Method for controlling late blight by late sowing of white potato
A potato late blight, potato technology, applied in the field of plant protection, can solve problems such as disease prevalence, and achieve the effects of reducing application amount, optimizing field distribution, and reducing field humidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
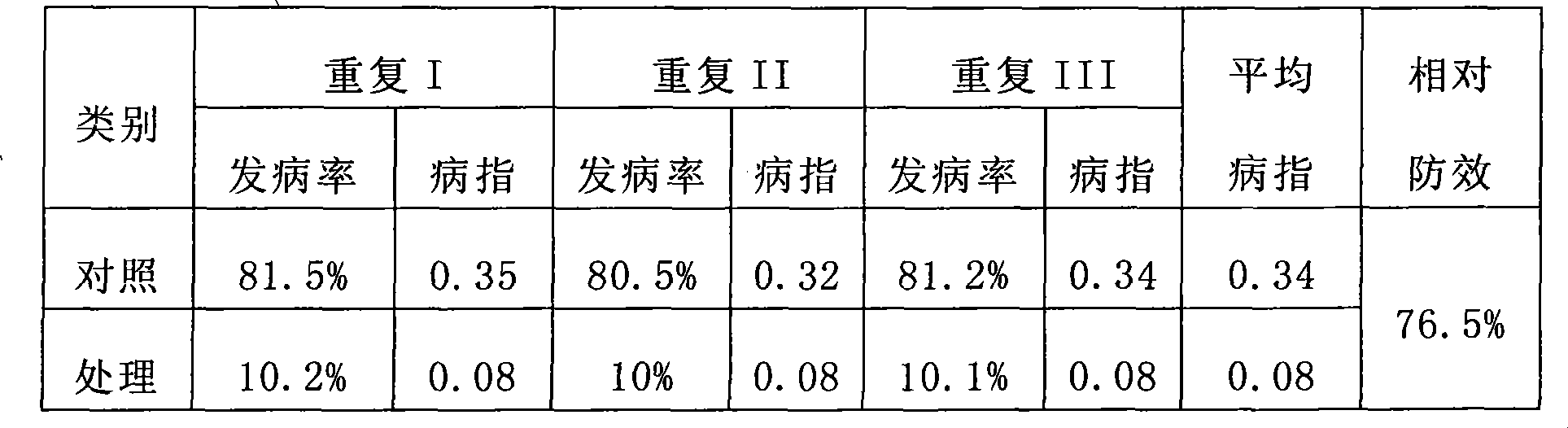
[0007] Contrast experiment in the same field: 2 treatments were set up, and the control was sown according to the conventional sowing date of potatoes, sowing on May 5th, the sowing specification was single row sowing, the row spacing was 60cm, and the plant spacing was 25cm; the treatment was late sowing, sowing on July 15th, and ridging Plum blossom ponds are planted with a ridge width of 50cm and a ridge spacing of 70cm. The plum blossom-shaped ponds are opened on the ridge, and the diagonal pond distance is 70cm. The potato variety is Hui-2, the planting density is 2200 plants per mu, and the field fertilization and management methods are carried out in a conventional manner. The incidence and control effects of potato late blight were investigated, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0008] Table 1 Effects of treatments and controls on controlling potato late blight
[0009]
Embodiment 2
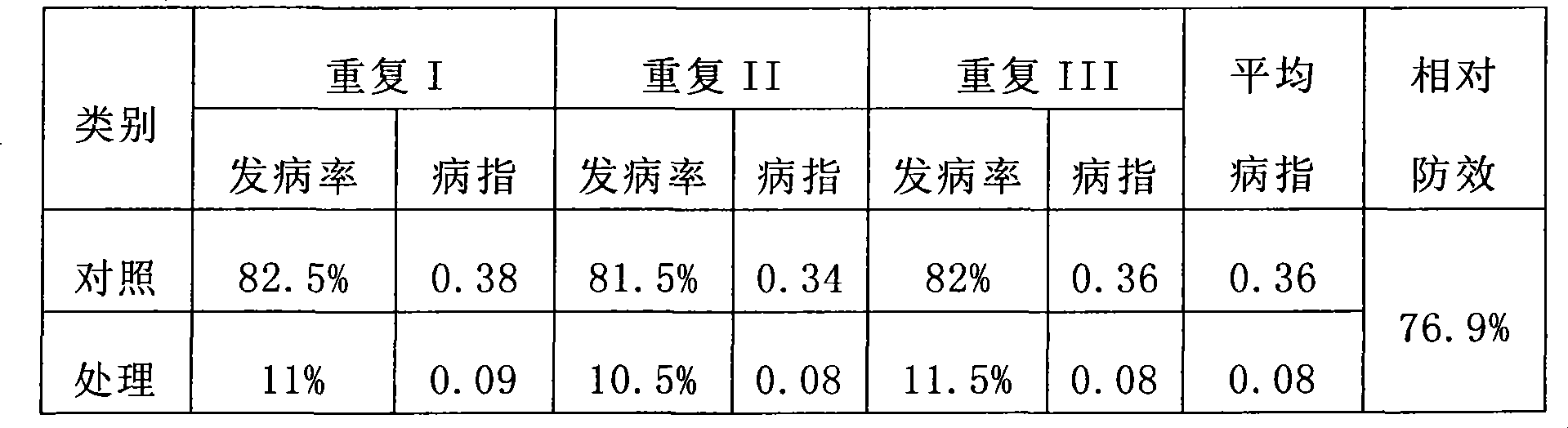
[0011] Contrast experiment in the same field: 2 treatments were set up, the control was planted according to the regular sowing date of potatoes, sowing on May 15, the sowing specification was single-row sowing, the row spacing was 60cm, and the plant spacing was 25cm; the treatment was late sowing, sowing on July 26, and ridging Plum blossom ponds are planted with a ridge width of 60cm and a ridge spacing of 60cm. The plum blossom-shaped ponds are opened on the ridge, and the diagonal pond distance is 65cm. The potato variety is Mira, and the planting density is 2,800 plants per mu. Field fertilization and management methods are carried out in a conventional manner. The incidence and control effects of potato late blight were investigated, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0012] Table 2 Effects of treatments and controls on controlling potato late blight
[0013]
Embodiment 3
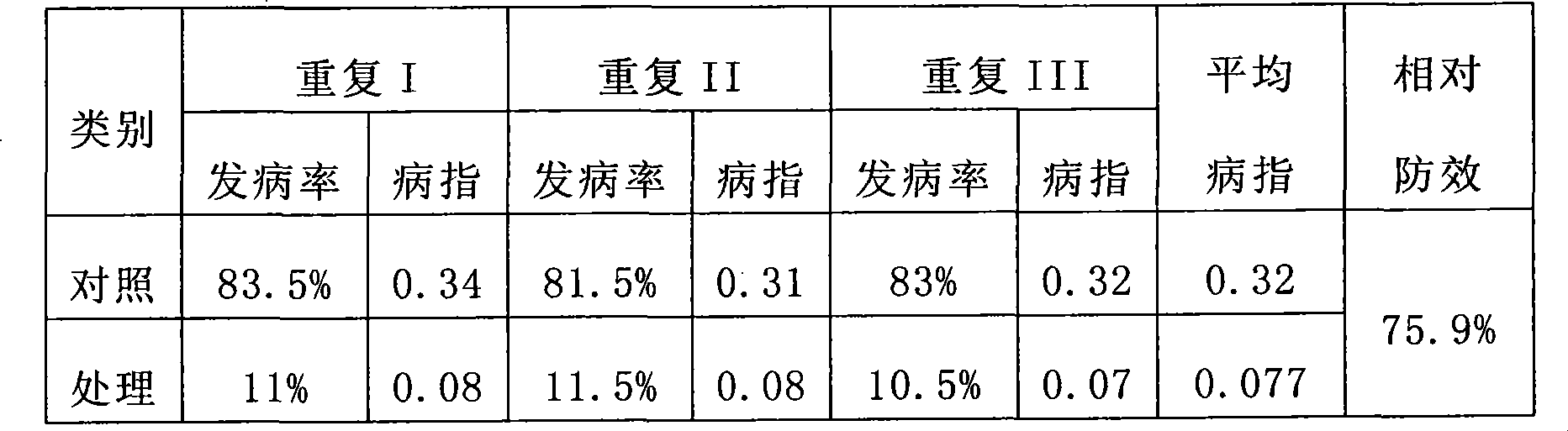
[0015] Contrast experiment in the same field: 2 treatments were set up, and the control was sown according to the regular sowing date of potatoes, sowing on May 25, the sowing specification was single-row sowing, the row spacing was 60 cm, and the plant spacing was 25 cm; the treatment was late sowing, sowing on August 9, and ridging Plum blossom ponds are planted with a ridge width of 55cm and a ridge spacing of 65cm. The plum blossom-shaped ponds are opened on the ridge, and the diagonal pond distance is 60cm. The potato variety is Hezuo 88, the planting density is 3300 plants per mu, and the field fertilization and management methods are carried out in a conventional way. The incidence and control effects of potato late blight were investigated, and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0016] Table 3 Effects of treatments and controls on controlling potato late blight
[0017]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com