In-situ degrading bacteria in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons polluting soil and identification method of bioremediation capability
A technique for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polluted soil, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe determination/inspection, food testing, etc., can solve problems that are difficult to connect and achieve high-precision results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
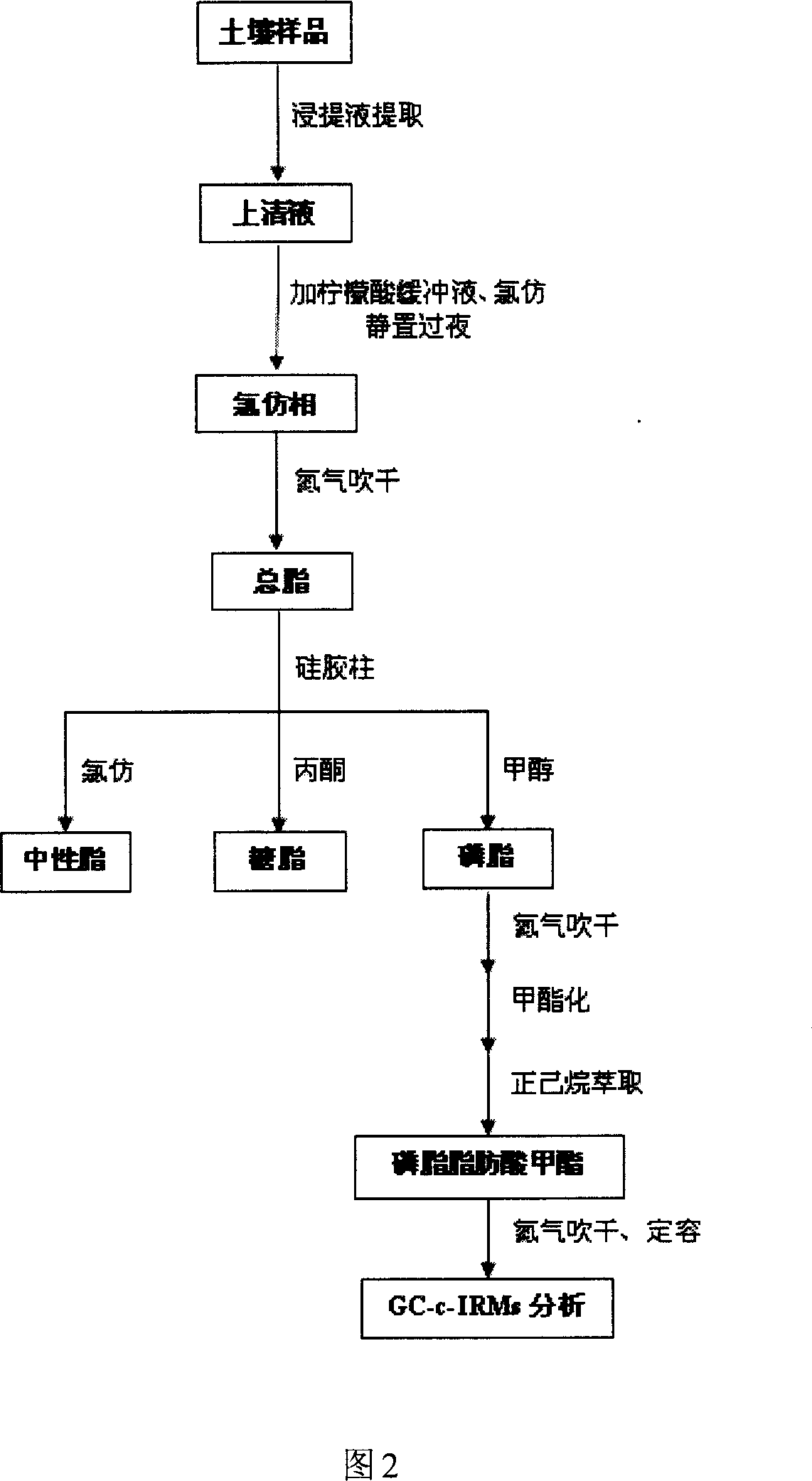
[0060] Through the above experiments, it was detected that there were 8 kinds of 13 C isotopically enriched phospholipid fatty acids are 10Me18:0, 16:1ω7c, 16:1ω7t, 16:1ω9, 18:1ω9c, 18:1ω9t, a15:0 and 16:0 (numbers before ":" represent carbon The number of atoms; the number after ":" represents the number of double bonds; "10Me" indicates that a methyl group is on the 10th C from the end of the molecule; "ω" indicates that there is a double bond at the seventh C at the end of the molecule; "c " means cis; "t" means trans; "a" means branched anti isomerism). Different fatty acids can indicate different microbial groups, such as branched fatty acids for Gram-positive bacteria, monounsaturated fatty acids for Gram-negative bacteria, fatty acid 10Me18:0 for actinomycetes, fatty acid 18:2ω6,9 for fungi. The experimental results show that G + Bacteria, G - Bacteria and actinomycetes were involved in the metabolism of phenanthrene, whereas the involvement of fungi was detected.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com