Rare earth alloy
A rare earth alloy and alloy technology, which is applied in the field of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet materials, can solve the problems of reducing the coercive force of magnets and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
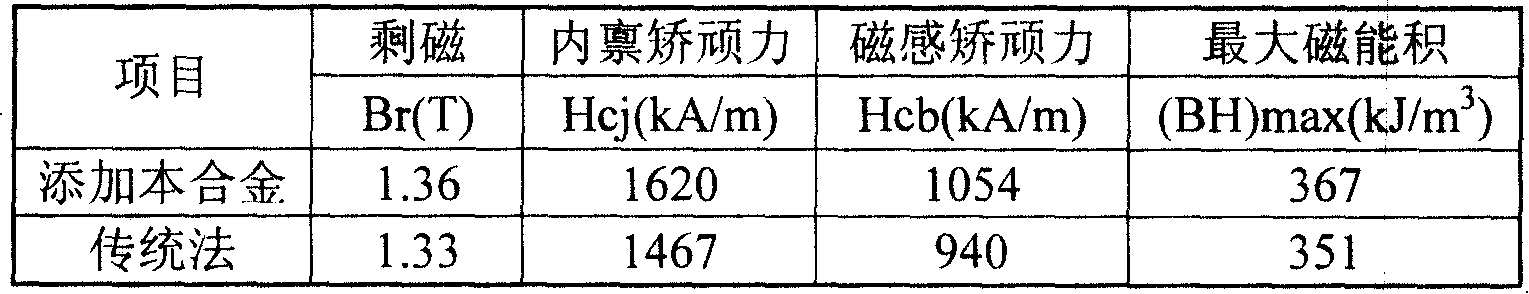
[0029] The R1R2M alloy in this embodiment is a NdDyFe alloy, and its preparation method is as follows: a graphite crucible is used as a reactor and an iron rod is used as a cathode to obtain it by electrolysis. The electrolyte is 50wt% neodymium fluoride, 30wt% dysprosium fluoride, 20wt% lithium fluoride, direct current electrolysis, average current intensity 2200A, cathode current density 12A / cm 2 , Electrolysis temperature maintained at 1000 ~ 1020 ℃. Add dysprosium oxide Dy with a purity of 99.5% during electrolysis 2 O 3 1.8 kg and 99.5% purity neodymium oxide Nd 2 O 3 3 kilograms, make 5.3 kilograms of NdDyFe alloys. Its main components, oxygen content and other impurities are shown in Table 1-1.
[0030]The alloy prepared in this example is added to the main component of NdFeB, and the sintered NdFeB magnet is prepared by smelting strip→hydrogen crushing and jet milling→magnetic field forming→vacuum sintering process, and the chemical composition and Magnet perform...
Embodiment 2
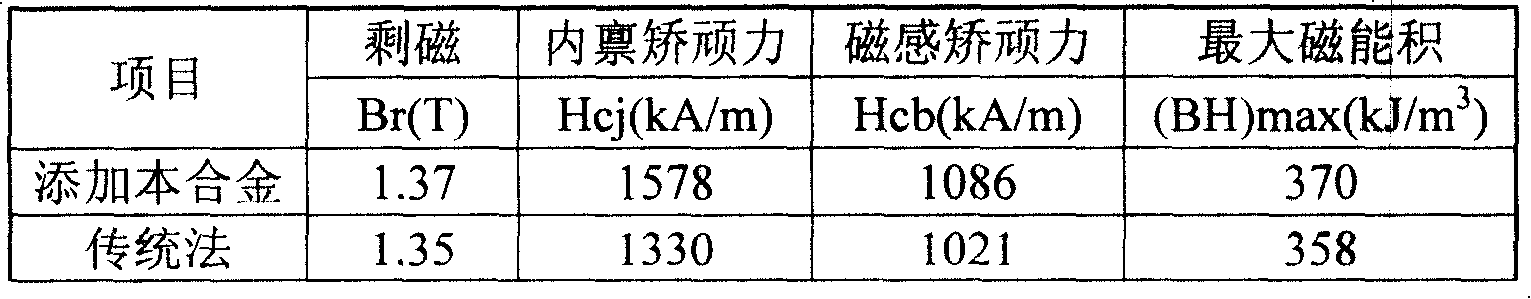
[0038] The R1R2M additive alloy in this embodiment is a PrDyFe alloy, and its alloy preparation method is: using a graphite crucible as a reactor and an iron rod as a cathode to obtain it by electrolysis. The electrolyte is praseodymium fluoride 78wt%, dysprosium fluoride 12wt%, lithium fluoride 10wt%, direct current electrolysis, average current intensity 2400A, cathode current density 8A / cm 2 , Electrolysis temperature maintained at 1000 ~ 1020 ℃. Add dysprosium oxide Dy with a purity of 99.5% during electrolysis 2 O 3 0.8 kg and 99.5% purity of praseodymium oxide Pr 6 O 11 3 kilograms, make 4 kilograms of PrDyFe alloys. Its main components, oxygen content and other impurities are shown in Table 2-1. This example was compared with the sintered NdFeB magnet prepared by the corresponding conventional method, including the standard deviation of the chemical composition and the performance of the magnet. The results are shown in Table 2-2 and 2-3 respectively.
[0039] Tab...
Embodiment 3
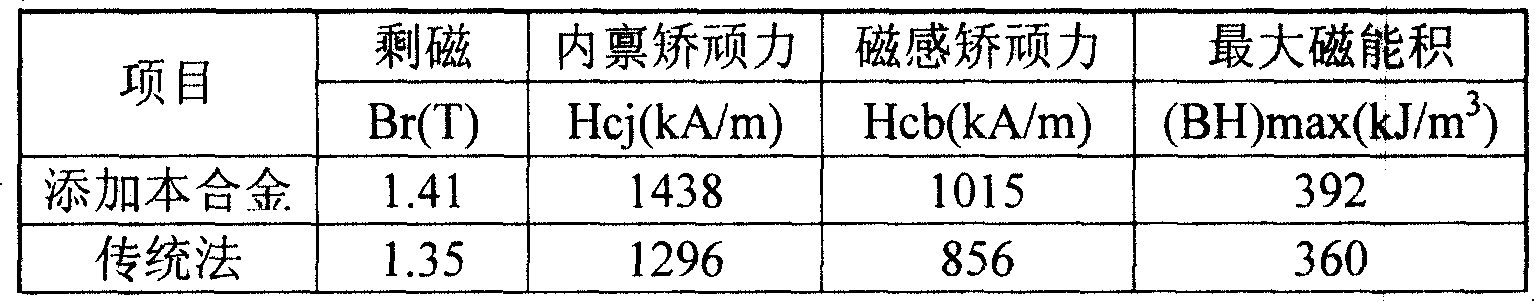
[0046] The R1R2M additive alloy in this embodiment is a PrNdDy alloy, which is prepared by electrolysis using a graphite crucible as a reactor and a tungsten rod as a cathode. The electrolyte is praseodymium neodymium fluoride 37wt%, dysprosium fluoride 53wt%, lithium fluoride 10wt%, direct current electrolysis, average current intensity 2400A, cathode current density 13A / cm 2 , Electrolysis temperature maintained at 1000 ~ 1020 ℃. Each furnace is electrolyzed for about 1 hour, and dysprosium oxide Dy with a purity of 99.5% is added during the electrolysis process 2 O 3 2 kg, 1.2 kg of praseodymium neodymium oxide with a purity of 99.5%, and 3 kg of PrNdDy alloy. Its main components, oxygen content and other impurities are shown in Table 3-1. This example was compared with the sintered NdFeB magnet prepared by the corresponding conventional method, including the standard deviation of the chemical composition and the magnet performance. The results are shown in Table 3-2 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com