2D linear graphics coding anti-fake method
A technology of linear graphics and linear graphics, which is applied in the anti-counterfeiting field of two-dimensional linear graphic coding, can solve the problems of anti-counterfeiting failure, inability to read out information, and increase the difficulty for consumers to read numbers, etc., and achieve good anti-counterfeiting performance and wide application range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
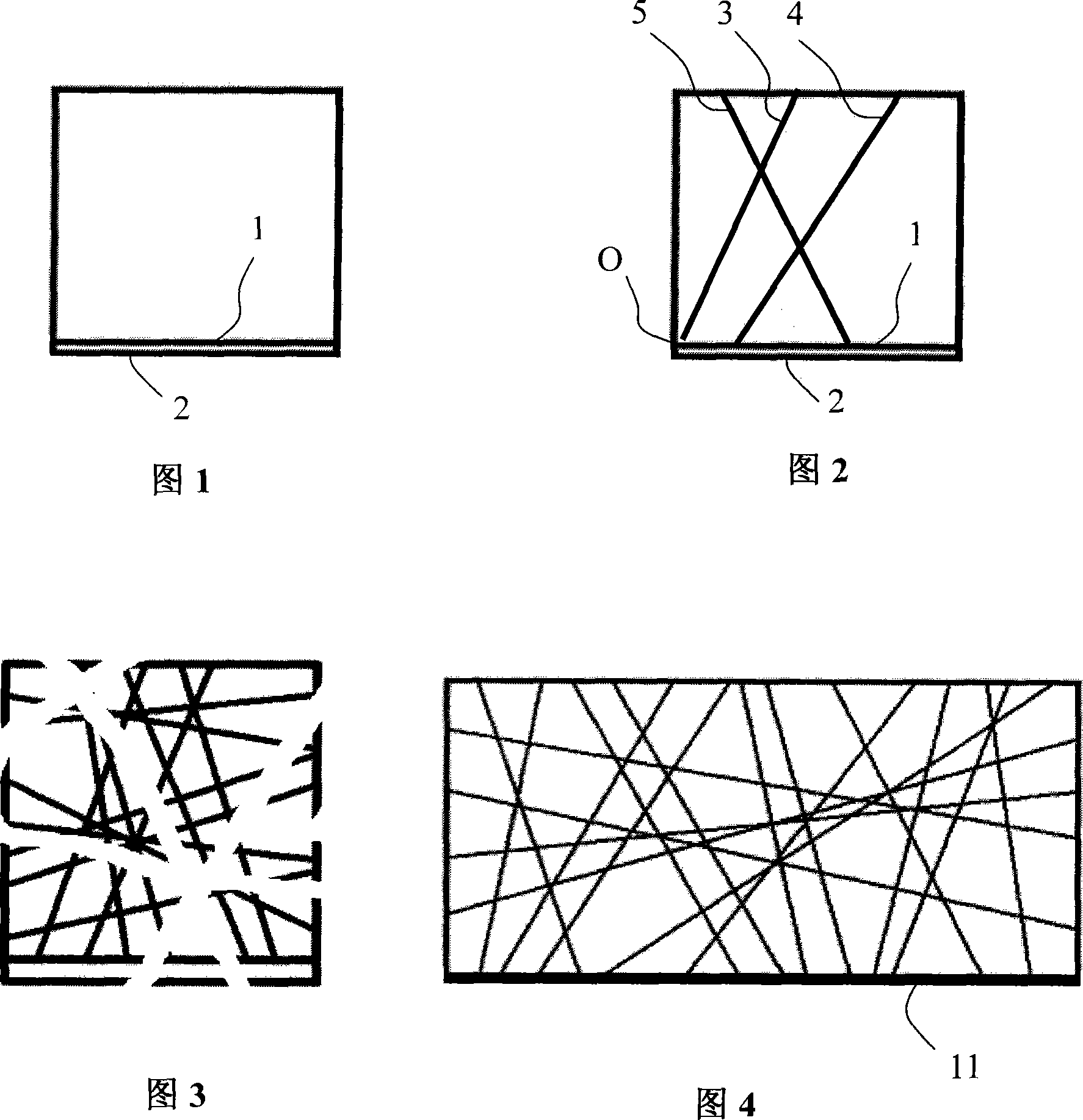
[0037] Definition: the letter a represents the rectangular reference frame, b represents the square reference frame; the letter d represents the angle, and the Arabic numerals represent the angle value between the straight line and the reference line. Each code is composed of the letter d plus a number.
[0038] For the generation of two-dimensional linear graph codes, see Figure 1 and Figure 2:
[0039] Step 1: First, determine the number of codes (each code corresponds to a straight line), usually the range can be from 8 to 20 bits, and this example uses 3-digit codes to illustrate. According to the above definition, the computer randomly generates a set of codes, such as: ad60d50d120, and its three codes are d60, d50, and d120 respectively.
[0040] Step 2: Generate a reference frame according to the code. The first letter of the code ad60d50d120 is a, so the generated reference frame is a square, as shown in Figure 1. The frame is composed of five straight lines, of which...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The code given by the computer is: 1060050120, a total of three codes, each code is composed of three numbers, the first number 1 of the code represents the square reference frame; the first code 060 represents the distance between the first coded straight line and the reference side The included angle is 60°; the second code 050 represents that the angle between the second coding line and the reference side is 50°; the third code 120 represents that the angle between the third coding line and the reference side is 120°. The process of forming, printing and identifying and verifying its pattern code is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0060] The code given by the computer is: 1060105021201, a total of three codes, each code is composed of four numbers, the first number 1 of the code represents the square reference frame; the first code is 0601, and the first three digits "060" represent The angle between the first coded straight line and the reference side is 60°, and the last number "1" means that the ratio of the width of the coded straight line to the straight line width of the reference border is 1; the second code is 0502, and the first three digits represent the second The angle between the coding straight line and the reference side is 50°, and the last number represents that the ratio of the coding straight line width to the reference border line width is 2; the third code is 1201, and the first three digits represent the third coding straight line and the reference frame The included angle of the side is 120°, and the last number represents that the ratio of the width of the coding line to the line ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com