Process for making paper using cationic amylopectin starch
An amylopectin and cationic technology, applied in the field of papermaking, can solve problems such as weakening ink transfer, and achieve the effects of improving the ability to resist paper lint, reducing papermaking costs, and reducing paper lint.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] In this example, the following two cationic starch products containing quaternary ammonium substituents (degree of substitution 0.035) were used as wet end additives for papermaking.
[0037] A. Cationic potato starch (contains about 20% by weight amylose based on dry matter, Amylofax PW)
[0038] B. Cationic amylopectin potato starch (contains about 2% by weight amylose on dry matter basis according to the invention, PR0602A)
[0039] The cationic starch product was slurried in water to form a suspension containing 10% by weight starch. The suspension was gelled with steam. The resulting starch solution was diluted with water to 1% by weight dry matter.
[0040] The test pulp consisted of a mixture of 38% long fiber, 28% short fiber (eucalyptus) and 34% CTMP. Calcium carbonate was added as filler to give a final ash content of 16% in the paper. The amount of cationic starch added was 1.0% by weight (dry matter). The test pulp is made into handmade paper (paper wei...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In this example, the same two cationic starch products containing quaternary ammonium substituents (degree of substitution 0.035) as in Example 1 were used.
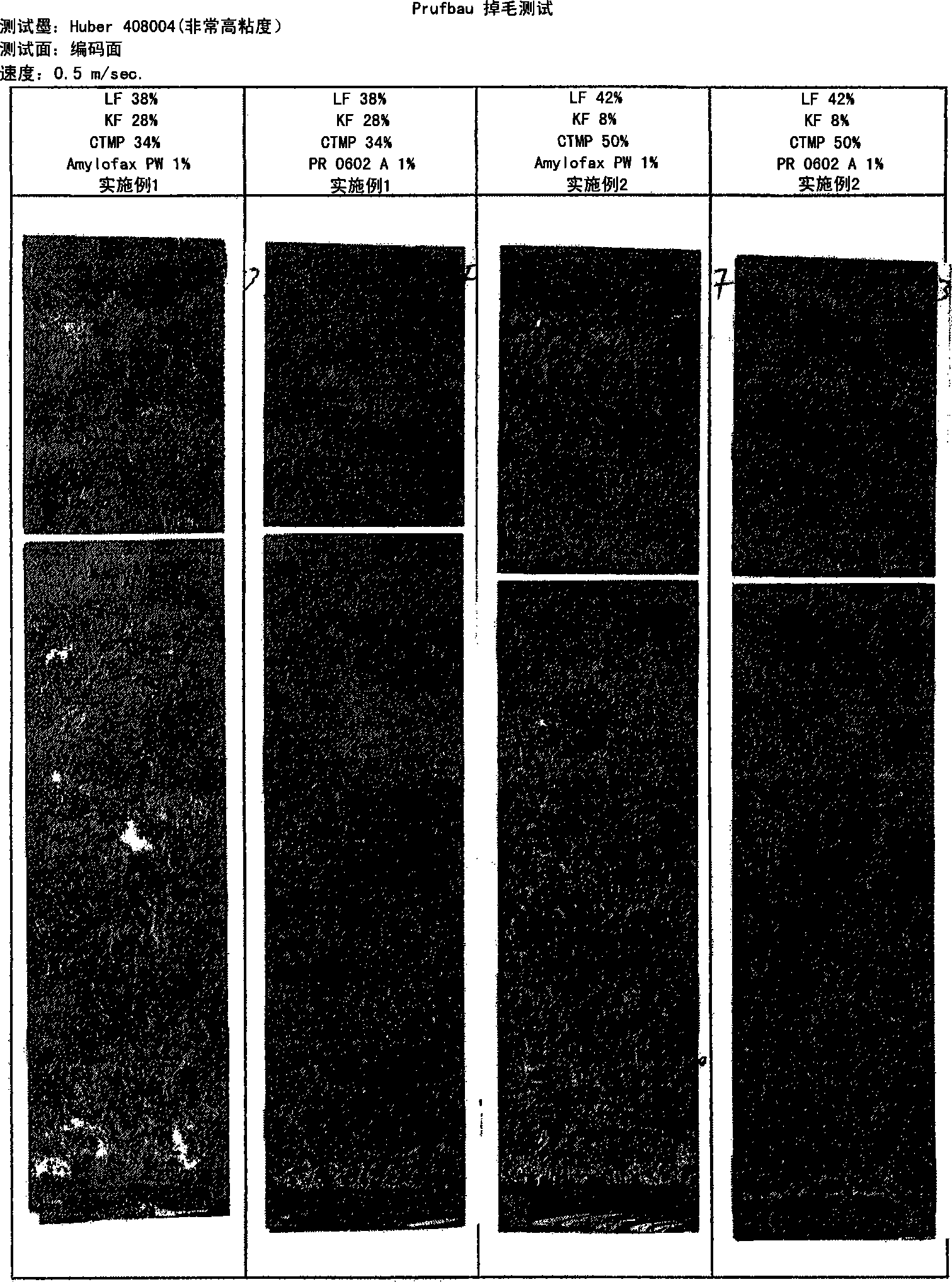
[0044] The test pulp consisted of a mixture of 42% long fibers, 8% short fibers (eucalyptus) and 50% CTMP. Calcium carbonate was added as filler to give a final ash content of 16% in the paper. The amount of cationic starch added was 1.0% by weight (dry matter). The test pulp is made into handmade paper (paper weight is 80g / m2) with a paper sample picker 2 ). The handsheets were dried to a moisture content of 7% by weight.
[0045] Paper lint tendency was determined by performing lint using the Prufbau dry pick test described in Tappi Journal, July 1994, p. 185. The test ink was a high viscosity ink (Huber 408004). Paper lint tendency was estimated visually and the results are shown in figure 1 middle.
[0046] in conclusion
[0047] For both pulp qualities (ie Examples 1 and 2) a significant improvement i...
Embodiment 3
[0049] In this example, the same two cationic starch products containing quaternary ammonium substituents (degree of substitution 0.035) as in Example 1 were used. The test pulp consisted of a mixture of 38% long fiber, 28% short fiber (eucalyptus) and 34% CTMP. Calcium carbonate was added as filler to give a final ash content of 10% in the paper. The amount of cationic starch added was 1.0% by weight (dry matter).
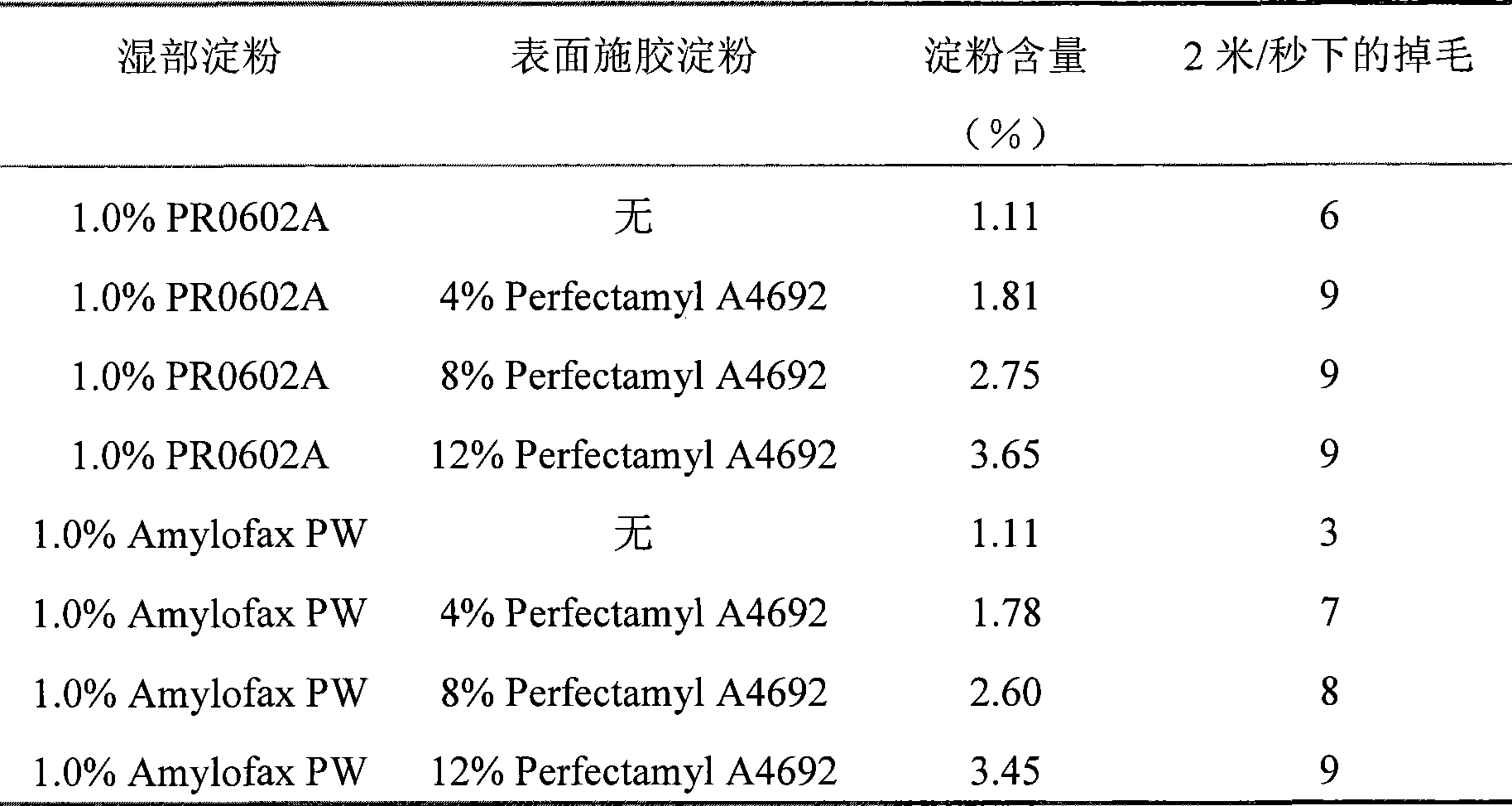
[0050] Paper pulp is made into paper (paper weight is 200g / m 2 ). The resulting paper was surface sized using a Dixon size press at an operating speed of 50 meters per minute.
[0051] As surface sizing starch, an aqueous solution of Perfectamyl A4692 (AVEBE) was applied at concentrations of 4%, 8% and 12%. The starch content of the different papers was determined by conversion of amylase into glucose followed by glucose determination with the hexokinase method according to Boehringer. Paper lint tendency was determined by linting using the Prufbau dry pick t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com