Alkaline process and system for producing pulp
A technology of pulp and cooking method, which is applied in the system field of implementing the method, can solve the problems of impossible high HS concentration, cannot use cellulose for AQ, and does not show convenience, etc., and achieves improved evaporation equipment and improved pulp. Yield and demand reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Pulp was cooked in the laboratory from eucalyptus chips under state-of-the-art conditions whereby the temperature in the first step of impregnation was 110°C (duration 45 minutes) and the temperature in the second step was 120°C (15 minutes) . The cooking temperature was maintained at 152° C. for 120 minutes to obtain a cellulose pulp with a kappa number of 17, which indicates the degree of delignification of the cellulose pulp. The cooking liquor used was conventional in terms of its HS and dry solids content. The H factor, which expresses the ratio of temperature to cooking time, is about 460. The pulp yield obtained from the chips was 53.7% based on the amount of chips used.
Embodiment 2
[0049] Using the same material, by circulating and concentrating the steeping liquid in multiple cookings, the following conditions corresponding to the present invention are established: the duration of the steeping is as in Example 1, the steeping temperature is 130° C., and the same as the cooking conditions in Example 1 In comparison, the dissolved dry solid components and HS concentrations were about twice as high. Cooking at a temperature of 149° C. for 100 minutes resulted in almost the same degree of delignification (Kappa number 18), which corresponds to an H factor of 230, which is half that of Example 1. The yield of cellulose pulp was 54.5% based on the amount of wood chips used.
Brief description of the drawings
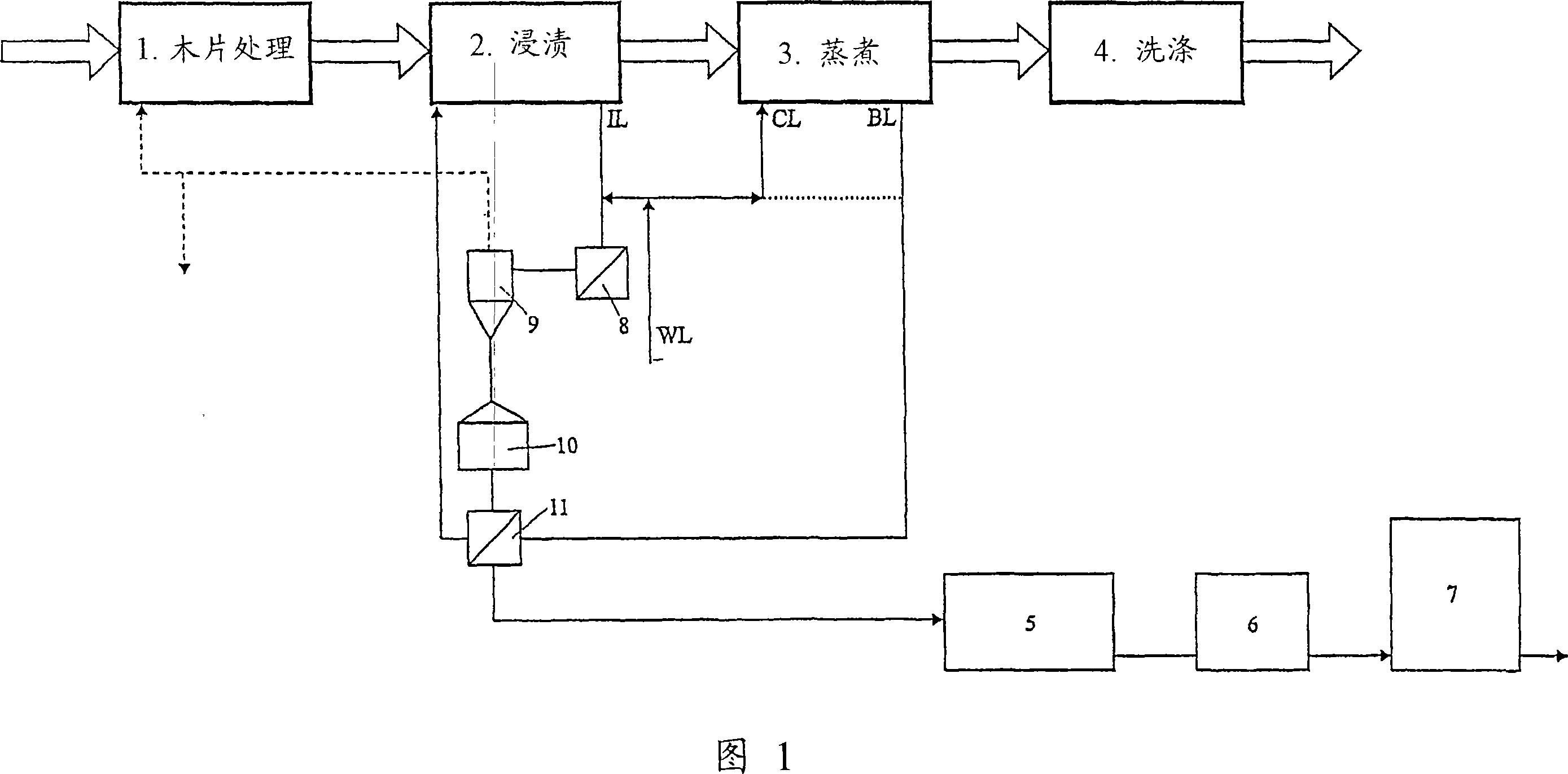
[0050] Figure 1 schematically shows a preferred embodiment of the invention.
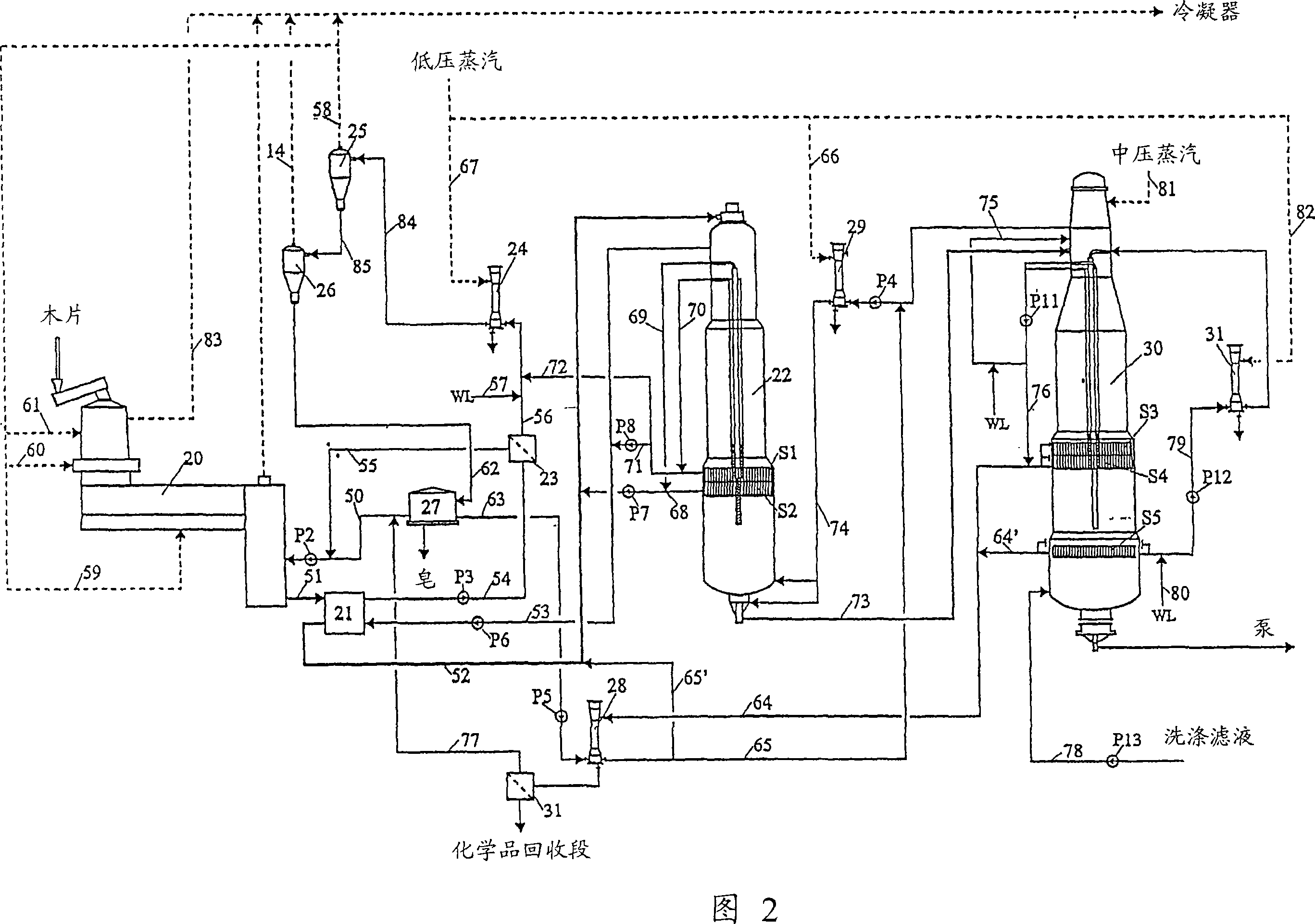
[0051] Figure 2 shows a preferred embodiment of the invention with a separate impregnation vessel.
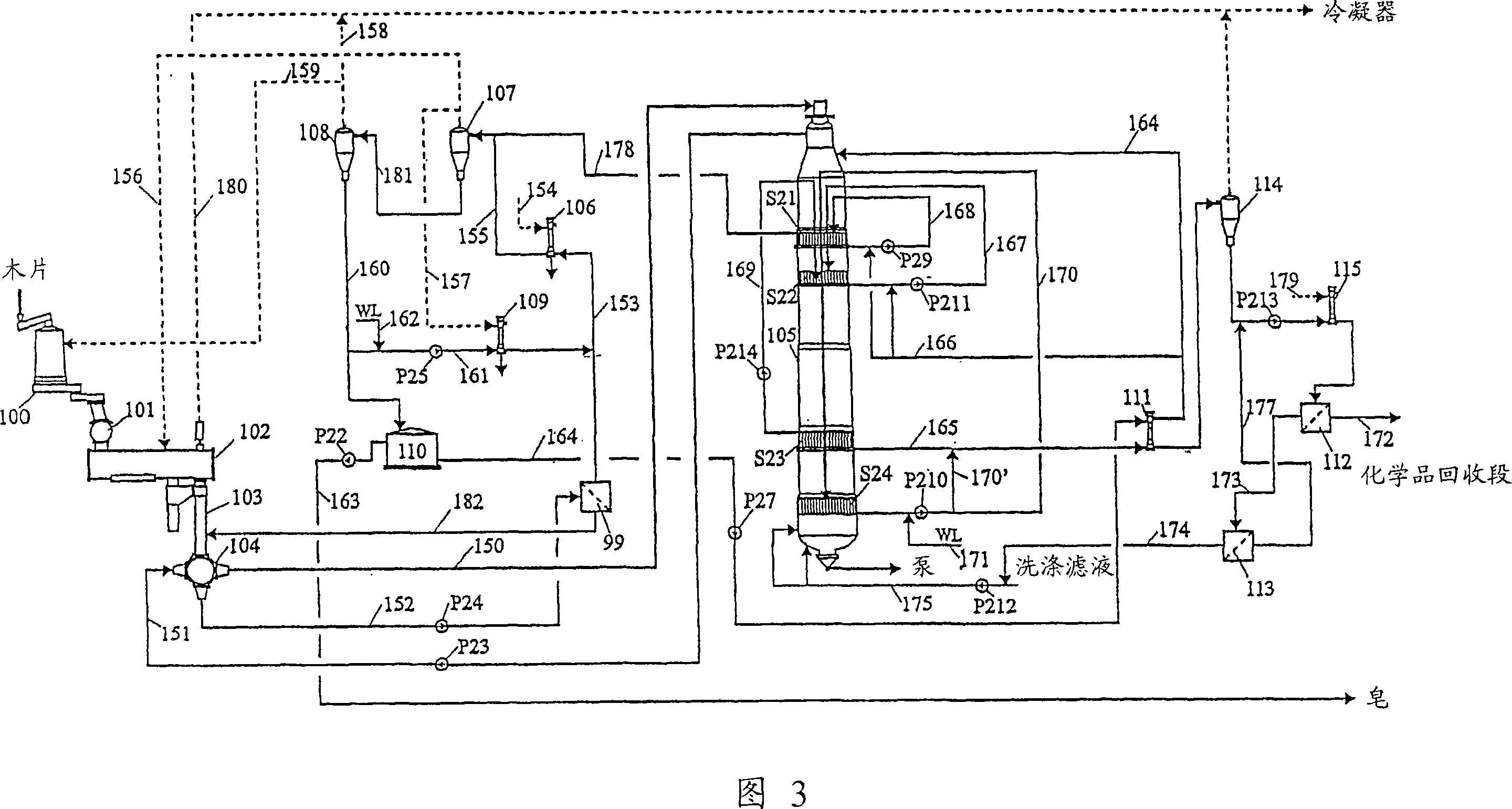
[0052] Figure 3 shows a preferred embodiment of the invention wherein ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com