Method for screening pluripotent cell and special culture medium thereof
A technology for screening pluripotent cells and culture media, which is applied in the field of screening pluripotent cells, and can solve problems such as lack of methods and inducible pluripotent cells not yet obtained
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
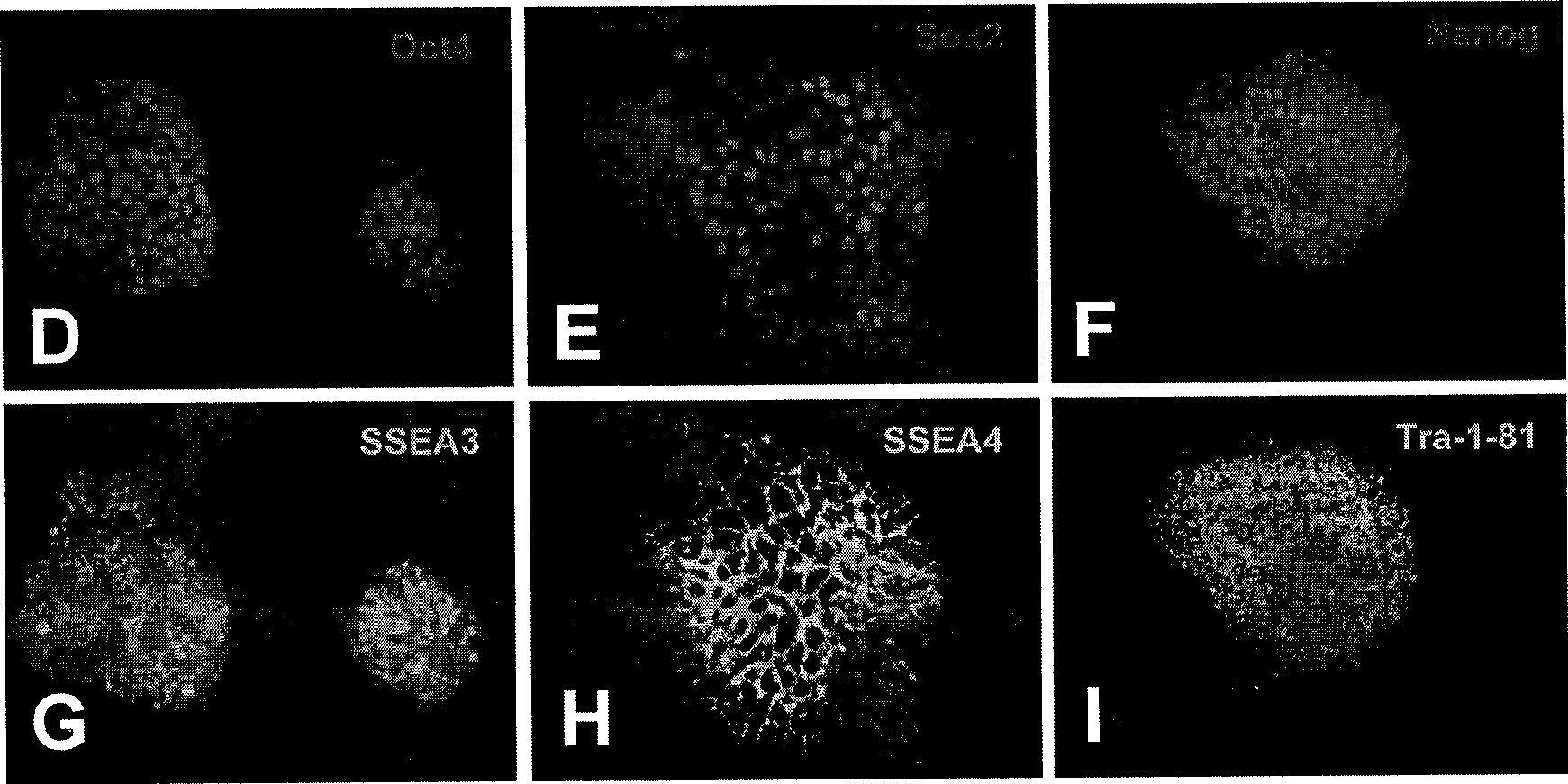
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1, Screening of mESC-like human pluripotent stem cells
[0069] 1. Acquisition of human fibroblasts (target cells)
[0070] 1) The fresh embryonic foreskin (Fsf) was sterilized with 75% ethanol and washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (fetal lung (FL) or adult foreskin (HFF) can be used instead of embryonic foreskin (Fsf)).
[0071] 2) Carefully separate the subcutaneous tissue with ophthalmic scissors and cut it into pieces.
[0072] 3) Wash several times with PBS, take small tissue pieces and inoculate them in culture dishes, and place them in a 37°C, 5% carbon dioxide incubator.
[0073] 4) After two hours, add DMEM high glucose medium II.
[0074] 5) After culturing for 2-3 days, remove the tissue pieces that cannot adhere to the wall.
[0075] 6) Continue culturing for 7-9 days, and remove the remaining tissue pieces.
[0076] 7) Digest the cells with the digestion solution at room temperature for 5 minutes, neutralize them with DMEM high glucose...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Example 2, Screening of mESC-like Rat Pluripotent Stem Cells
[0148] 1. Acquisition of rat fibroblasts (target cells)
[0149] 1) Remove the head, limbs and viscera of fresh 12.5-day-old rat embryos, and wash them with PBS.
[0150] 2) Shred the tissue with ophthalmic scissors.
[0151] 3) Wash several times with PBS, take small tissue pieces and inoculate them in culture dishes, and place them in a 37°C, 5% carbon dioxide incubator.
[0152] 4) After two hours, add DMEM high glucose medium II.
[0153] 5) After culturing for 2-3 days, remove the tissue pieces that cannot adhere to the wall.
[0154] 6) Continue culturing for 7-9 days, and remove the remaining tissue pieces.
[0155] 7) Digest the cells with the digestion solution at room temperature for 5 minutes, neutralize them with DMEM high glucose medium II, and inoculate them in a new culture dish at a ratio of 1:3.
[0156] 8) After that, the medium was changed every 2 days, and the cells were subcultured ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com