Linear friction welding process between aluminium part and steel part
A technology of linear friction welding and steel parts, applied in welding equipment, manufacturing tools, non-electric welding equipment, etc., which can solve the problems of reduced mechanical properties of connectors, inability to use welded joints, and low production efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
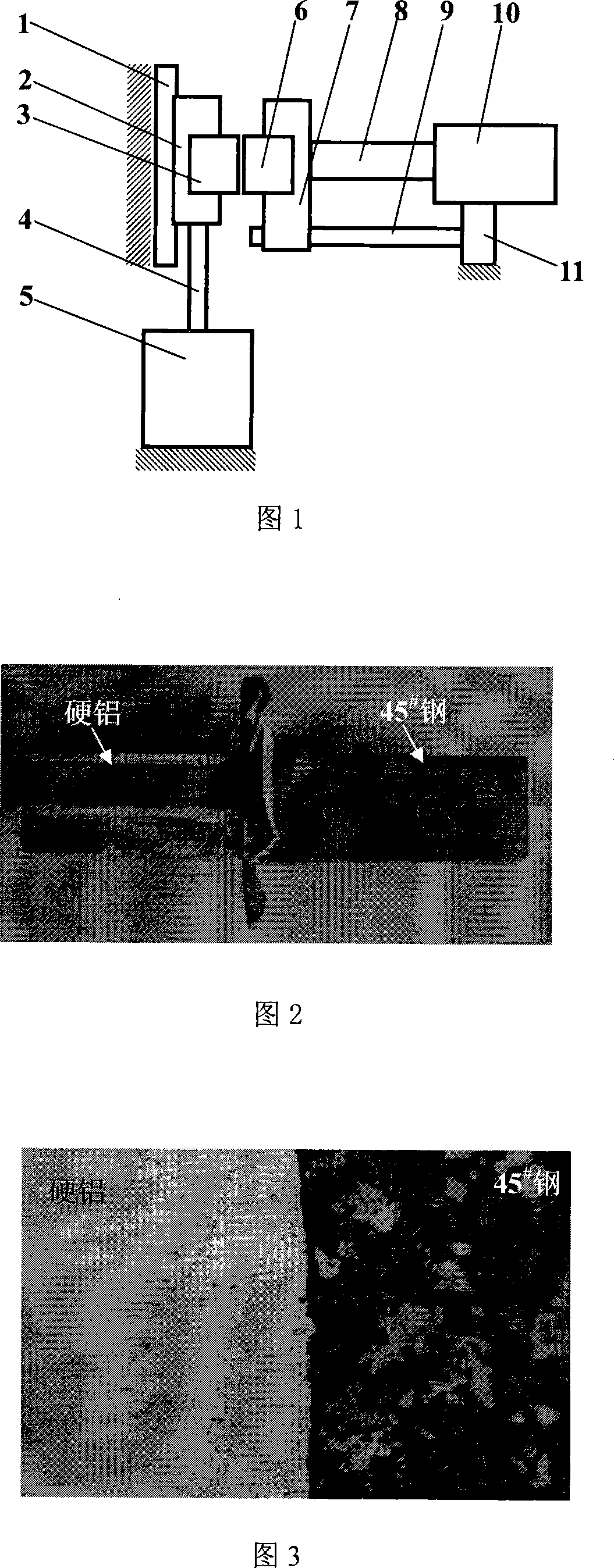
[0015] Embodiment 1: Referring to FIG. 1 , the welding of an aluminum part with a rectangular cross section and a steel part. Install and fix the steel part 3 in the vibrating fixture 2. The vibration source 5 drives the vibration fixture 2 to reciprocate up and down along the linear guide rail 1 with a vibration frequency of 24 Hz and an amplitude of 2 mm through the connecting rod 4 . The steel part 3 vibrates up and down with the vibrating fixture 2 at the same frequency. The aluminum parts 6 are installed and fixed in the mobile fixture 7 . The afterburner cylinder 10 makes the movable fixture 7 move left and right along the slide bar 9 through the thrust rod 8, and the aluminum part 6 is promptly subjected to left or right thrust at the same time.
[0016] During welding, under the promotion of the booster cylinder 10, the steel part 3 and the aluminum part 6 are in contact with each other. At this time, the vibration source 5 drives the steel part 3 to vibrate rapidly...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Embodiment 2: Referring to FIG. 1 , the welding of an aluminum part with a circular cross section and a steel part. Install and fix the steel part 3 in the vibrating fixture 2. The vibration source 5 drives the vibration fixture 2 to reciprocate up and down along the linear guide rail 1 with a vibration frequency of 26 Hz and an amplitude of 2.6 mm through the connecting rod 4 . The steel part 3 vibrates up and down with the vibrating fixture 2 at the same frequency. The aluminum parts 6 are installed and fixed in the mobile fixture 7 . The afterburner cylinder 10 makes the movable fixture 7 move left and right along the slide bar 9 through the thrust rod 8, and the aluminum part 6 is promptly subjected to left or right thrust at the same time.
[0020] During welding, under the promotion of the booster cylinder 10, the steel part 3 and the aluminum part 6 are in contact with each other. At this time, the vibration source 5 drives the steel part 3 to vibrate rapidly ...
Embodiment 3
[0021] Embodiment 3: Referring to FIG. 1 , the welding of an aluminum part with a regular hexagonal cross section and a steel part. Install and fix the steel part 3 in the vibrating fixture 2. The vibration source 5 drives the vibration fixture 2 to reciprocate up and down along the linear guide rail 1 with a vibration frequency of 28 Hz and an amplitude of 2.6 mm through the connecting rod 4 . The steel part 3 vibrates up and down with the vibrating fixture 2 at the same frequency. The aluminum parts 6 are installed and fixed in the mobile fixture 7 . The afterburner cylinder 10 makes the movable fixture 7 move left and right along the slide bar 9 through the thrust rod 8, and the aluminum part 6 is promptly subjected to left or right thrust at the same time.
[0022] During welding, under the promotion of the booster cylinder 10, the steel part 3 and the aluminum part 6 are in contact with each other. At this time, the vibration source 5 drives the steel part 3 to vibrate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com