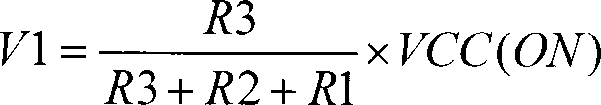Under voltage locking circuit with temperature compensation
A technology of undervoltage lockout circuit and temperature compensation circuit, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability of the switching threshold value of the undervoltage lockout circuit and insufficient system reliability, and achieves enhanced stability and reliability. Reliability, Avoiding Drift, Improving Accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
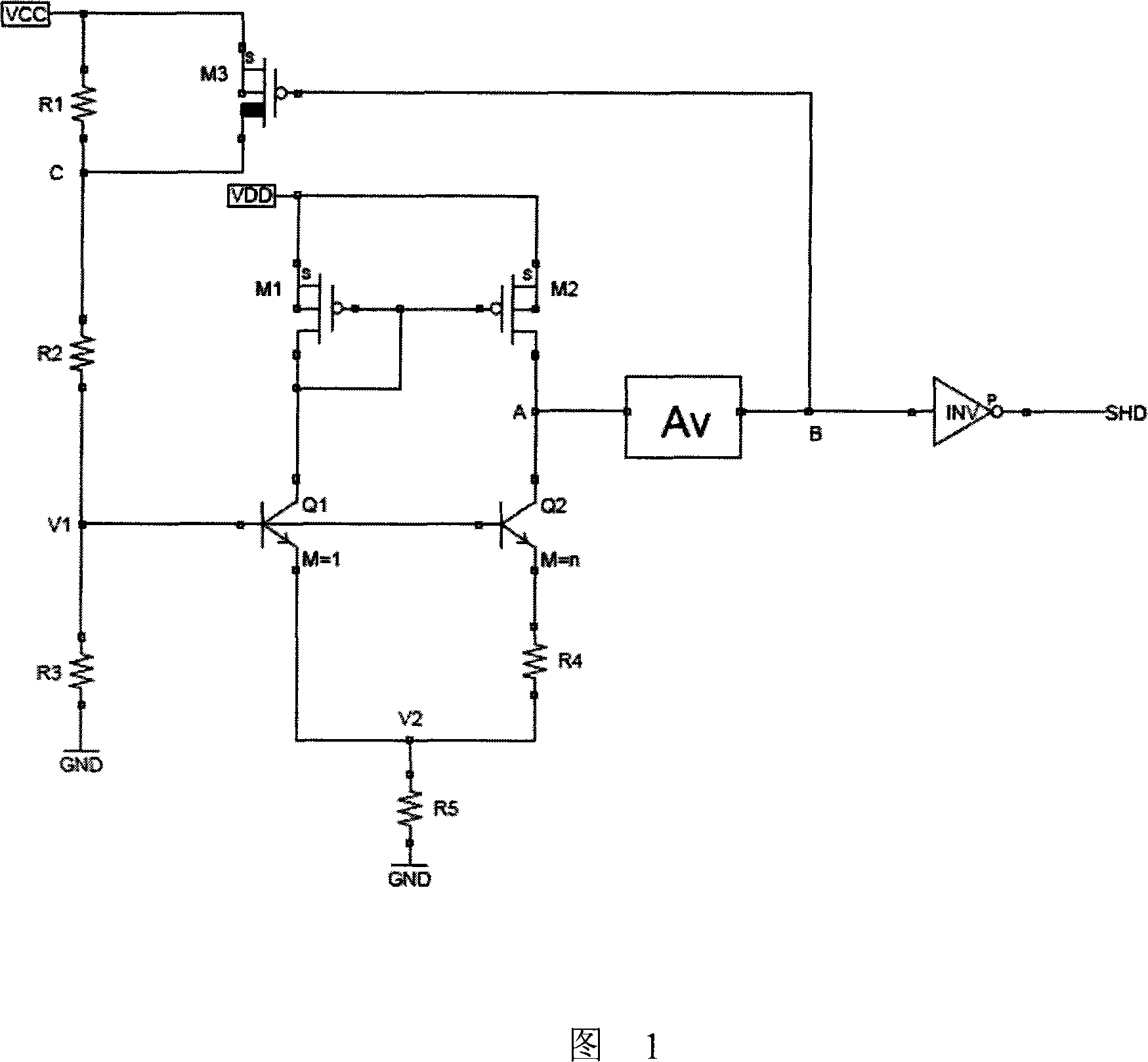
[0021] Embodiment 1 As shown in FIG. 1 , an undervoltage lockout circuit with temperature compensation includes a voltage sampling circuit, a temperature compensation circuit, a buffer circuit and a feedback circuit. The voltage sampling circuit includes a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2 and a third resistor R3 connected in series between the first voltage source VCC and the ground terminal GND, and the output of the voltage sampling circuit is formed between the second resistor R2 and the third resistor R3 A node C is formed between the terminal V1, the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2.
[0022] The temperature compensation circuit adopts a bandgap reference circuit, including a first field effect transistor M1, a second field effect transistor M2, a first transistor Q1, a second transistor Q2, a fourth resistor R4 and a fifth resistor R5. The gate and drain of the first field effect transistor M1 are connected together. The sources of the first field eff...
Embodiment 2
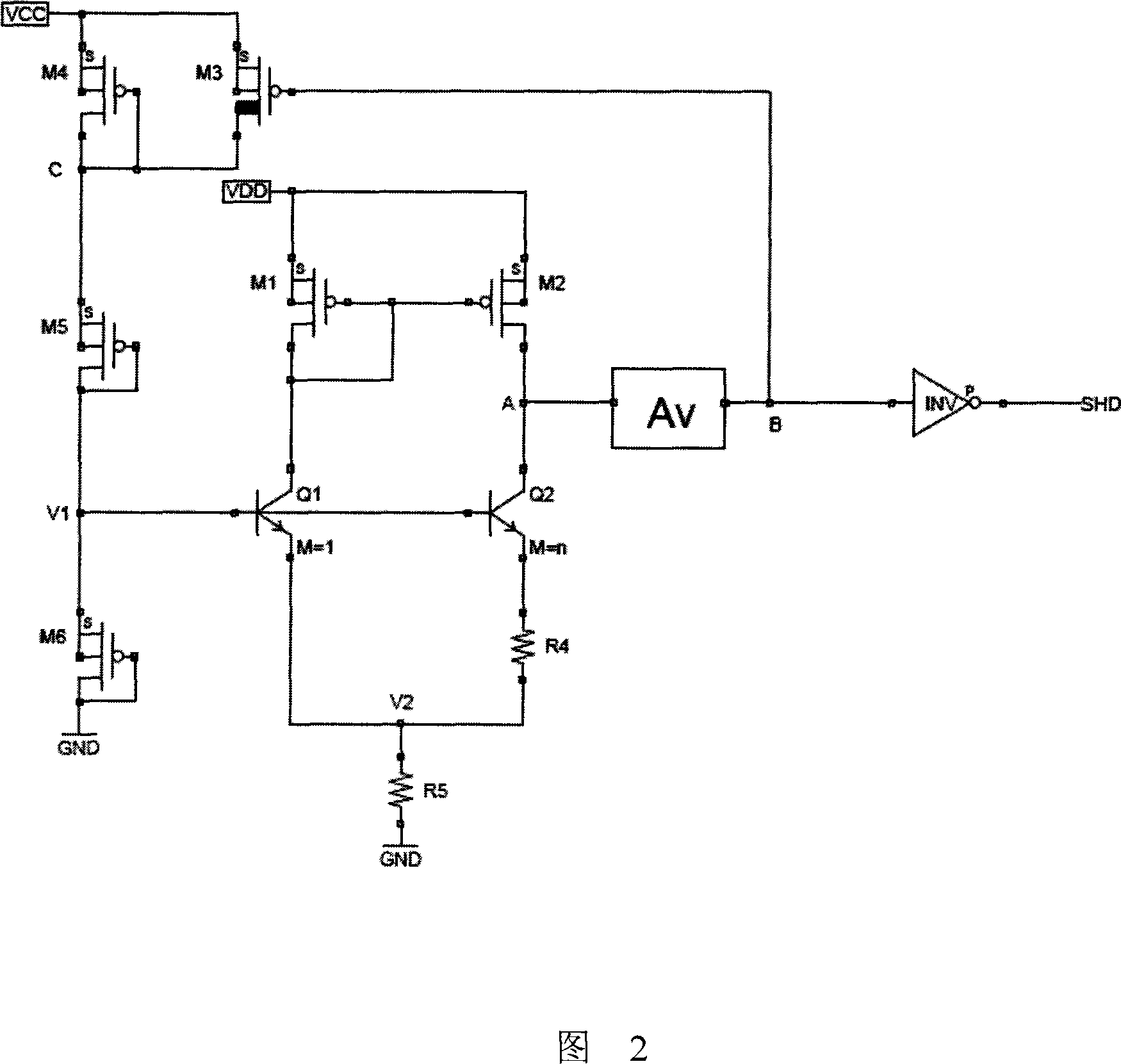
[0041] Embodiment 2 As shown in Figure 2, in this embodiment, the first resistor R1, the second resistor R2, and the third resistor R3 used in the voltage sampling circuit in Embodiment 1 use the fourth field effect transistor M4 and the fifth field effect transistor respectively. The effect transistor M5 and the sixth field effect transistor M6 are replaced. The field effect tube can not only play the role of resistive voltage divider, but also reduce the starting current of the circuit and reduce the static power consumption of the circuit when it is working normally. Other structures of the circuit and the principle of temperature compensation are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com