Microarray-mediated diagnosis of herpes virus infection by monitoring host's differential gene expression upon infection
A herpes virus infection, herpes virus technology, applied in the field of monitoring, treatment and treatment of herpes virus infection in mammals, can solve the problems of not getting enough antiviral treatment, increasing persistent pain, latent infection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0298] Identification of specific diagnostic genes for herpes virus infection
[0299] Experimental Disease Trial Design
[0300] Equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1 ) infection was induced in two groups of 13 foals at different times. Six young foals were followed for 20 days (group 1) and infected on day 0 (experimental inoculation). Seven foals were followed for 42 days (group 2) and infected on day 21 (experimental inoculation). All foals were infected with in vitro cultured EHV-1 nasopharyngeal aerosols. Blood samples from group 1 were collected at 8 time points on days 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 10, 13 and 20. Group 2 blood samples were collected at 16 time points on days 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 10, 13, 20, 21, 22, 23, 25, 27, 31, 34 and 41. Day 0 samples were used as controls for individual horses.
[0301] Animals of group 2 were then found to have been infected naturally and asynchronously with EHV. All animals in Group 2 were seroconverted, and the time of natural infection was estimated...
Embodiment 2
[0478] Identification of diagnostic marker genes and prioritization of these genes
[0479] For group 1, the differences in gene expression of animals before and after infection with EHV were analyzed according to the empirical Bayes method of Lonnstedt and Speed (Lonnstedt and Speed, 2002, Statistica Sinica, 12: 31-46). The time points after infection were compared with the time points before infection for analysis. Using multiple terms for each animal's effect, the clinical state (before and after EHV infection) terms were fitted to a general linear model by each gene. The genes were ranked according to their posterior odds of differential expression between the clinical status groups. Only those genes with statistically significant changes (assessed with t-statistics based on empirical Bayesian shrunken standard deviation) were recorded. A strong control over the Type 1 error rate was maintained using Holm's correction of p-values (Holm, S., 1979, Scandinavian Journal...
Embodiment 3
[0484] Demonstrated diagnostic potential for assaying herpes virus infection
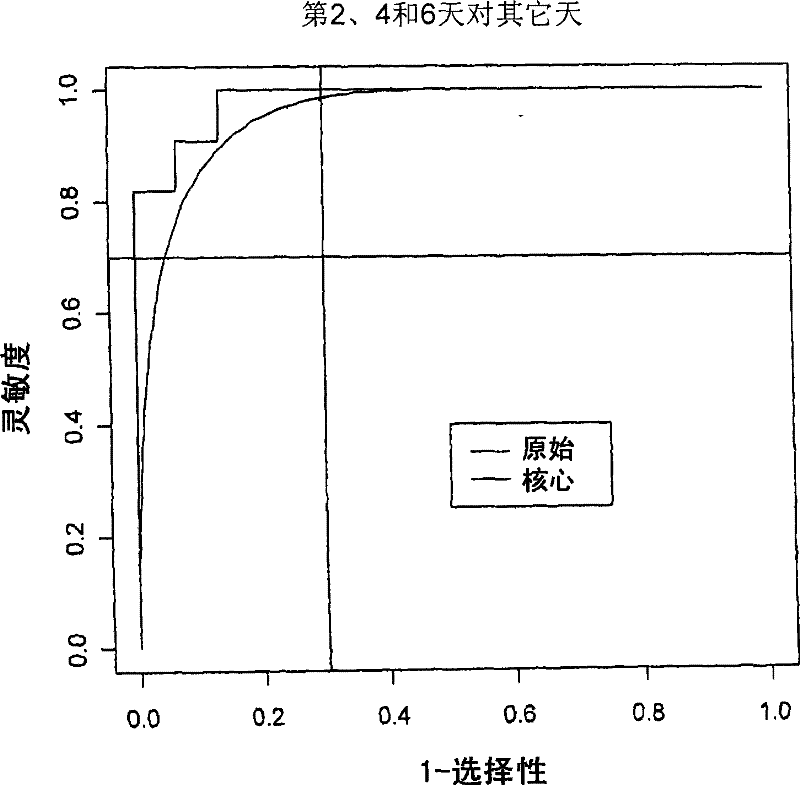
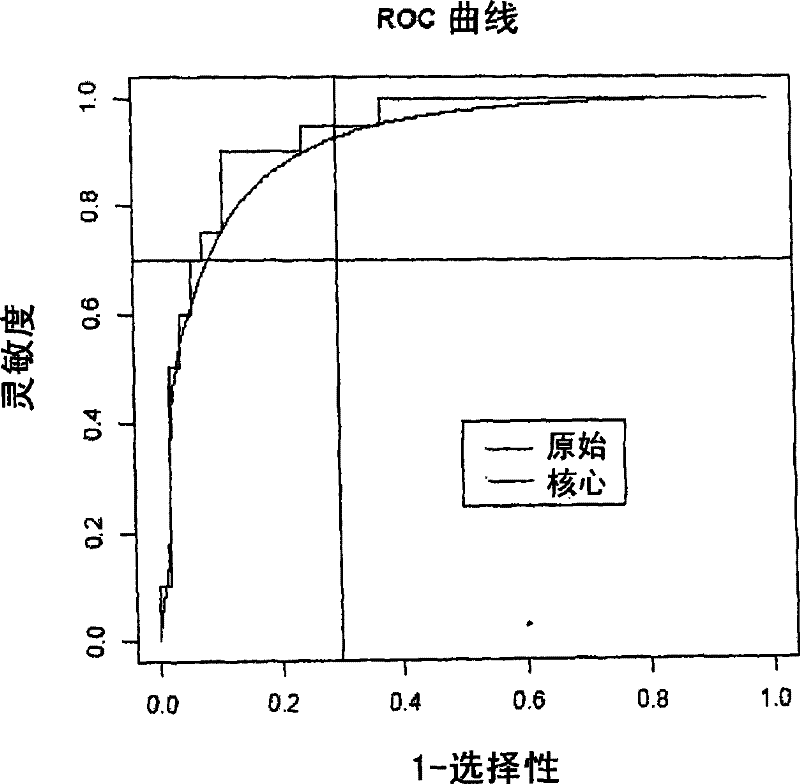
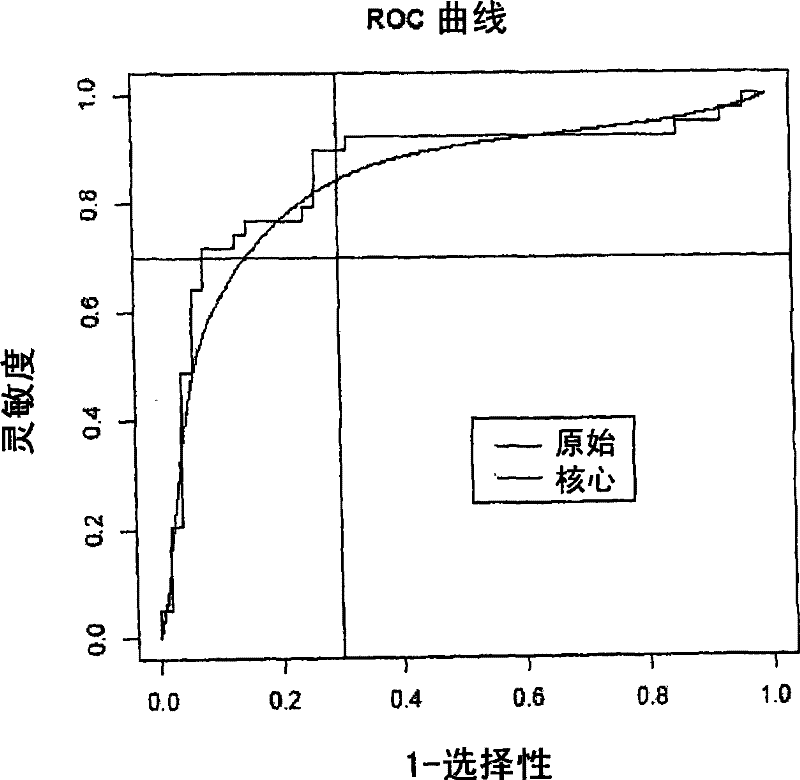
[0485] Principal component scores calculated from gene expression (Jolliffe, I.T., Principal components analysis, Springer-Verlag, 1986) were analyzed using discriminant analysis (Venables and Ripley, 2002, Statistics in Modern Applications" (Modern Applied Statistics in S, Springer) assessed the diagnostic potential of the entire panel of genes at various time points after infection. The whole method is cross-validated. One animal was dropped at a time for cross-validation (instead of one observation). Both sensitivity and specificity were calculated as uniform prior. This can be interpreted as a form of downscaling, shrinking these estimates into a reduced space.
[0486] Receiver operating curves were estimated using cross-validated discriminant function scores. The receiver operating curve is calculated by shifting the critical threshold along the axis of the discriminant function score. Tw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com