Service load balancing method for wireless mesh network
A wireless mesh network and balanced technology, applied in the field of wireless communication, can solve problems such as operation and management difficulties, increasing the difficulty of balancing business loads and optimizing network resource allocation, and loose connection relationships
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
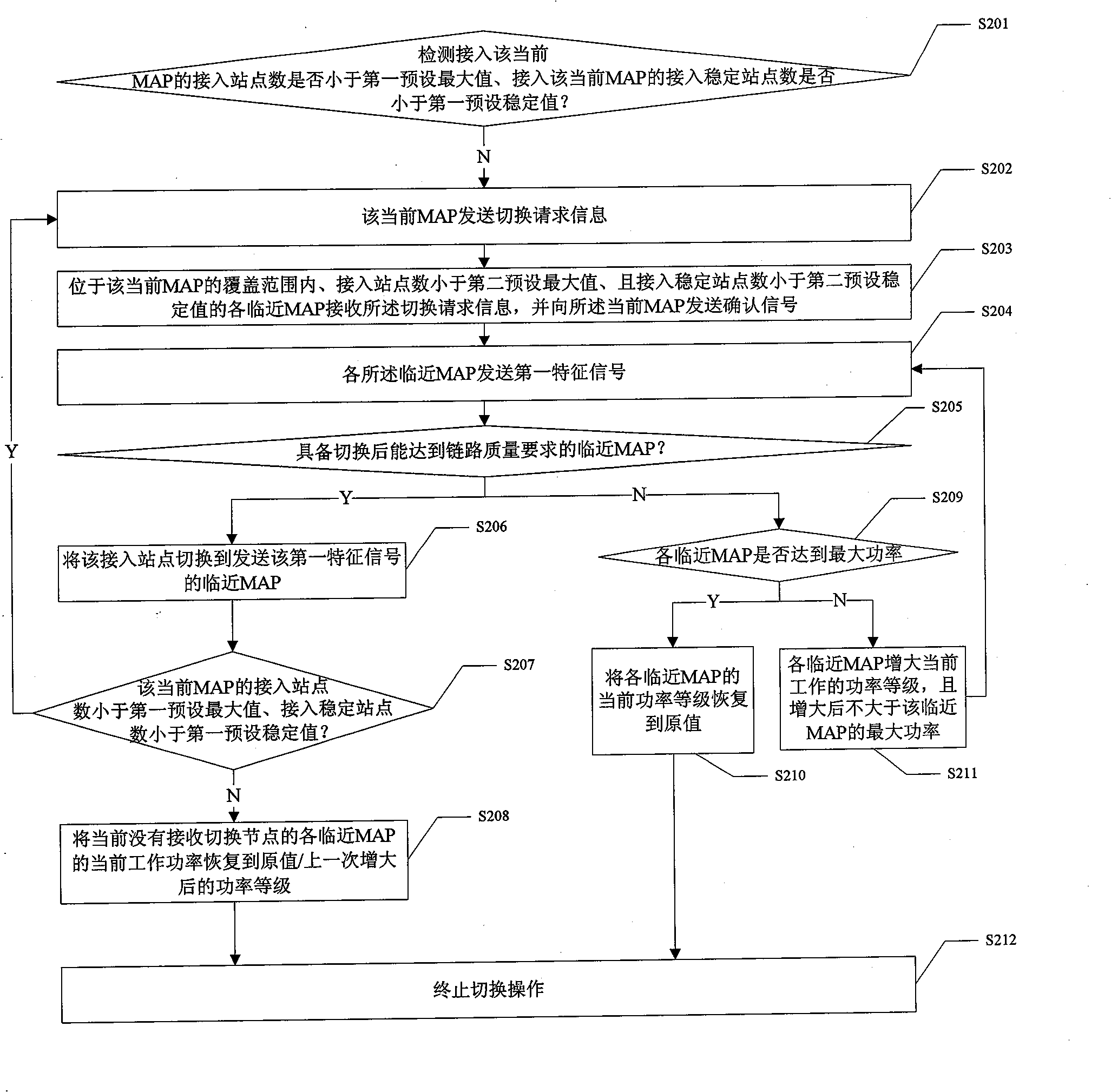
[0030] see figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic flow chart of Embodiment 1 of the method of the present invention. In this embodiment, it is mainly aimed at comparing the signal strength of each adjacent MAP with the signal strength of the MAP when a certain MAP is in a busy state. To determine whether to switch the MAP accessed by the access station for illustration.
[0031] Such as figure 2 As shown, in the present embodiment, the method of the present invention mainly includes steps:
[0032] Step S101: Detect and judge whether the number of access stations connected to the current MAP is less than the first preset maximum value, and whether the number of stable stations connected to the current MAP is smaller than the first preset stable value. If any one of the judgment results is no, Then it is determined that the current MAP is in a saturated state, and enters step S102; wherein, the first preset maximum value is the maximum value of the number of stations that the...
Embodiment 2
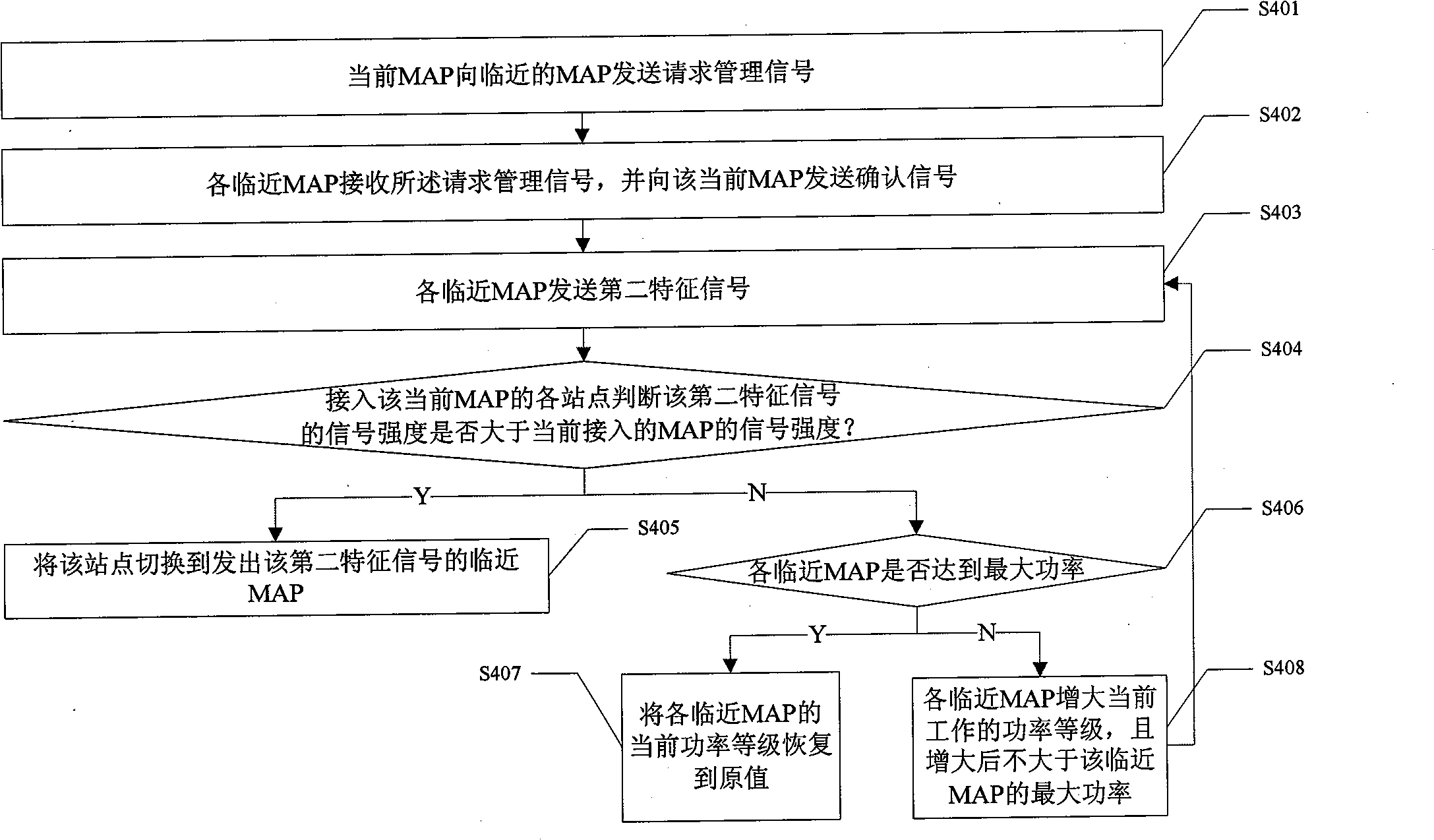
[0051] see image 3 As shown, it is a schematic flow chart of Embodiment 2 of the method of the present invention. In this embodiment, the main difference from Embodiment 1 above is that in this embodiment, it is judged whether the working power of each adjacent MAP satisfies the requirements of the access station. link quality requirements to illustrate.
[0052] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the method of the present invention specifically includes steps:
[0053] Step S201: Detect and judge whether the number of access stations connected to the current MAP is less than the first preset maximum value, whether the number of stable stations connected to the current MAP is smaller than the first preset stable value, if any one of the judgment results is no, Then it is determined that the current MAP is in a saturated state, and enters step S202;
[0054] Step S202: the current MAP sends switching request information, and enters step S203;
[0055] Step S203...
Embodiment 3
[0069] see Figure 4 As shown, it is a schematic flow chart of Embodiment 3 of the method of the present invention. In this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 above is that when a certain MAP is in a busy state, the feature sent by each MAP The signal strength of the signal is compared, and whether the working power of each adjacent MAP meets the link quality requirement of the access node is used to judge whether to perform handover.
[0070] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in the present embodiment, the inventive method mainly comprises steps:
[0071] Step S301: Detect and judge whether the number of access stations connected to the current MAP is less than the first preset maximum value, and whether the number of stable stations connected to the current MAP is smaller than the first preset stable value. If any one of the judgment results is no, Then it is determined that the current MAP is in a saturated state, and enters step S302;
[0072] Step S302: the current...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com