Method for producing rigid and flexible printed circuit board
A technology for printed circuit boards and rigid circuit boards, applied in the fields of printed circuit manufacturing, printed circuit, multi-layer circuit manufacturing, etc., to achieve the effects of excellent reliability, improved adhesion, and stable adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
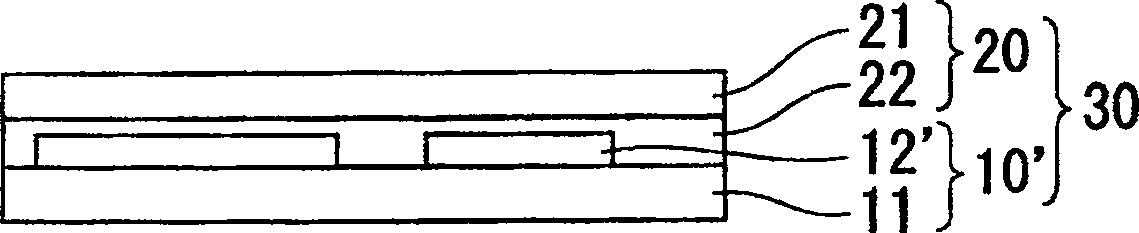
[0062] In this example, sodium hydroxide aqueous solution (NaOH (aq)) is used as the chemical solution used in the alkali treatment, and the concentration of the alkali treatment is varied in the range of 0.1 to 10.0 wt%, and the above steps (1) to (5), produced by Figure 1D A flexible rigid three-layer printed circuit board formed as shown. At this time, preparation conditions other than the alkali treatment concentration were made the same. Table 1 summarizes the production conditions. In addition, the printed wiring board produced in this example is called sample A.
[0063] Table 1
[0064] ◆Constituent material of printed circuit board
[Inner layer CCL] Copper foil 18μm on both sides, polyimide 25μm, adhesive 10μm
[Cover Layer (CL)] Polyimide 25μm, Adhesive 25μm
[Outer layer RPC] single-sided copper foil 18μm, epoxy glass 100μm
[Adhesive sheet] 25μm ◆Chemical solution treatment conditions of sample A
[Alkali treatment] concentration: 0...
Embodiment 2
[0073] In this example, sodium hydroxide aqueous solution (NaOH (aq)) is used as the chemical solution used in the alkali treatment, and the time of the alkali treatment is changed in the range of 10 to 600 sec, and the steps (1) to ( 5), produced by Figure 1D A flexible rigid three-layer printed circuit board formed as shown. At this time, the preparation conditions except for the alkali treatment time were made the same. Table 2 summarizes the production conditions. In addition, the printed wiring board produced in this example is called sample B.
[0074] Table 2
[0075] The constituent material of the printed circuit board
[Inner layer CCL] Copper foil 18μm on both sides, polyimide 25μm, adhesive 10μm
[Cover Layer (CL)] Polyimide 25μm, Adhesive 25μm
[Outer layer RPC] single-sided copper foil 18μm, epoxy glass 100μm
[Adhesive sheet] 25μm ◆Chemical solution treatment conditions of sample B
[Alkali treatment] concentration: 1.0[wt%], liqu...
Embodiment 3
[0084] In this example, sodium hydroxide aqueous solution (NaOH (aq)) is used as the chemical solution used in the alkali treatment, and the alkali treatment temperature (liquid temperature) is changed within the range of 15 to 55° C., and the above steps ( 1)~(5), produced the Figure 1D A flexible rigid three-layer printed circuit board formed as shown. At this time, the preparation conditions other than the alkali treatment temperature (liquid temperature) were made the same. Table 3 summarizes the preparation conditions. In addition, the printed wiring board produced in this example is called sample C.
[0085] The same peel strength test as in Example 1 was performed on the sample C prepared by changing the alkali treatment temperature (liquid temperature), and the tensile peel strength (referred to as peel strength) (N / cm) was calculated.
[0086] Figure 5 It is a graph showing the peel strength of sample C produced by changing the alkali treatment temperature (liqu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com