Driving circuit for semiconductor element
A driving circuit and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electronic switches, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve problems such as false detection, gate voltage exceeding, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0040] Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described below based on the drawings.
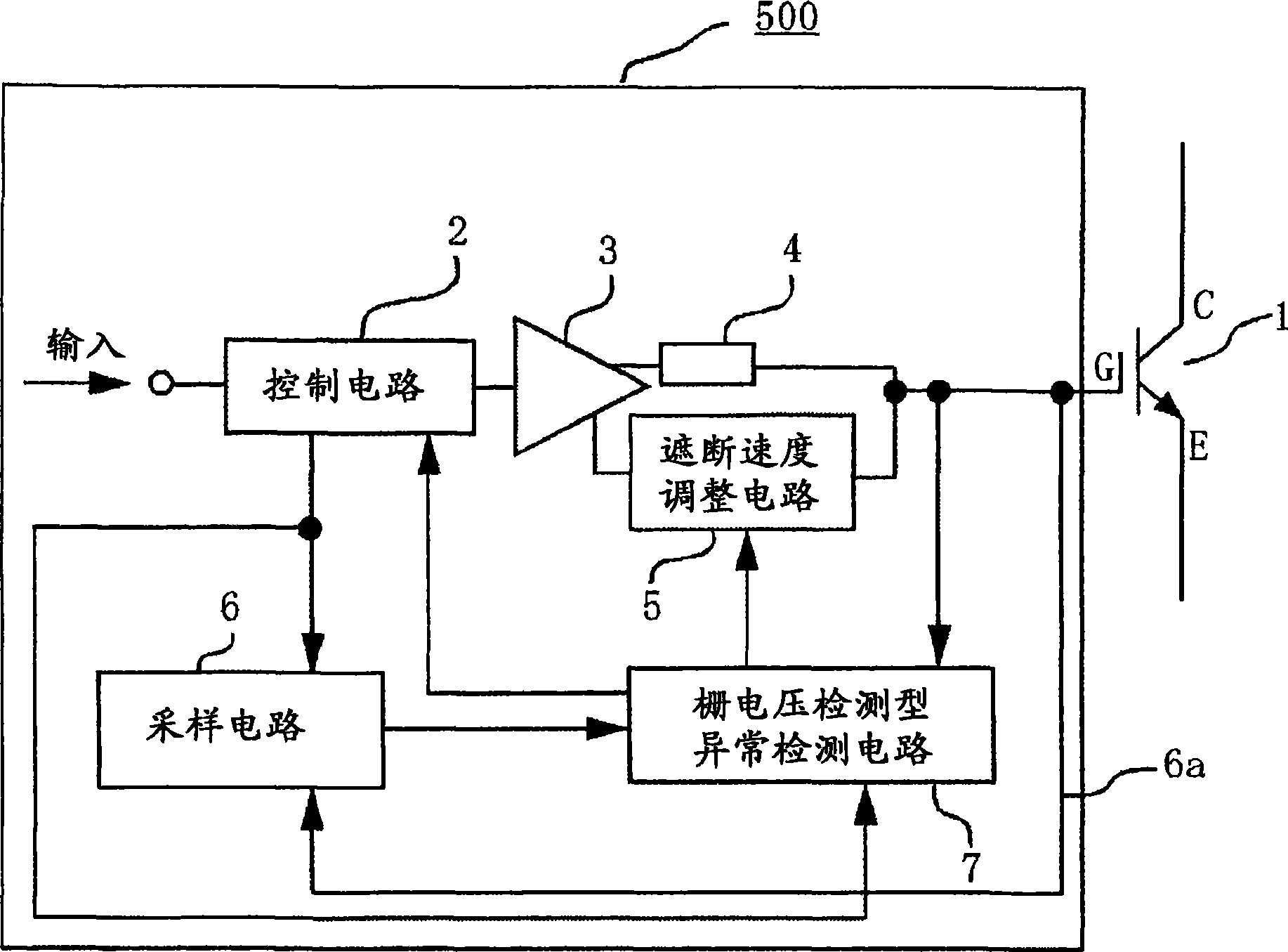
[0041] figure 1 It is a schematic configuration diagram of the driving circuit 500 for the semiconductor element of the first embodiment.
[0042] exist figure 1 Among them, the semiconductor element 1 is, for example, a power semiconductor element IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor). However, the semiconductor element 1 is not limited to an IGBT, and may be a voltage-driven semiconductor element such as a MOSFET, as long as it is necessary for abnormality detection.
[0043] The control circuit 2 outputs a gate command to turn on the IGBT 1 to the buffer 3 when an external turn-on command is input, and outputs a gate command to turn off the IGBT 1 to the buffer 3 when an external turn-off command is input. Buffer 3 drives IGBT 1 according to a gate command output from drive circuit 2 , and is connected to gate resistor 4 and shutoff speed adjustment circuit 5 . The shutoff s...
Embodiment approach 2
[0069] Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described below based on a drive circuit 500 a shown in FIG. 17 .
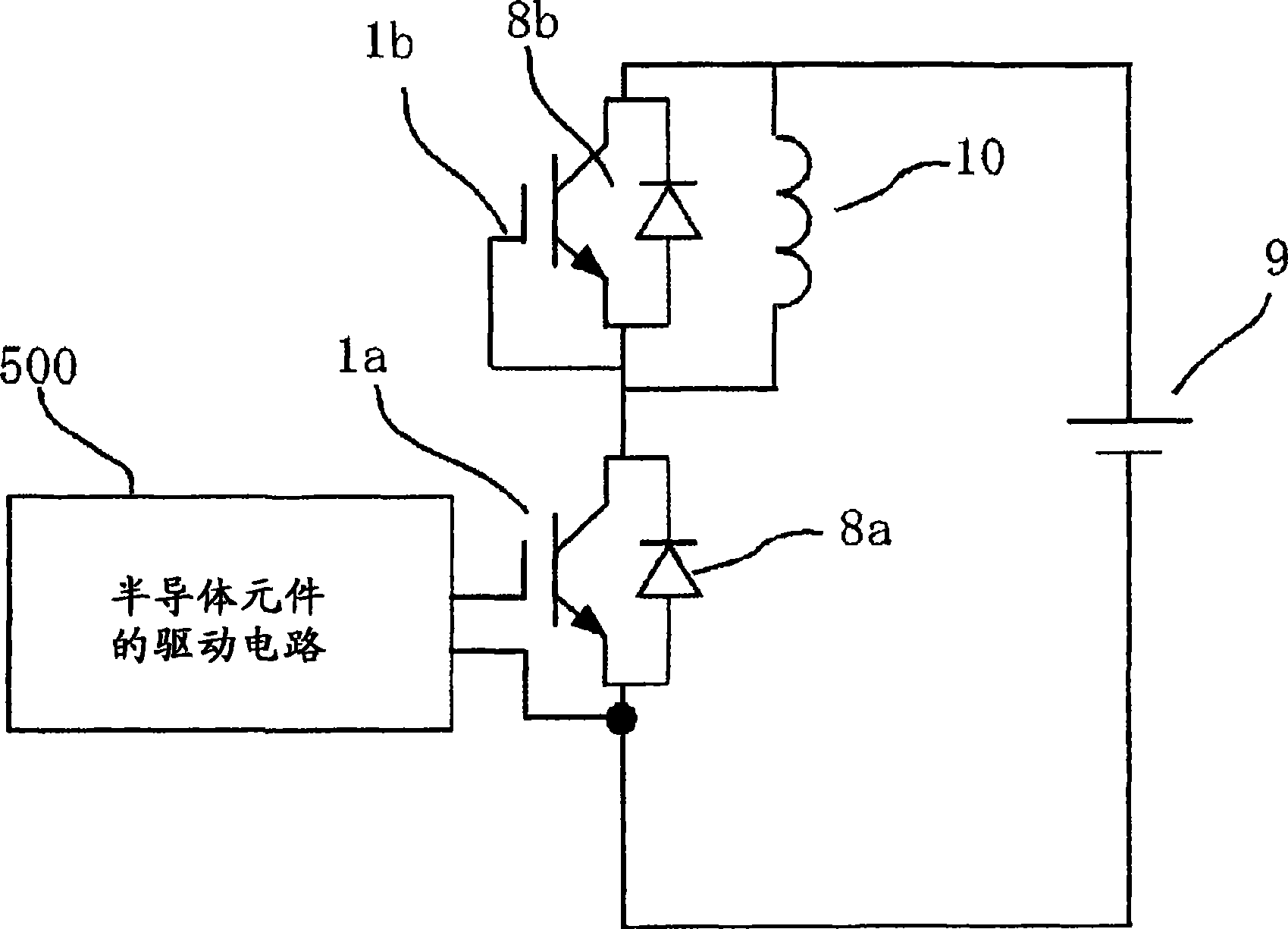
[0070] In Embodiment 1, the gate voltage Vg of the IGBT 1 is directly detected, and the gate voltage detection period T2 and the reference voltage Vgr are changed. In Embodiment 2, as shown in FIG. 17 , in Embodiment 1 figure 1 A gate voltage estimating circuit 8 is added to the configuration of the drive circuit 500 shown. The gate voltage estimating circuit 8 estimates a gate voltage using a control signal from the control circuit 2 and outputs it to the sampling circuit 6 and the gate voltage detection type abnormality detection circuit 7 , and operates in the same manner as in the first embodiment.
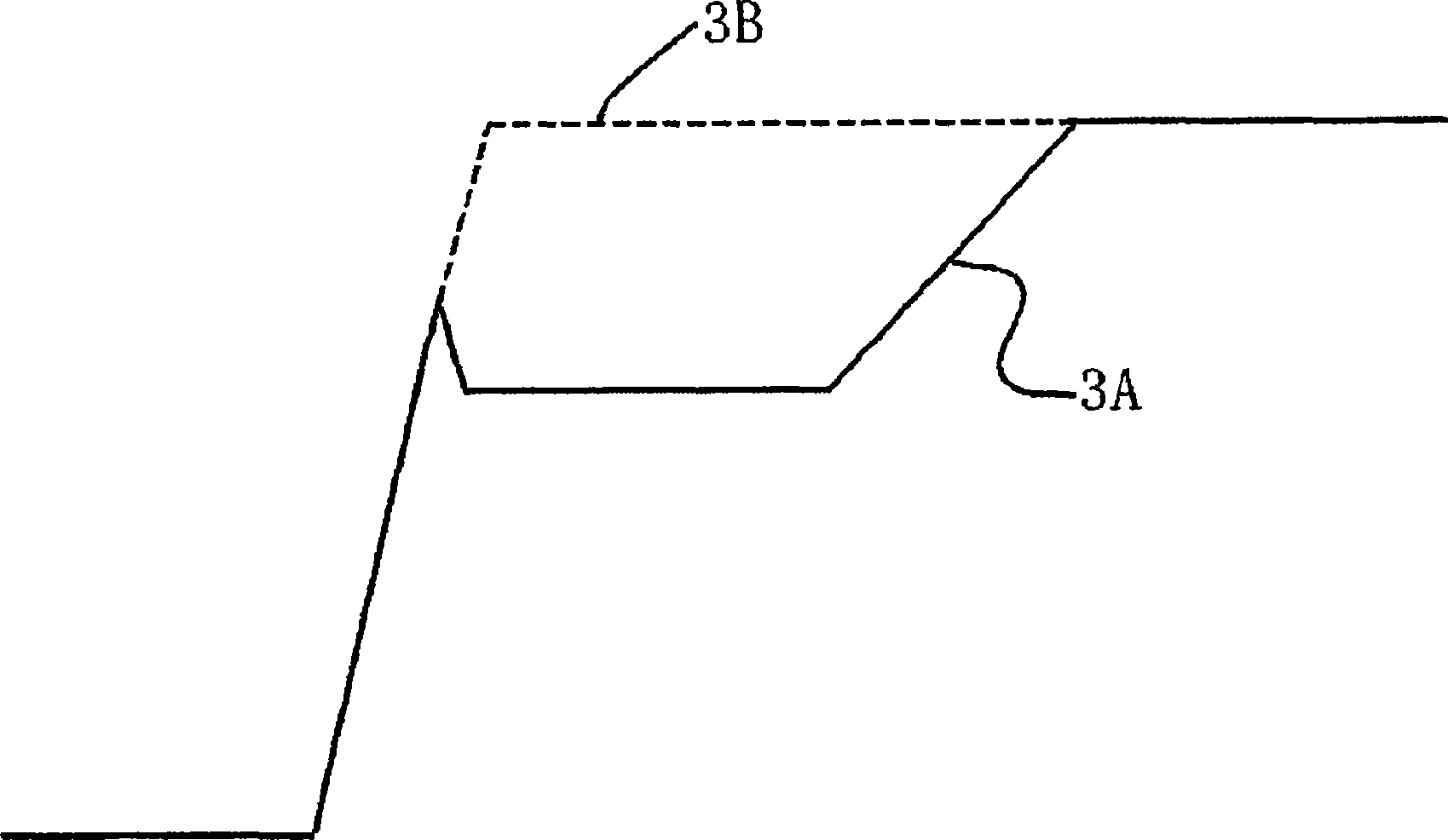
[0071] Figure 18 A control signal, a gate voltage, and an estimated value of the gate voltage are shown. With the delay circuit 79 shown in FIG. 17, the time from when the control signal sends out the turn-on pulse to when the gate voltage Vg rises is de...
Embodiment approach 3
[0075] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described.
[0076] FIG. 19 is a schematic configuration diagram of a driving circuit 500b for a power semiconductor element according to the third embodiment. In FIG. 19 , the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 10 of Embodiment 1 denote the same or corresponding parts, and description thereof will be omitted. In addition, 4c is a turn-on gate resistance, 4d is a turn-off gate resistance, 7a is a gate current detection type abnormality detection circuit, and 87 is a gate current comparison circuit. The gate current detection type abnormality detection circuit 7a uses the differential amplifier 85 to detect the voltage across the turn-on gate resistor 4c, and detects the abnormality of the IGBT 1 by detecting that the gate current Ig within the detection period set by the sampling circuit 6 is smaller than the threshold value. The gate current threshold value Igr of the gate current detection type abnormality det...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com