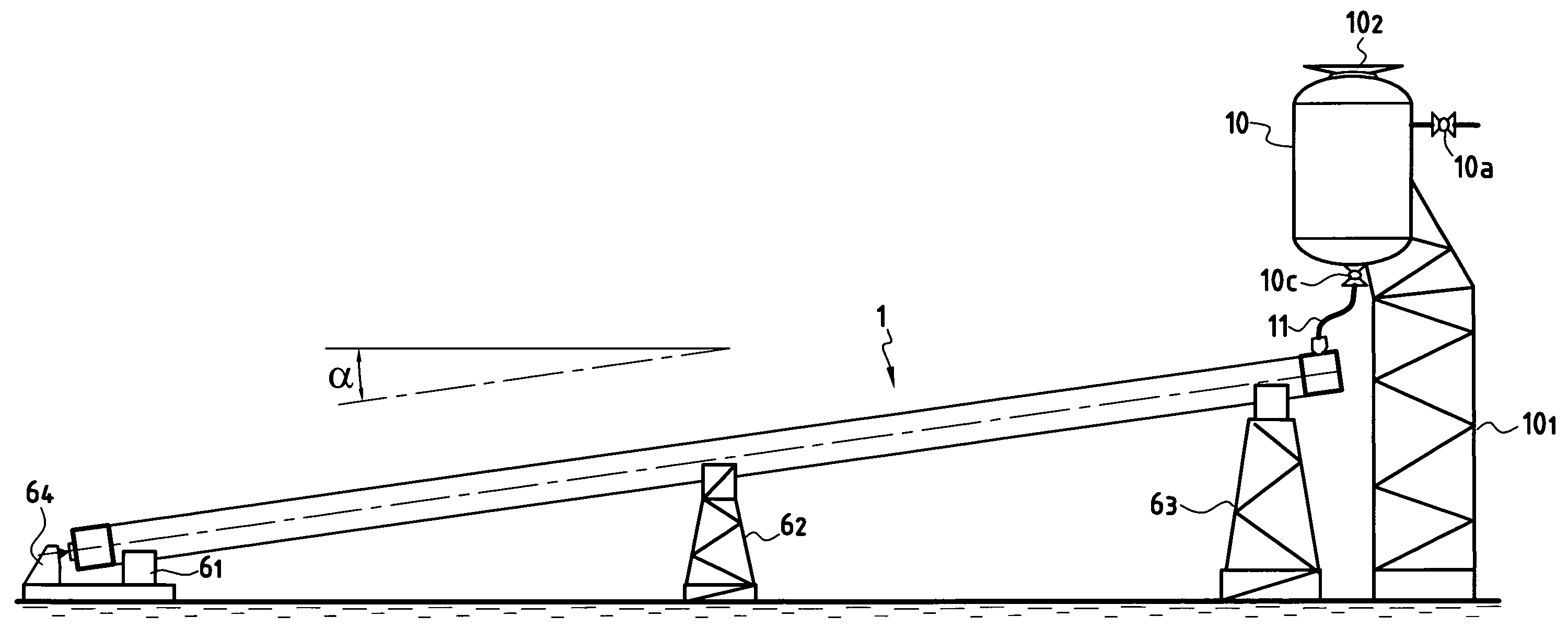
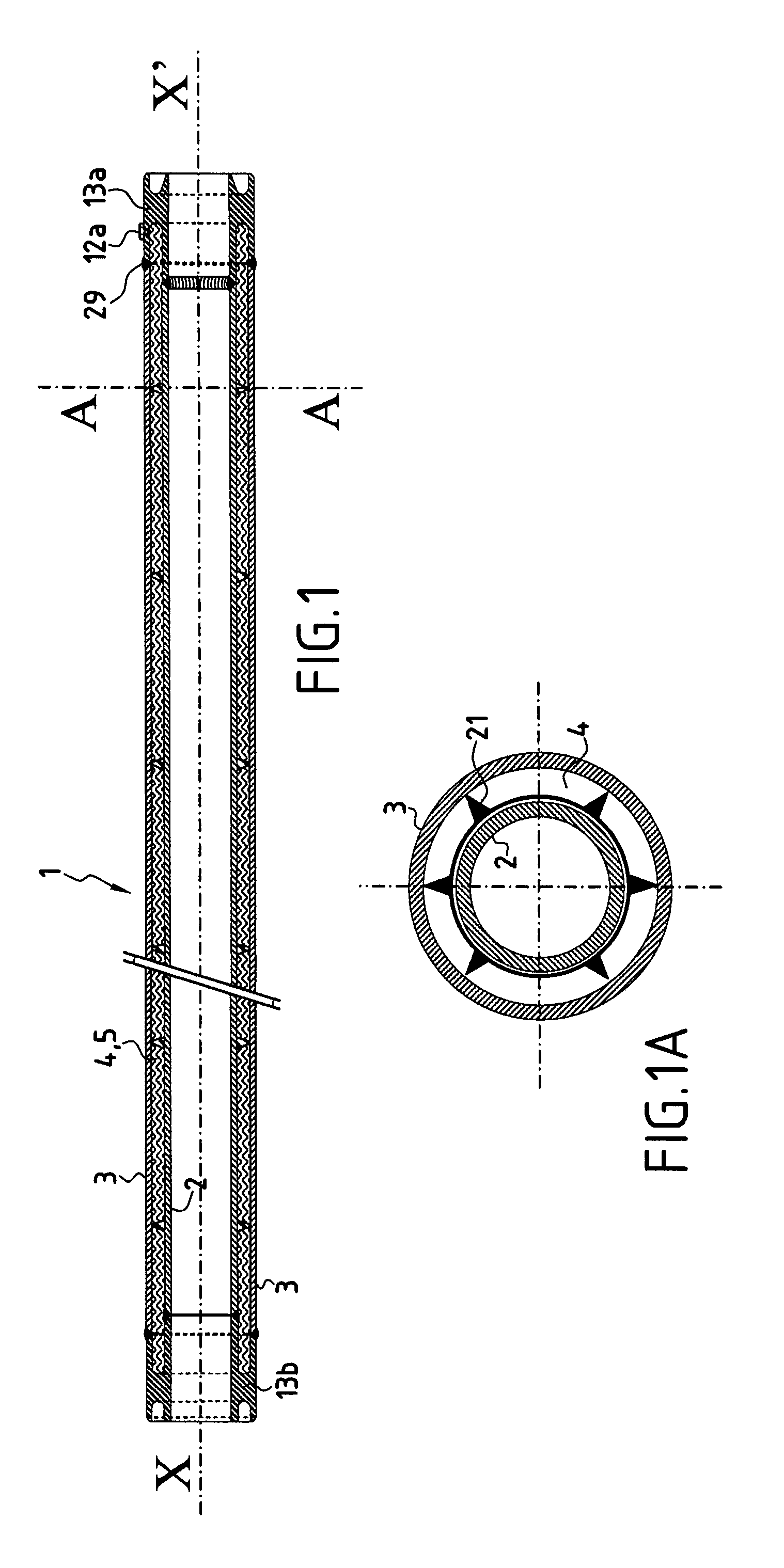
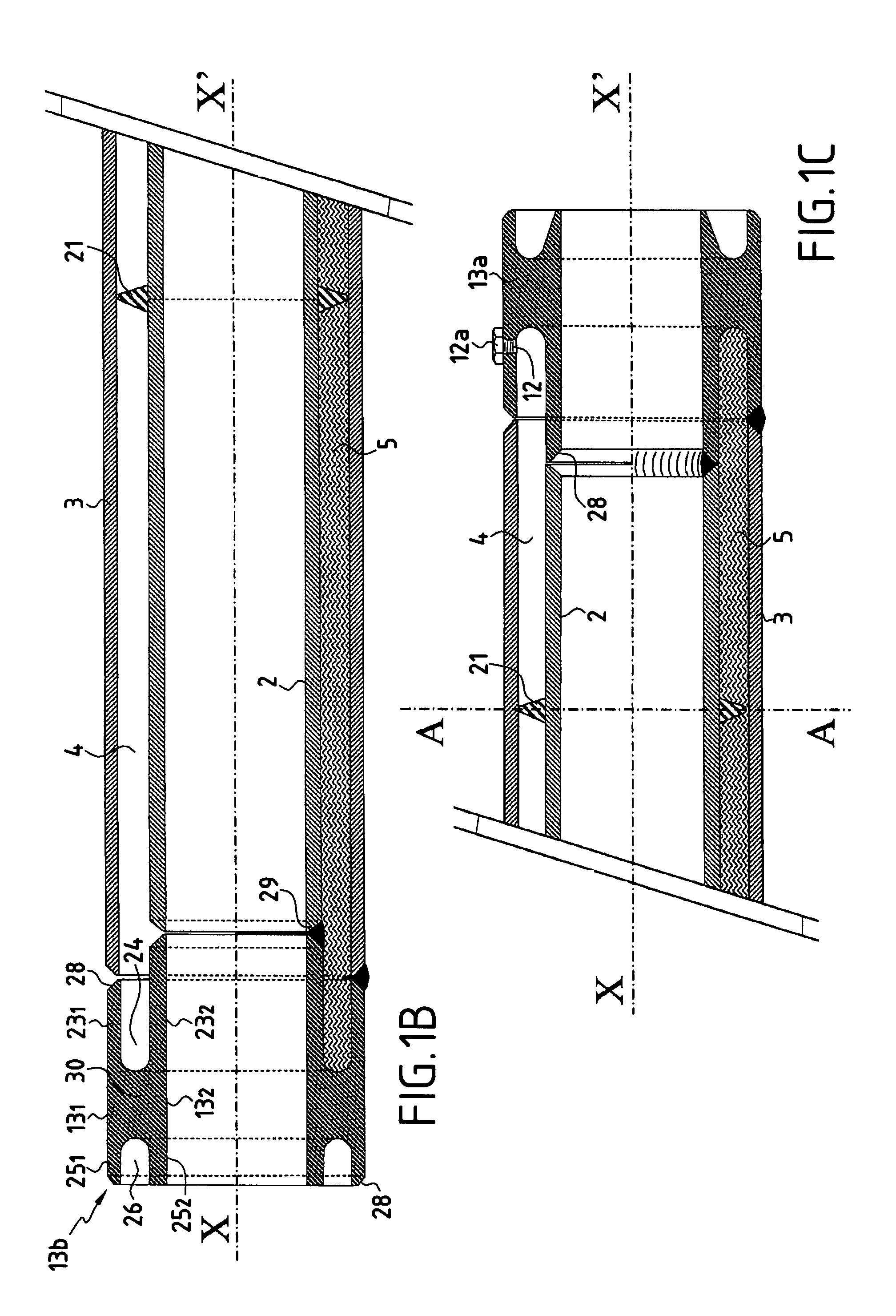
[0100]In FIGS. 1, 1B, and 1C, there can be seen a PiP type pipe 1 constituted by an outer pipe 3 and an inner pipe 2 secured by welding to a first junction forging 13b situated to the left in FIG. 1B and to a second junction forging 13a situated to the right in FIG. 1C, the annular space between said inner and outer pipes being filled with a micro- or nanoporous insulating material 4, with centralizer elements 21 around the circumference of the inner pipe and spaced apart, preferably in regular manner, along the length thereof. These centralizers maintain the radial distance between the inner and outer pipes and thus they maintain the thickness of said annular space at a value that is substantially constant.
[0101]Said junction forgings 13a and 13b are defined as follows:[0102]in a radial direction relative to a longitudinal axis XX′ of symmetry of said forging, said forgings are defined by a cylindrical inside wall 132 having substantially the same diameter as the main portion of sa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com