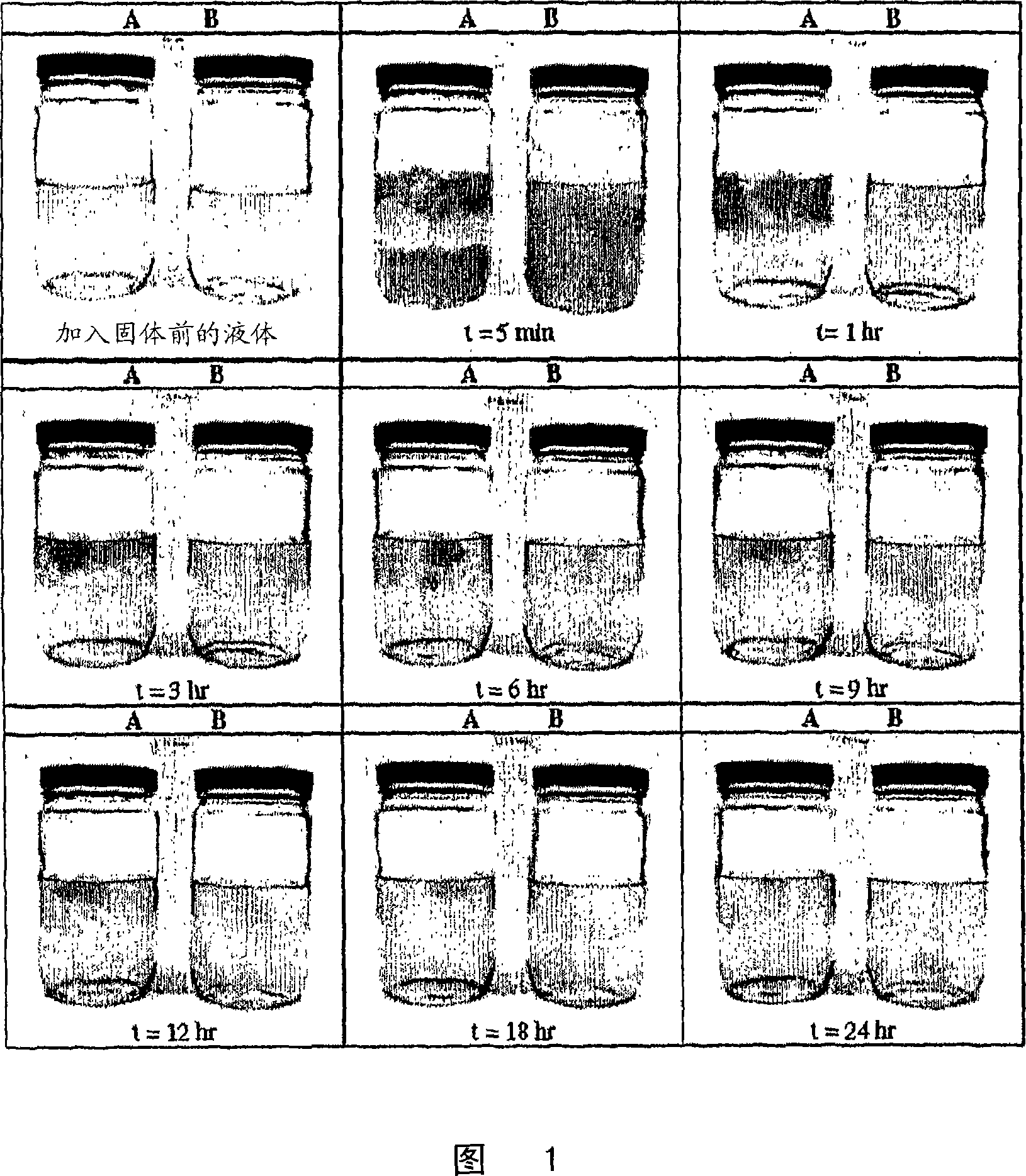
Method for compounding polymer pellets with functional additives
A technology of mixtures and additives, applied in the field of mixtures of cellulose and functional additives, can solve problems such as cellulose ester form destruction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Impregnation of plasticizers and stabilizers in pellets
[0083] Cellulose triacetate ("CTA", CA-436-80 from Eastman Chemical Company) (300 g) was mixed with acetone (300 g) and diethyl phthalate (DEP) (150 g) containing 1% t-butylphenol Mix in a 32 oz glass bottle. The bottle was rotated for 16 hours during which time all the liquid had been drawn into the cellulose triacetate pellets and the pellets had swollen and filled the bottle. Pellets were poured into shallow pans and allowed to air dry at room temperature for 78 hours. Weigh dry pellets to 446g. This gave pellets with a theoretical plasticizer content of 32.8% plasticizer. The dry pellets were free flowing and similar in shape to the original pellets, but slightly larger in size and slightly more irregular in shape. Plasticizer analysis of the pellets yielded 32.36% DEP and 0.17% tert-butylphenol. This indicates that both plasticizer and stabilizer have been impregnated into the pellets.
Embodiment 2
[0085] Impregnation of plasticizers in pellets
[0086] Cellulose triacetate (CA-436-80 from Eastman Chemical Company) (440 g) was mixed with acetone (450 g) and triphenyl phosphate (60 g) in a 32 oz glass bottle. The bottle was rotated for 24 hours during which time all the liquid had been drawn into the cellulose triacetate pellets and the pellets had swollen and filled the bottle. The pellets were then poured into shallow pans and air dried at room temperature followed by drying in a forced air oven at 60°C for 6 hours. The dry pellets were weighed at 506 g, which is consistent with the target 12% plasticizer content. The dry pellets were free flowing and similar in shape to the original pellets, but slightly larger in size and slightly more irregular in shape.
Embodiment 3
[0088] Impregnation of UV stabilizers in pellets
[0089] Cellulose triacetate (CA-436-80, from Eastman Chemical Company) (200 g) was mixed with 200 g of acetone and 1.0 g of Tinuvin7 292 (UV stabilizer, obtained from Ciba) and 1.0 g of Tinuvin7 1130 (UV absorber, obtained from Ciba ) in a 32 oz glass jar. The bottle was rotated for 15 hours during which time all the liquid was absorbed into the cellulose triacetate pellets and the pellets increased in size significantly. The free-flowing pellets were poured into shallow pans and allowed to air dry at room temperature for 78 hours.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com