Absolute encoder
An absolute encoder and absolute encoding technology, applied in the field of absolute encoders, can solve the problems of increased error possibility, excitation magnetic flux change, sensor size increase, etc., to eliminate errors in reading absolute codes, correct temperature characteristics, reduce small size effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
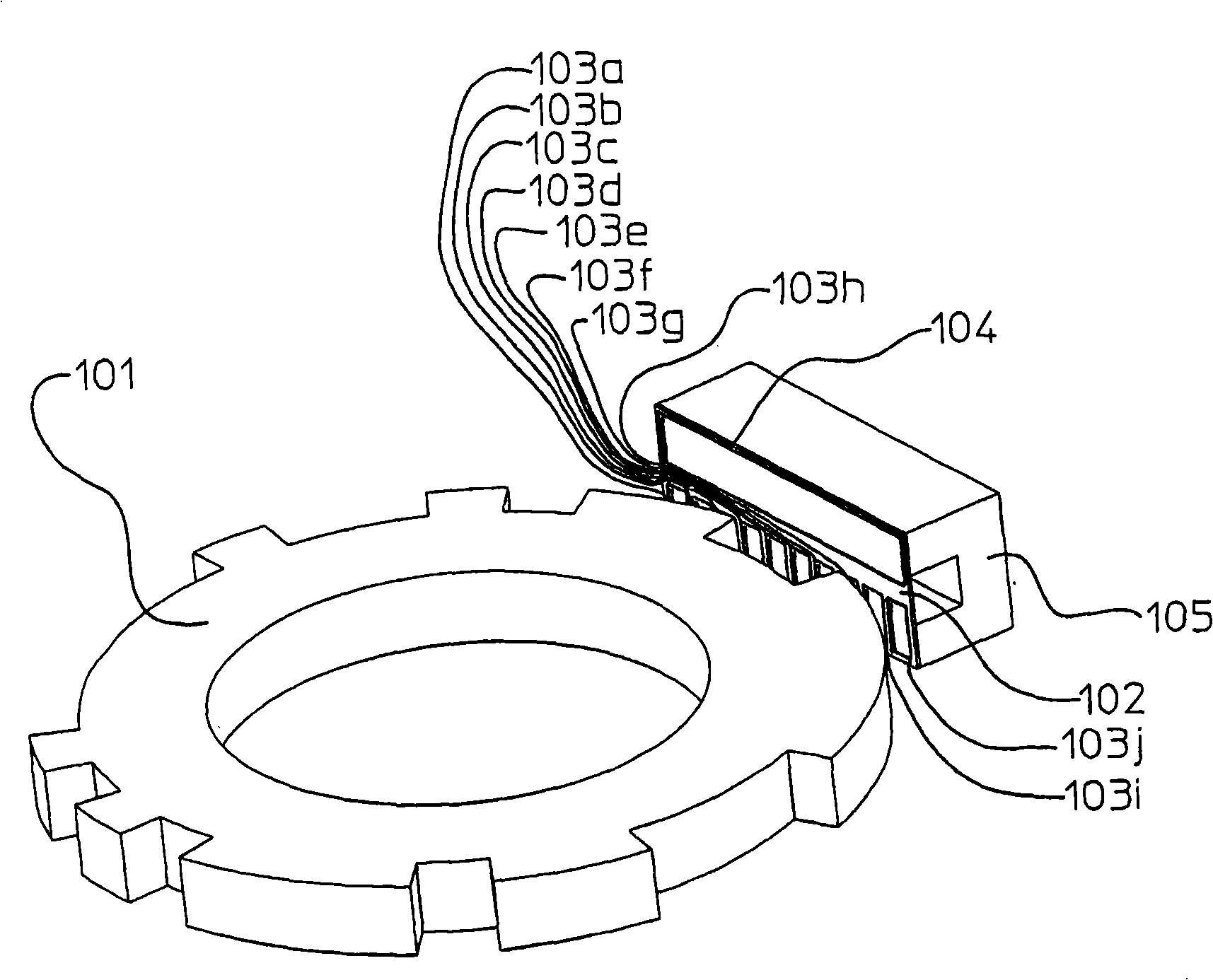
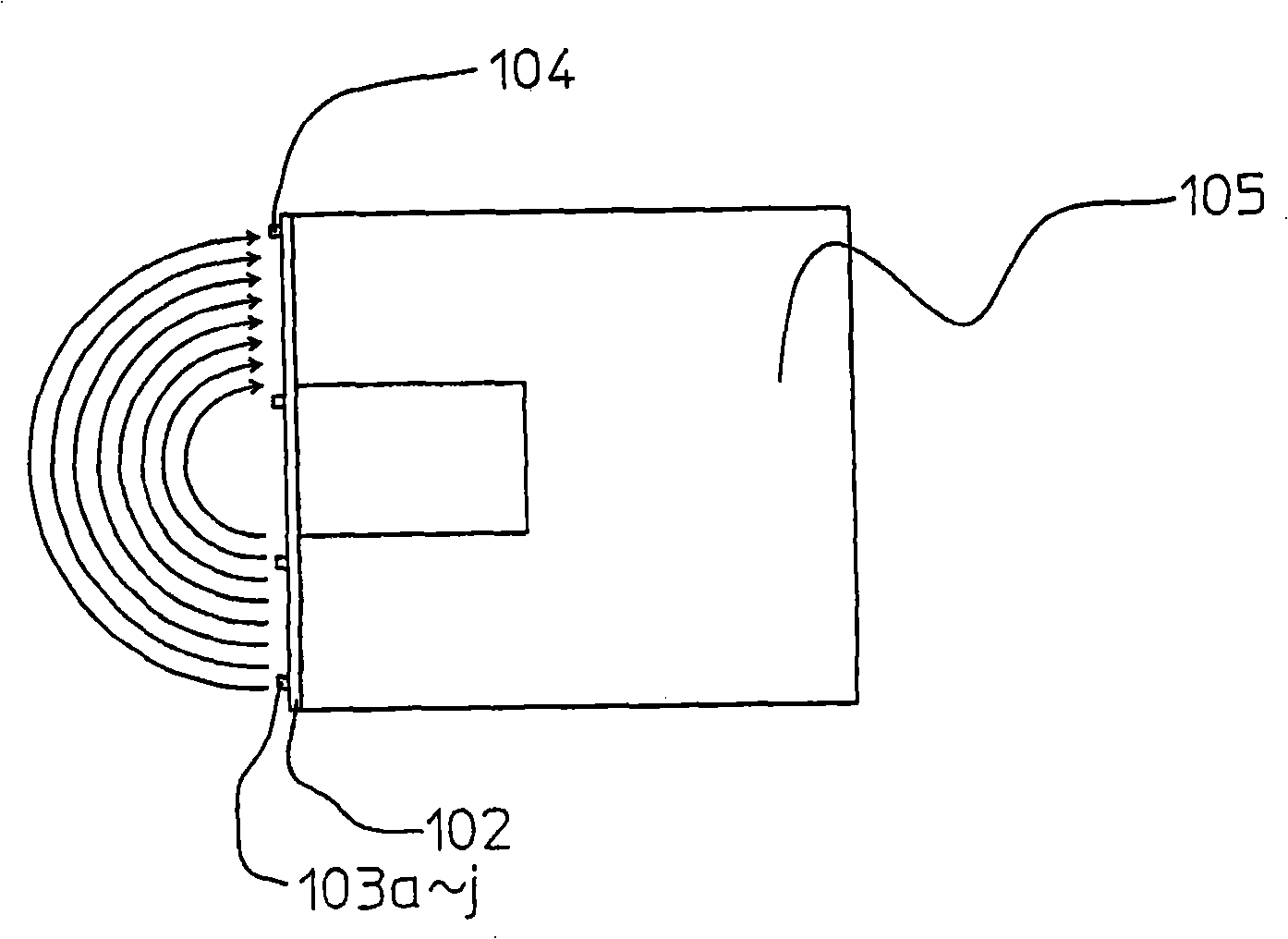
[0021] Next, Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. figure 1It is a perspective view showing an example of the absolute code detection unit of the absolute encoder in this embodiment. The binary cyclic random number sequence encoding disk 101 has an unillustrated shaft fixed thereon so as to be rotatable. Each detection winding 103a-103j made of a conductor pattern, and an excitation winding 104 made of a conductor pattern are arranged on the printed circuit board 102, and the printed circuit board 102 is relatively binary by a predetermined gap amount. The cyclic random number sequence encodes the arrangement on the outer peripheral surface of the disc 101 . A U-shaped field core 105 made of a magnetic member such as a ferrite core is arranged on the rear surface of the printed circuit board 102 . That is, when the U-shaped field core 105 is cut by a plane passing through the rotational axis of the code disk 101 , a U-shaped...
Embodiment approach 2
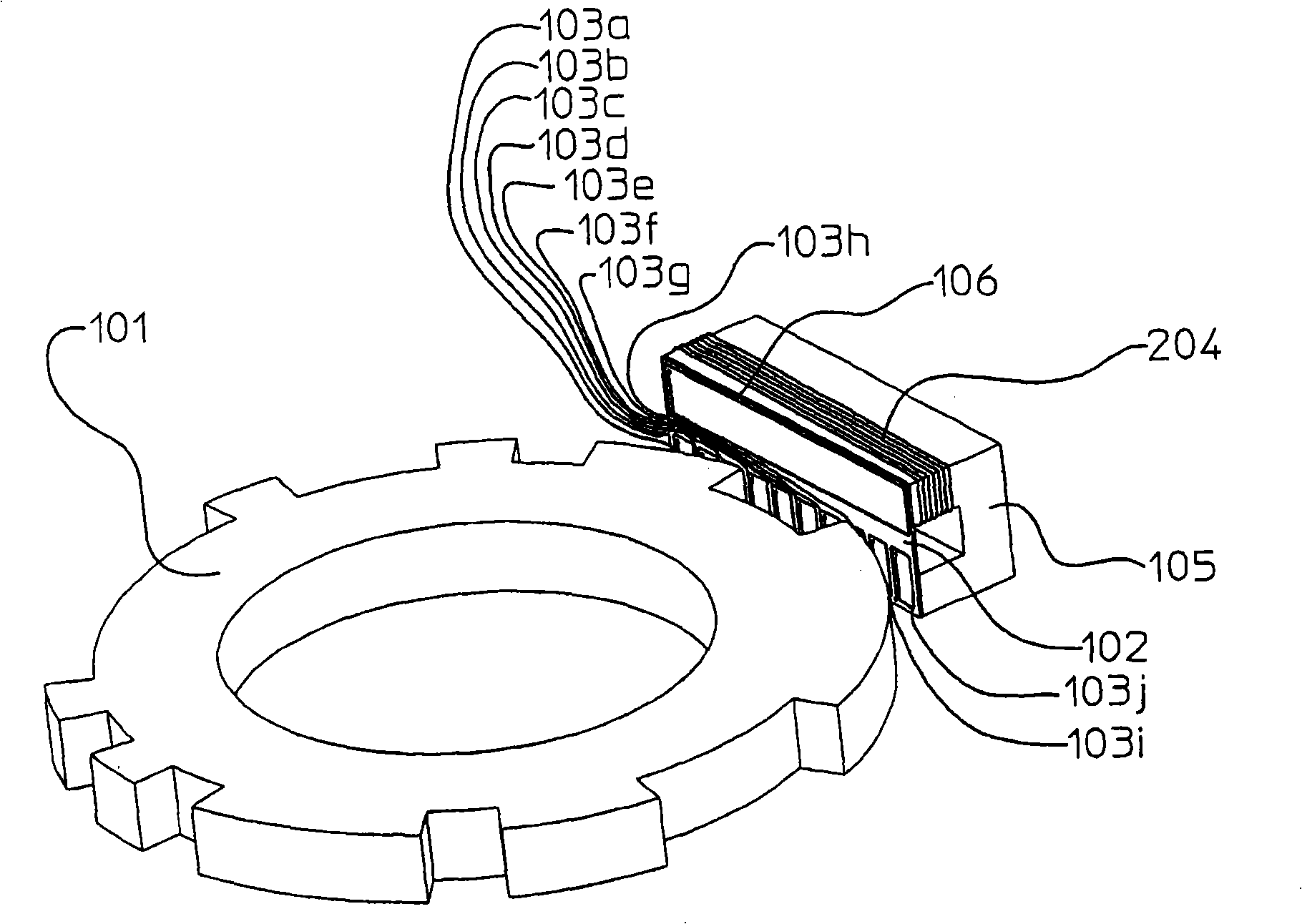
[0025] image 3 to show the figure 1 A perspective view of an example of a detection unit of an absolute encoder in Embodiment 2 in which the absolute encoder is different from that of FIG. exist image 3 in, with figure 1 Like components are assigned the same numbers and marks. However, as with figure 1 One difference is that the excitation winding 204 is directly wound on the excitation core 105 , and the upper winding on the printed circuit board 102 is the excitation flux detection winding 106 . Correspondingly, with figure 2 The same magnetic flux in is formed by the field winding 204 .
[0026] In this way, the excitation magnetic circuit formed is basically the same as figure 1 in the same. Therefore, the role of the field magnetic flux detection winding 106 will be explained here. The excitation winding 204 and the excitation core 105 made of magnetic materials have the following characteristics: when the temperature changes, the winding impedance, magnet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com