Data relocation in a memory system
A memory system and memory technology, applied in the field of memory systems, can solve problems such as performance changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
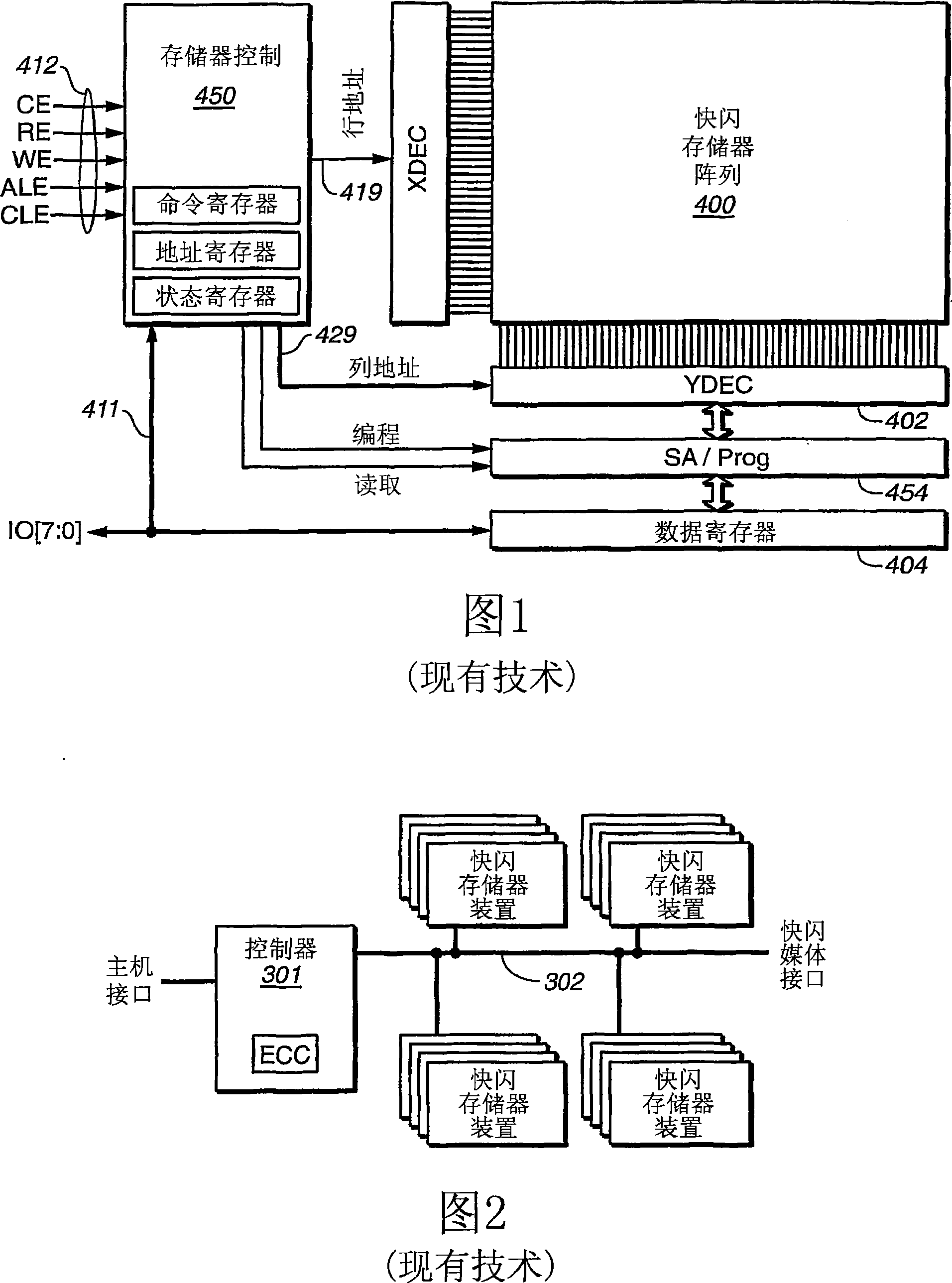
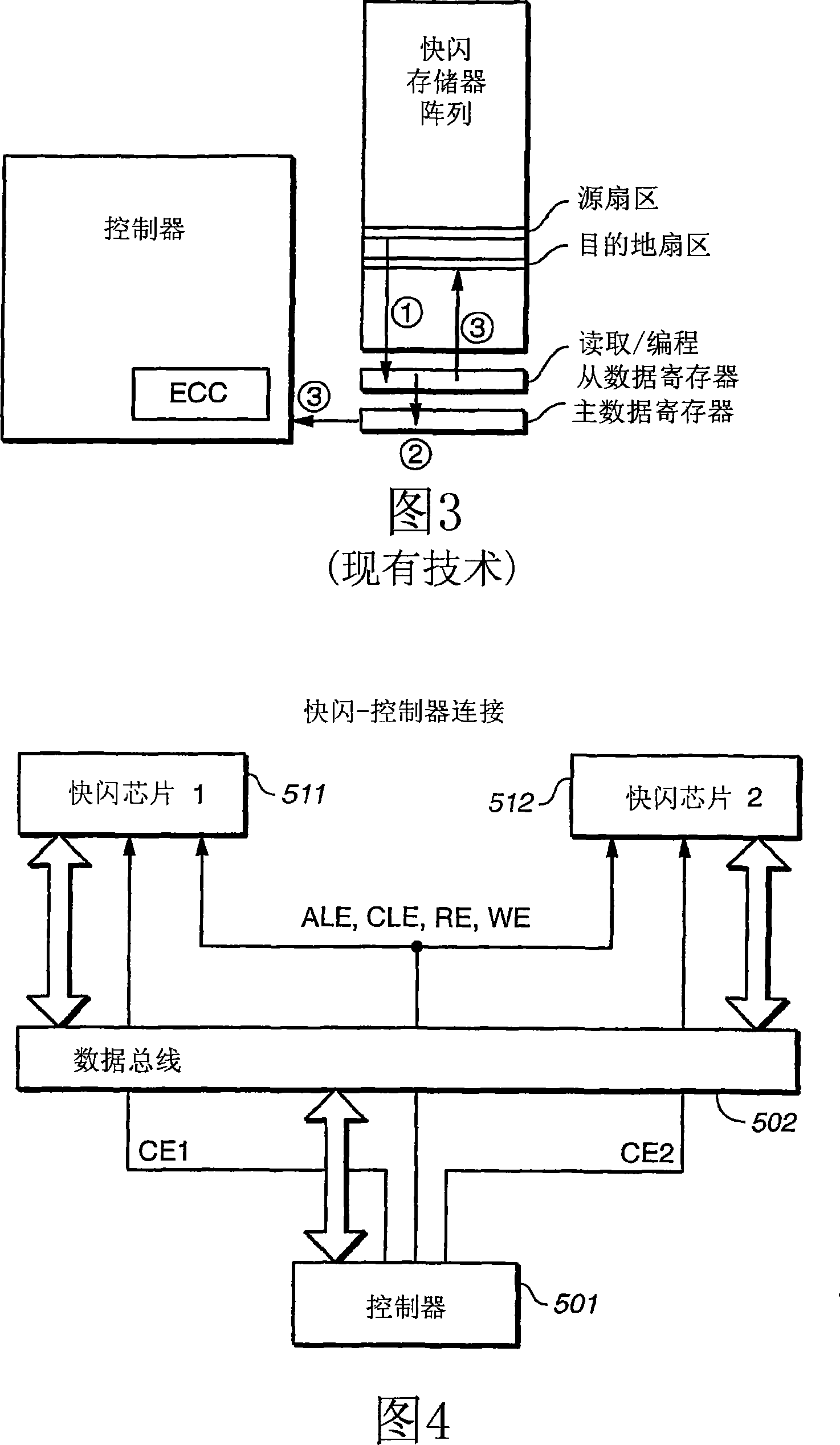
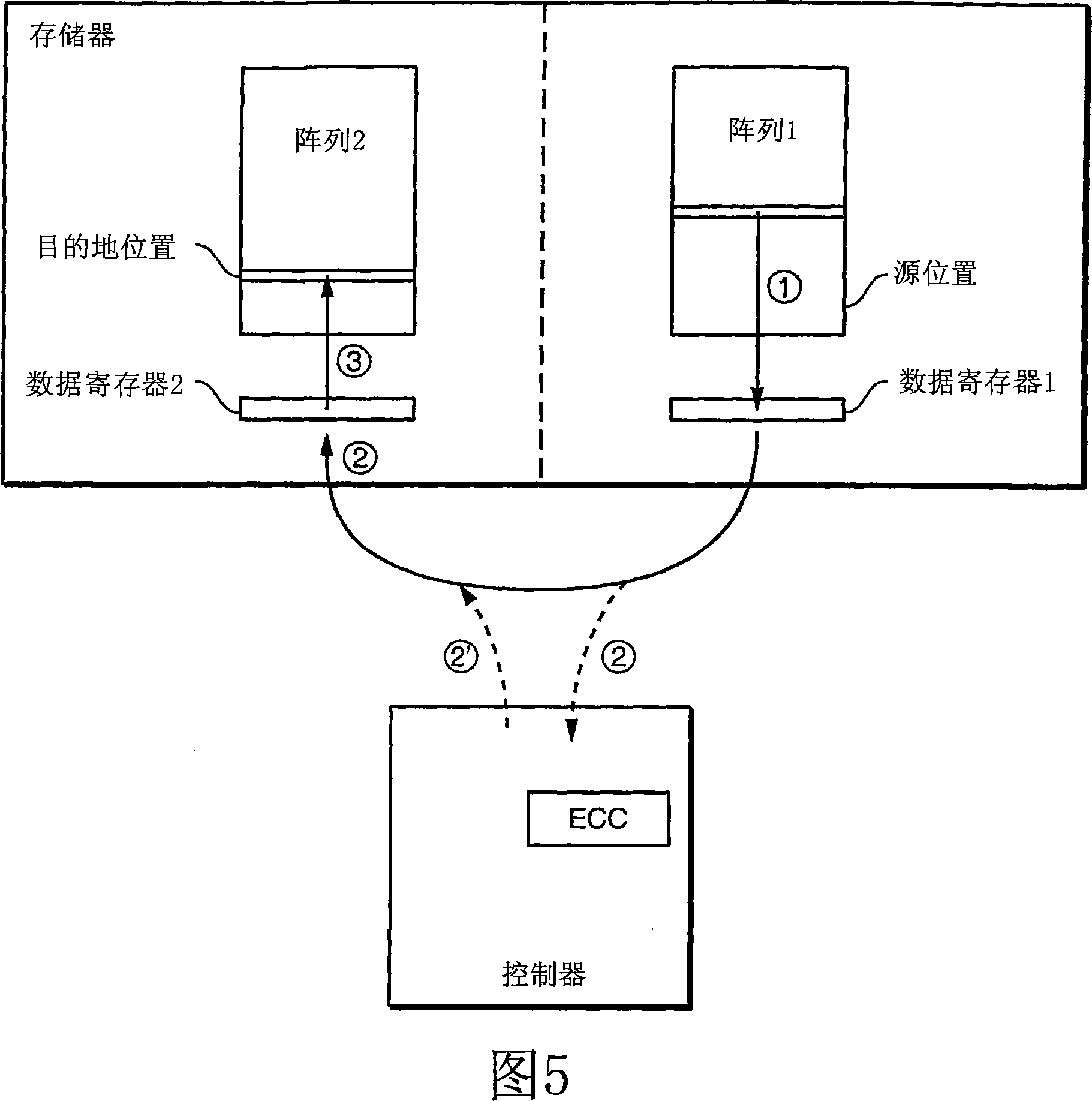
[0050] In a first aspect, the invention generalizes a copy operation that allows data to be copied between two memory blocks, which may be on two different chips, on two planes on the same chip, or on on the same plane on the same chip. Thus, the methods described herein provide a single data copy mechanism that allows data to be copied between any two locations in a flash memory or other memory array. The performance of this more general replication is the same as that of on-chip replication commonly used in the prior art. Removing restrictions on data locality results in improved algorithmic operation that reduces the frequency of data replication.
[0051] In general, the methods described here allow data in a memory bank to be copied to another memory bank that can:
[0052] 1) In different chips;
[0053] 2) in different planes of the same chip; or
[0054] 3) In the same plane of the same chip.
[0055] To support this functionality, the control logic and data paths...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com