Method for producing zinc alloy from zinc dross
A zinc alloy and zinc slag technology, applied in the field of hot-dip galvanized zinc slag recycling, can solve problems such as consumption, inability to fundamentally eliminate, excessive energy consumption, etc., and achieve low energy consumption, high production efficiency, and production operation The effect of cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Using 2030 hot-dip galvanizing waste slag, its main chemical composition is as follows: Al 3.1%, Pb 0.15%, Fe 1.3%, Zn 94.5%, Cd 0.11%.
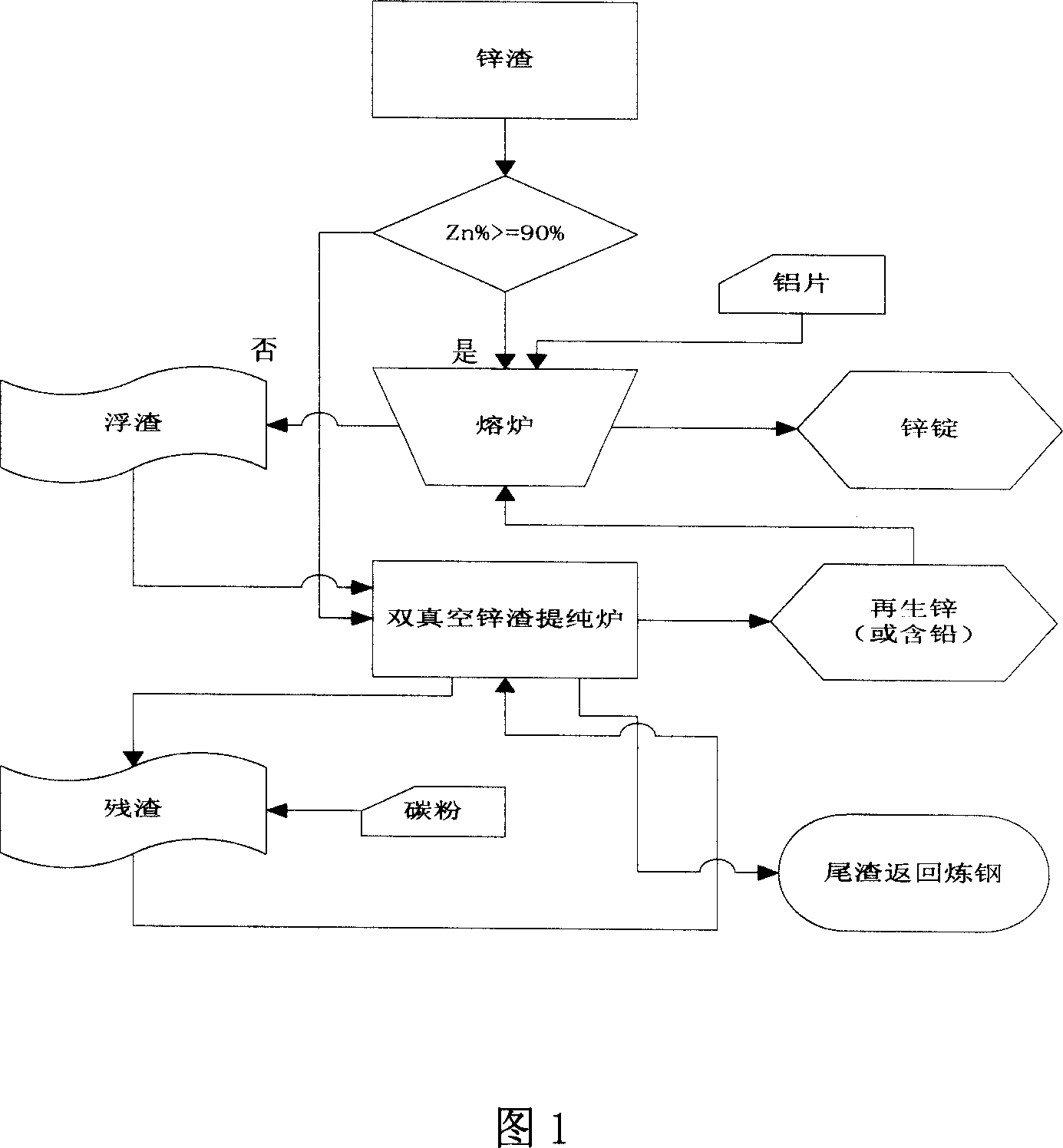
[0024] Combined with the process flow chart shown in Figure 1, take 5 kg of zinc slag and 100 grams of aluminum flakes into the furnace, heat to 550 ℃, constant temperature to completely melt, and then mechanically stir to make the liquid part uniformly mixed. In this process, the furnace uses Sealing measures, only set up flue gas cooling channels, reduce the occurrence of oxidation or other reactions. Then reduce the furnace temperature to 475°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and then keep it at a constant temperature for 5 minutes to ensure that the zinc liquid and scum are fully separated. Take the surface scum into a special mold and enter it into the subsequent vacuum furnace for purification. The liquid part was poured into the ingot and weighed after cooling to obtain 3.9 kg of zinc ingot, with a zinc content of 98.3% and an aluminum conte...
Embodiment 2
[0032] If the zinc content of the zinc slag is less than 90%, it first enters the double vacuum zinc slag purification furnace for processing, and the regenerated zinc is obtained on the crystallizer, and the residue is left in the material basket. The regenerated zinc on the crystallizer was mechanically peeled off and directly transported to the furnace, and the steps in Example 1 were repeated.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com