Catalyzed hydrogen desorption in mg-based hydrogen storage material and methods for production thereof
A technology of hydrogen storage material and magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy, applied in the field of magnesium-based hydrogen storage materials, can solve the problems of impossible maintenance, short-range order not being preserved, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
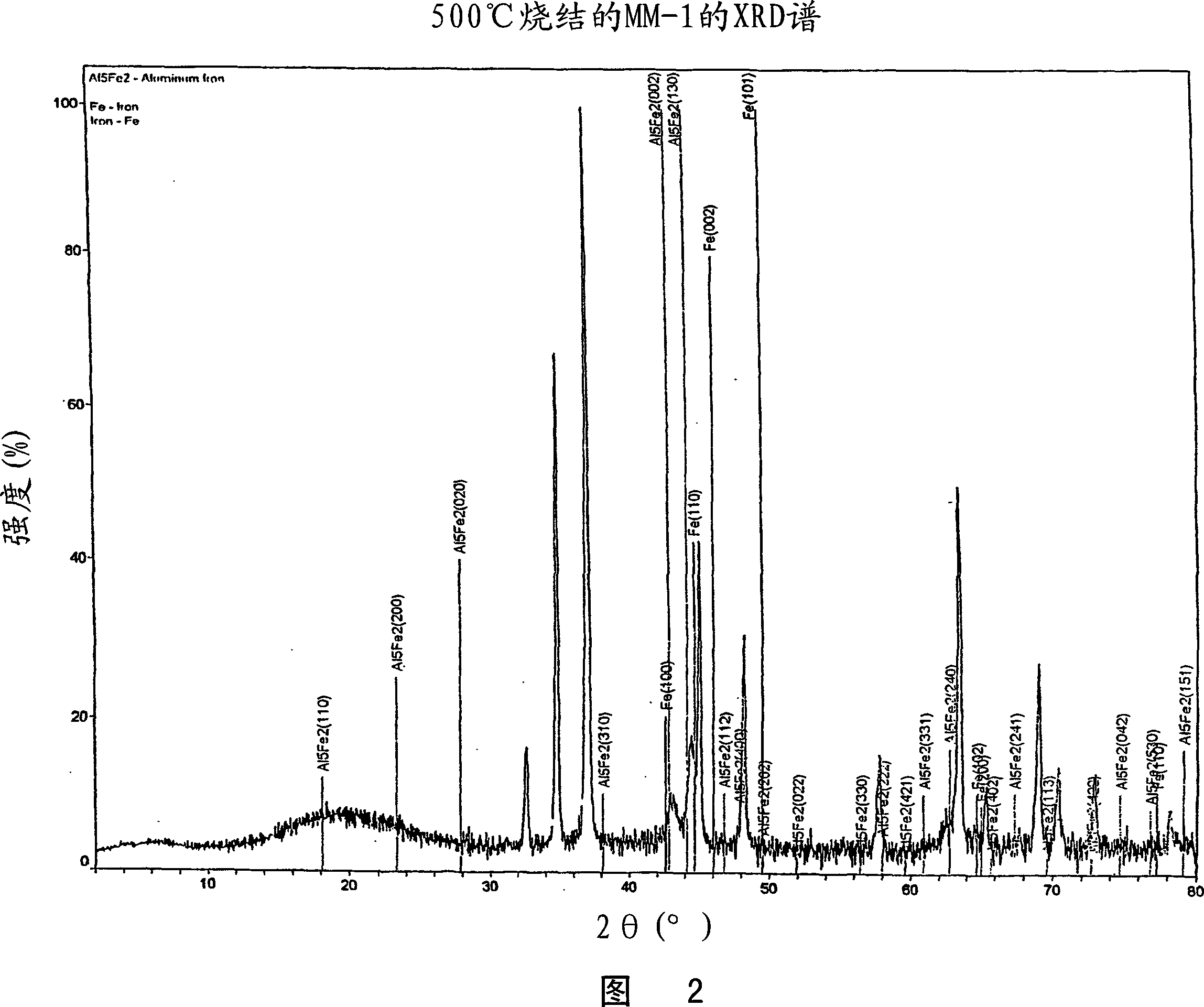
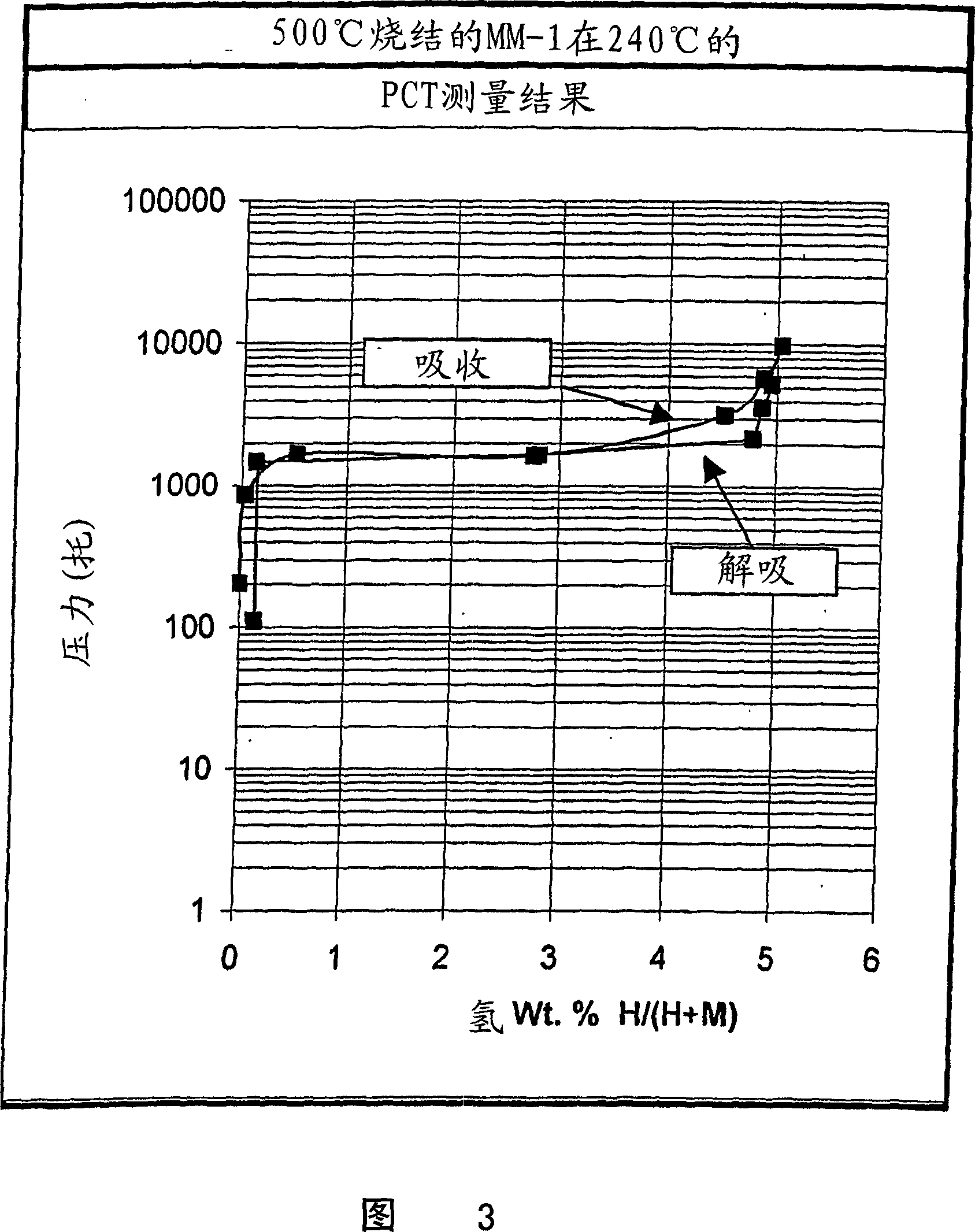
[0079] Raw materials consisting of pure metal powders magnesium (99.8%, 325 mesh), aluminum (99.5%, 325 mesh), iron (99.9+%, 10 microns) and other minor components were mixed in an agate mortar-pestle. Ten different compositions were prepared, and their weight percentage compositions are shown in Table 1. The mixed powders were pressed into pellets 1 cm in diameter and 1 cm in length using a hardened steel die. The pressed pellets were placed in a quartz tube and sintered under vacuum at a temperature above 500°C for 22 hours.
[0080] Table 1, chemical composition (all figures are percent by weight)
[0081] Alloy Number
Mg
Al
Fe
B
Cu
PD
V
Ni
C
sc
MM-1
88.8
2.7
8.5
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
MM-2
87
3
9
1
-
-
-
-
-
-
MM-3
86
3
9
2
-
-
-
...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Another MM-1 material was prepared by changing the sintering / annealing temperature by the method of Example 1. Figure 6 shows the PCT curves of the samples sintered / annealed at 570°C and 600°C, respectively. While the PCT of the material sintered / annealed at 570°C (sintered / annealed at 500°C) and the PCT of the material of Example 1 showed little deviation, the material sintered / annealed at 600°C provided an extended plateau at slightly higher pressures .
Embodiment 3
[0087] Mechanically alloyed (MA) powders of MM-1 were prepared from a mixture of pure elemental magnesium (99.8%, 325 mesh), aluminum (99.5%, 325 mesh) and iron (99.9+%, 10 microns). Grinding was carried out in an attritor equipped with Cr-steel balls. The mechanical alloying process was carried out under an argon atmosphere with the addition of 1% graphite and heptane to prevent agglomeration of the material on the walls of the attritor. Usually the ball milling time is 2 hours. Figure 7 is a SEM backscattered micrograph of the sample. The figure shows severe phase segregation in the material. Area 1 (bright contrast on the photo) is filled with Fe and Al powders, while area 2 (the darker area in the center) is all magnesium. Figure 8 is the XRD pattern of the sample, showing that this process did not form any amorphous intermetallic products. MA-MM-1 powder was pressed onto an expanded nickel metal substrate, and then coated with 100 Å of iron on both sides as a surface ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com