A management method for network data transmission of zero copy buffer queue
A management method and network data technology, which is applied in the field of network data transmission in which zero-copy data buffer queues are managed through separate handles, can solve problems such as the inability to realize simultaneous access to data buffer queues, and achieve improved flexibility and efficiency, flexible and efficient management , Improve the effect of timeliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
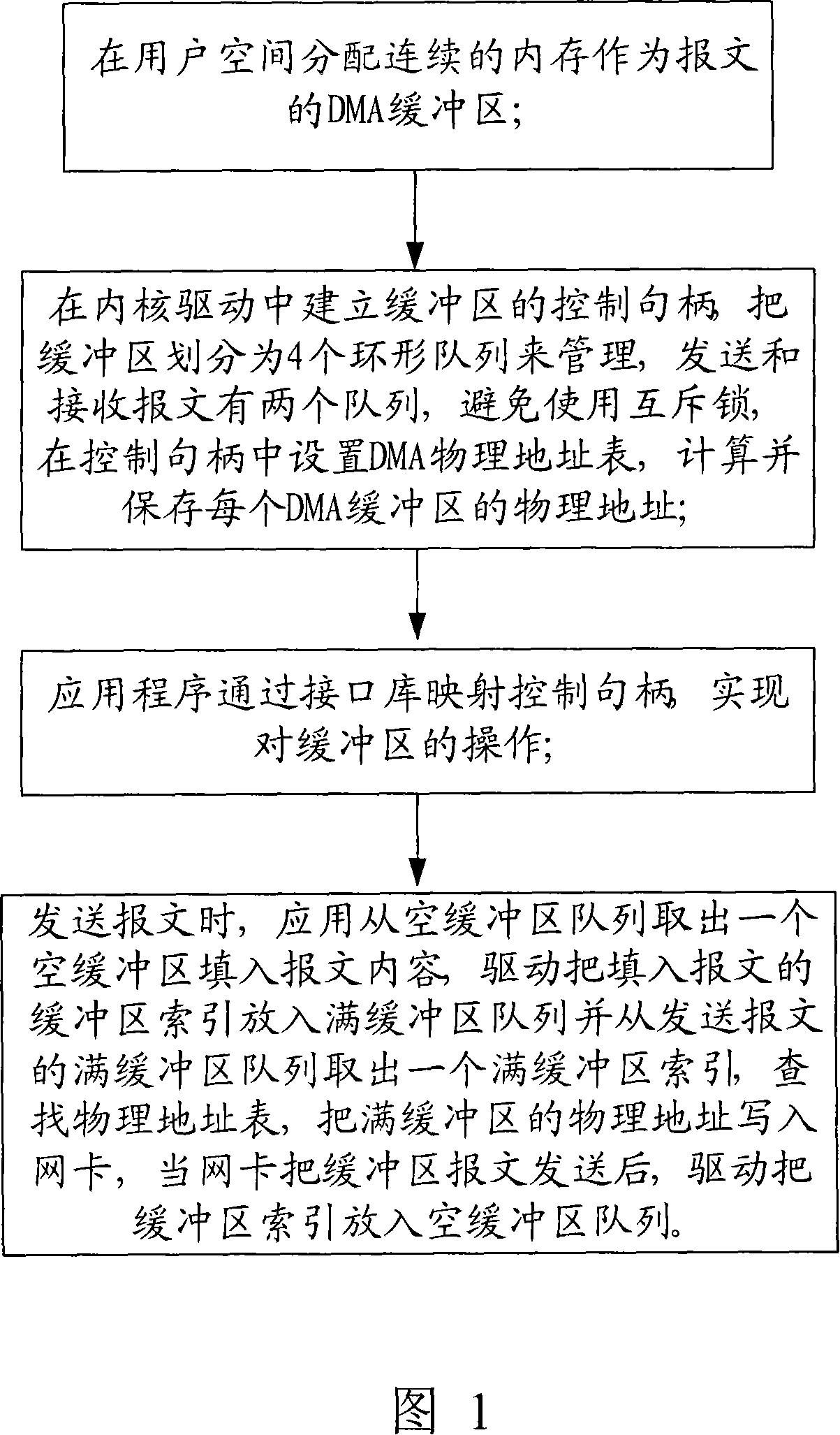
[0020] Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the operation process of the present invention, and Fig. 6 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the control handle of the present invention. As shown in Figure 1 and Figure 6, the present invention includes the following steps:
[0021] A. Allocate continuous memory in user space as the DMA buffer of the message;
[0022] In this step, check the maximum shared memory value initially set by the system. If the requested memory value is greater than the system default shared memory value, modify the system default memory value. Allocate shared memory according to the required memory size, and after successfully returning the starting address of the memory, you can save data or lock the memory. Return this memory to the system when you are done using it.
[0023] B. Establish the control handle of the buffer in the kernel driver, divide the buffer into 4 ring queues for management, there are two queues for sending and receiving messa...
Embodiment 2
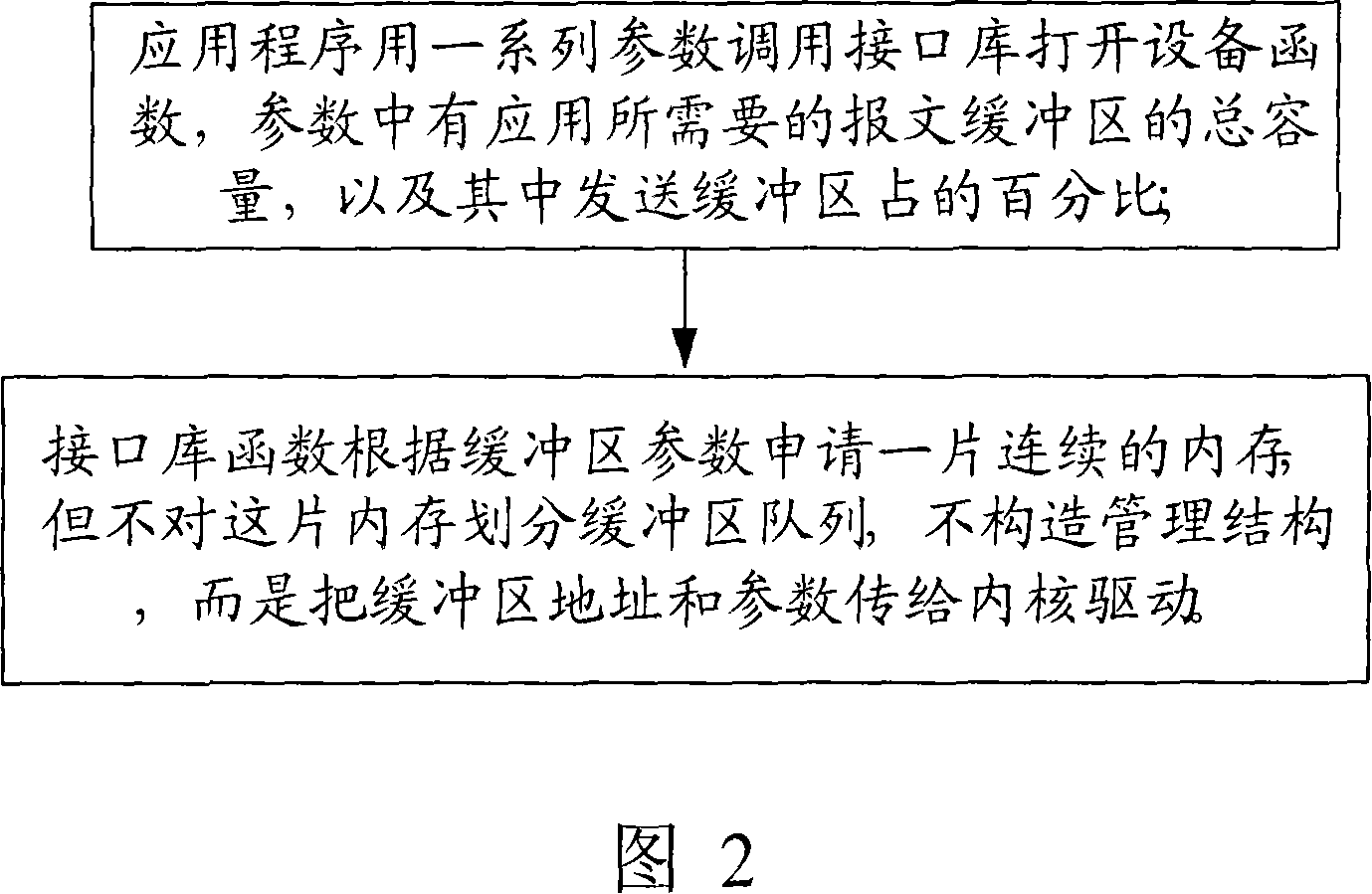
[0028] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the specific operation process of the operation step A is shown in Figure 2, which is:
[0029] A1. The application program uses a series of parameters to call the interface library to open the device function. The parameters include the total capacity of the message buffer required by the application and the percentage of the sending buffer.
[0030] A2. The interface library function applies for a piece of continuous memory according to the buffer parameters, but does not divide the memory into a buffer queue, does not construct a management structure, but passes the buffer address and parameters to the kernel driver.
Embodiment 3
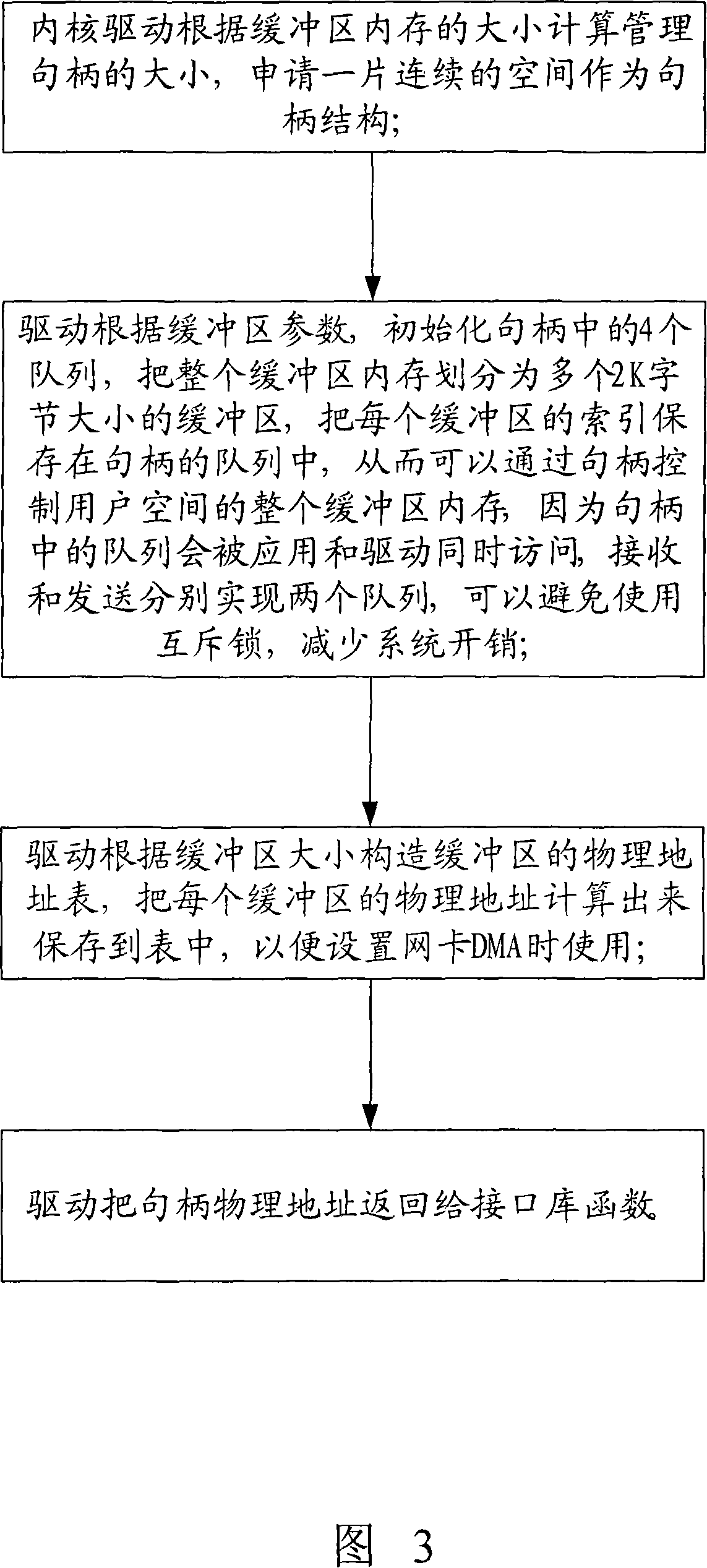
[0032] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that the specific operation process of the operation step B is as shown in Figure 3, which is:
[0033] B1. The kernel driver calculates the size of the management handle according to the size of the buffer memory, and applies for a continuous space as the handle structure.
[0034]B2. The driver initializes the 4 queues in the handle according to the buffer parameters, divides the entire buffer memory into multiple 2K byte buffers, and saves the index of each buffer in the queue of the handle, so that it can be passed The handle controls the entire buffer memory in user space. Because the queue in the handle will be accessed by the application and the driver at the same time, two queues are implemented for receiving and sending, which can avoid the use of mutexes and reduce system overhead.
[0035] B3. The driver constructs the physical address table of the buffer according to the size of the buffer, and calc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com