Walking assistance device
a technology of assistance device and walking aid, which is applied in the direction of walking aids, physical therapy, chiropractic devices, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to cause an assisting force, difficult to generate such an assisting force at each leg portion of the walking assistance device, and unsatisfactory reduction of load on the user, so as to reduce the propulsion power and reduce the load on the user
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
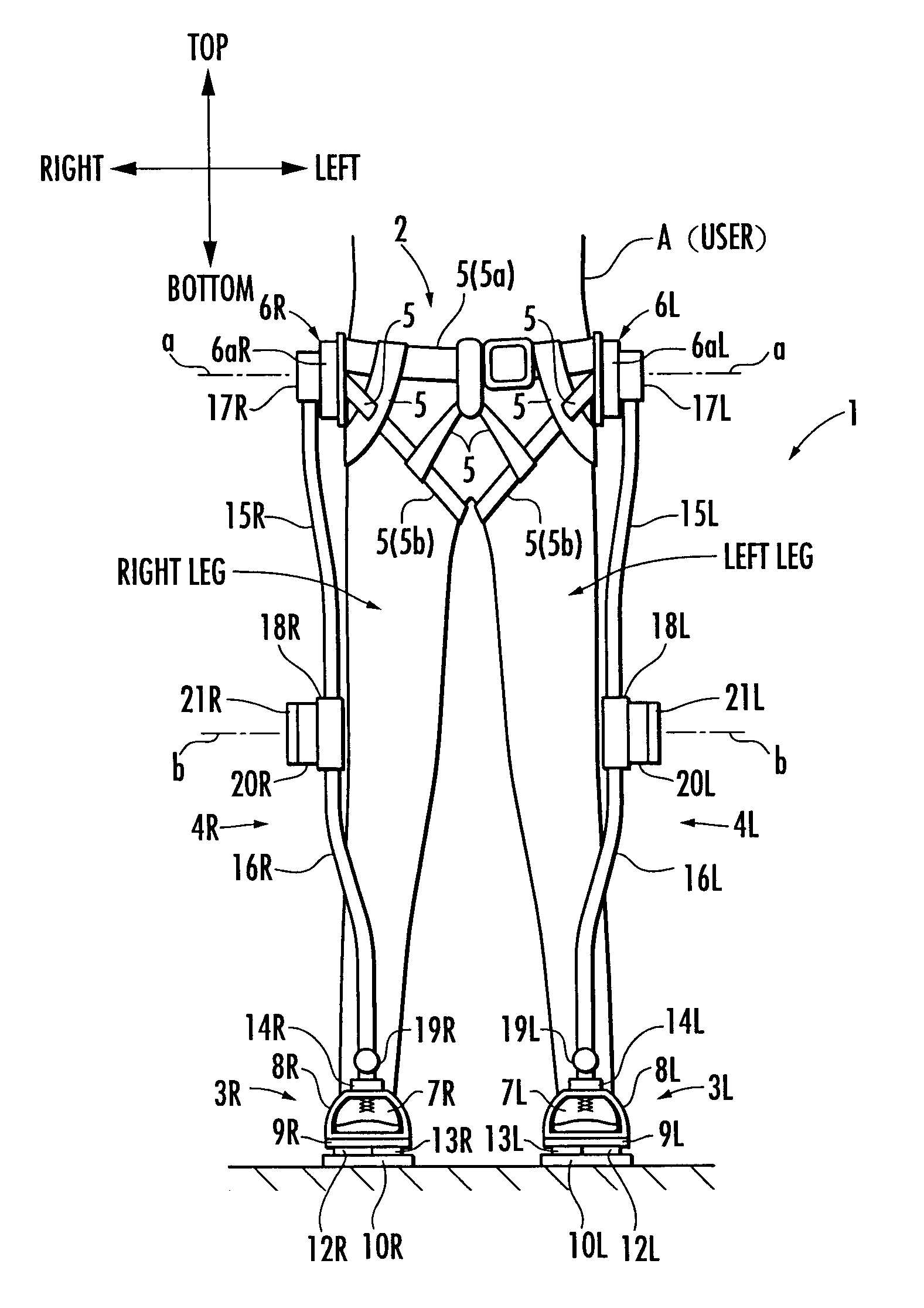
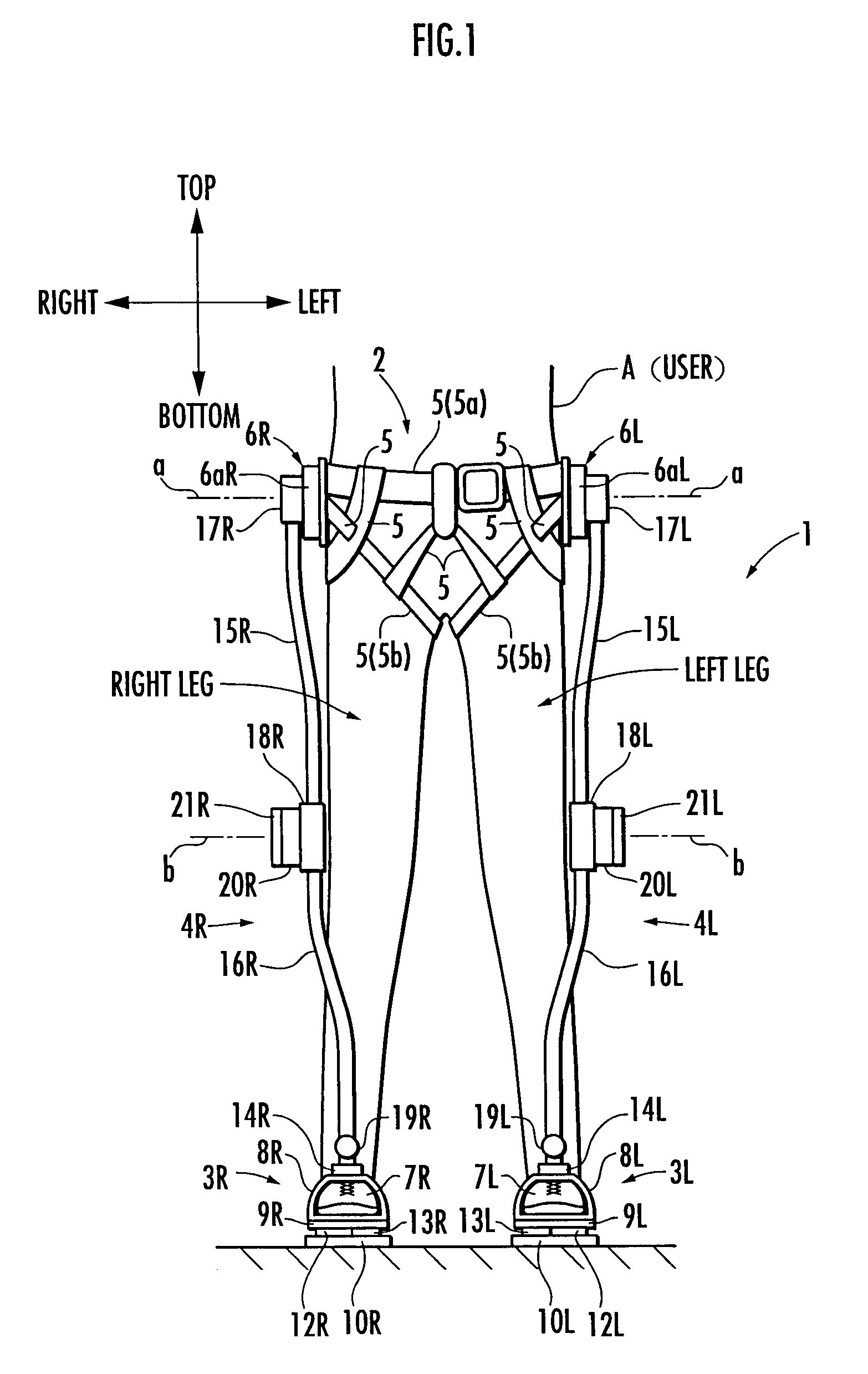
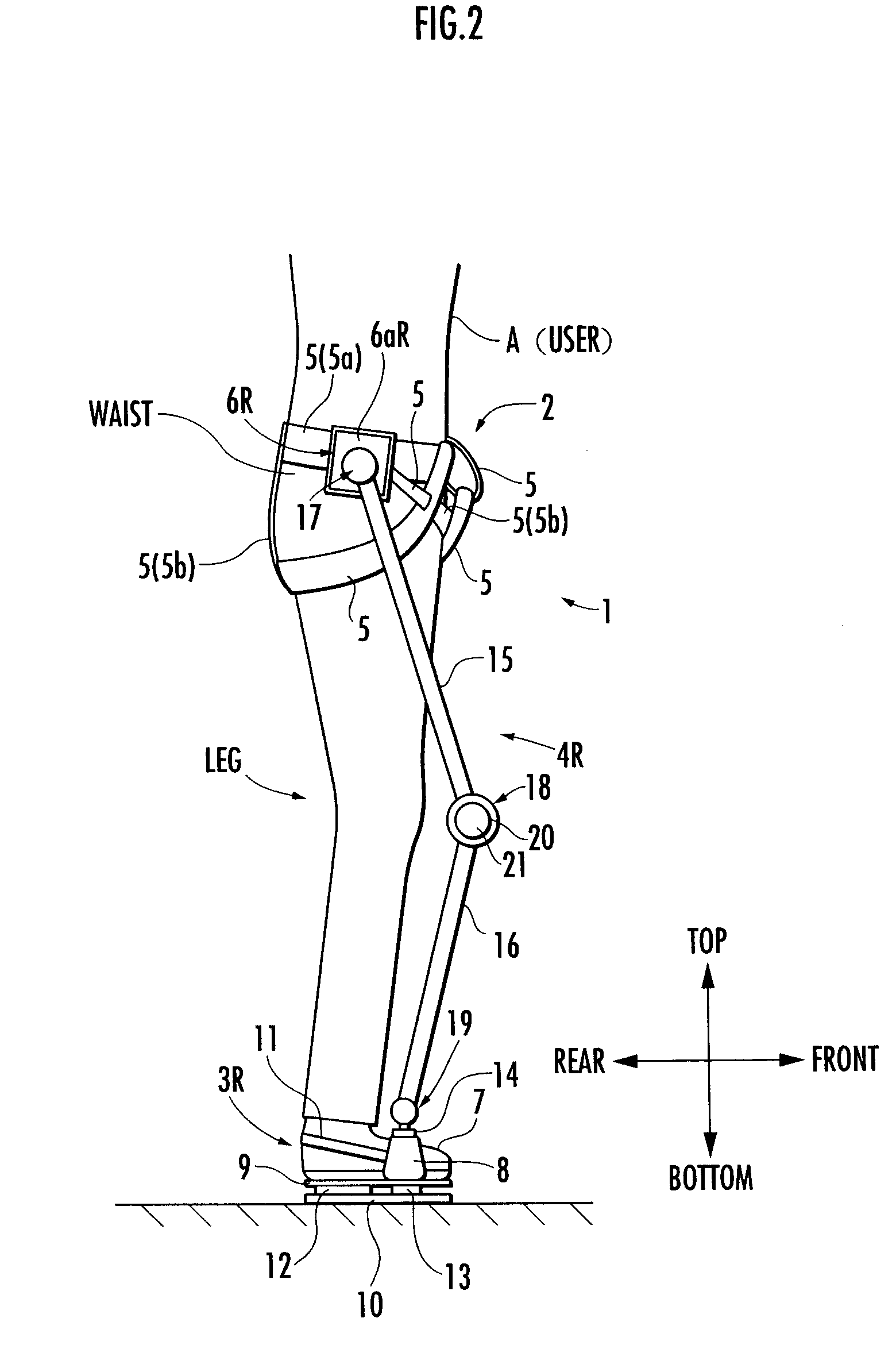
[0027]The following will explain the present invention with reference to FIG. 1 to FIG. 4. First, referring to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the structure of a walking assistance device according to the present embodiment will be explained. FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the walking assistance device according to the present embodiment and a user wearing the device viewed from the front (a diagram observed in a frontal plane), and FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the walking assistance device and the user viewed sideways (a diagram observed in a sagittal plane).
[0028]Referring to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, a walking assistance device 1 according to the present embodiment is provided with a body-mounted assembly 2 to be attached to the waist of a user A, a pair of left and right foot-mounted assemblies 3L, 3R to be attached to the left and right feet of the user A, and a pair of left and right leg links 4L, 4R, which connect the foot wear assemblies 3L and 3R, respectively, to the body wear assembly 2. The foo...
third embodiment
[0106]A third embodiment according to the present invention will now be explained with reference to FIGS. 8(a) and (b). FIGS. 8(a) and (b) are diagrams of a front view and a side view, respectively, of a portion near the waist of a walking assistance device according to the present embodiment and a user wearing the same.
second embodiment
[0107]The present embodiment differs from the first or the second embodiment described above only in the construction of a body-mounted assembly. More specifically, in a walking assistance device 1 according to the present embodiment, a body-mounted assembly 70 is wound around the waist of a user A and roughly divided into a back member 71 wound onto the back and a front member 72 wound onto the front.
[0108]The back member 71 is a member extended from one side of the waist of the user A to the other side via the back, and it is formed of a hard material, such as a resin. Hinge members 73L and 73R are provided at the left and right side locations of the back member 71 (locations at the sides of the waist of the user A). Each of the hinge members 73 is provided with a fixed component 74 secured to the back member 71 and a movable component 76 connected to the fixed component 74 through the intermediary of a shaft pin 75 (refer to FIG. 8(a)), the movable component 76 being installed su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com