A process for large-scale production of CdTe/CdS thin film solar cells, without the use of CdCl2
A solar cell, large-scale technology, applied in the field of solar cells, which can solve the problems of low evaporation temperature, uneven deposition, danger, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
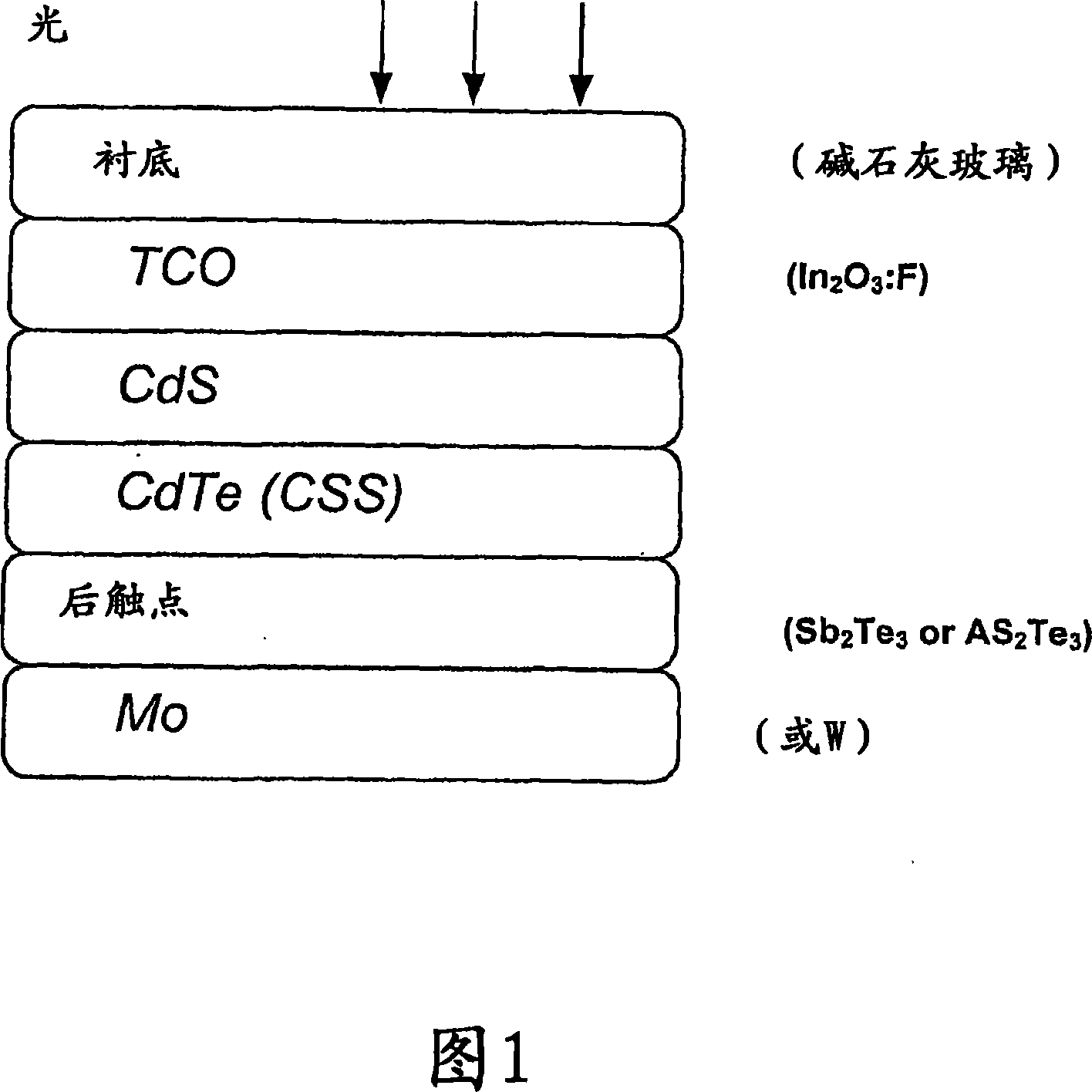
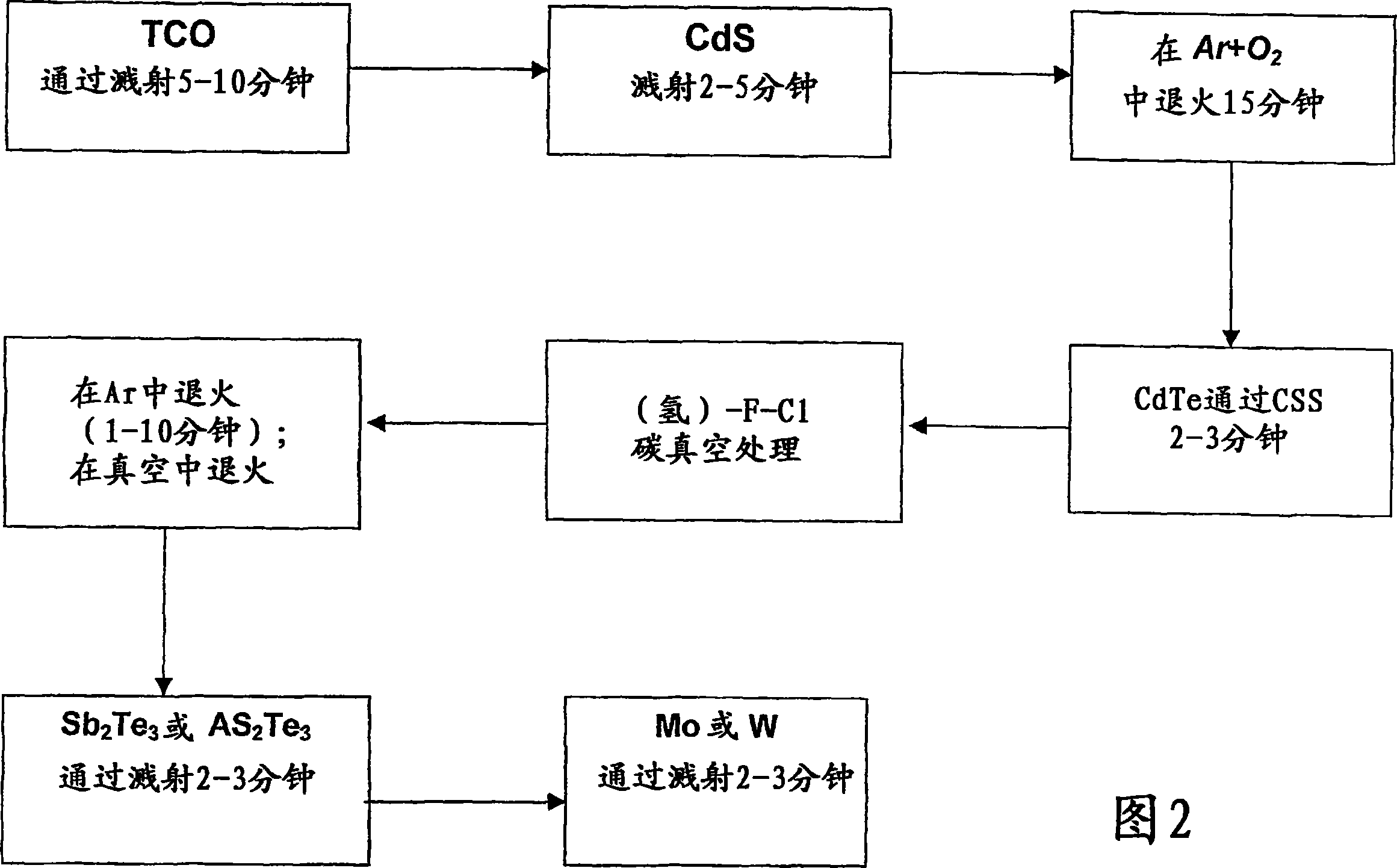
[0029] Referring to the figure, a CdTe / CdS solar cell produced by the method according to the present invention comprises five layers sequentially deposited on a transparent base layer or substrate, consisting of a 300-500 nm thick transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer, on top of the TCO layer Deposited 80-200 nm thick CdS layer, 4-12 μm thick CdTe layer on top of the CdS layer and at least 100 nm thick SB 2 Te 3 layer and a 100nm thick Mo layer to form the rear contact layer. In particular, the transparent base substrate is composed of soda-lime glass, and the transparent conductive oxide doped with fluorine (In 2 o 3 :F).
[0030] The TCO layer consists of fluorine-doped In during growth 2 o 3 composition. Different from ITO, In 2 o 3 The target does not form any needles. By introducing a gaseous fluoroalkyl compound, such as CHF, into the sputtering chamber 3 A small amount of fluorine and a mixture with an inert gas, such as Ar+H 2 A small amount of H in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com