Driving method for liquid crystal sub-pixel
A driving method and sub-pixel technology, applied in instruments, static indicators, etc., can solve the problem of limited image quality improvement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
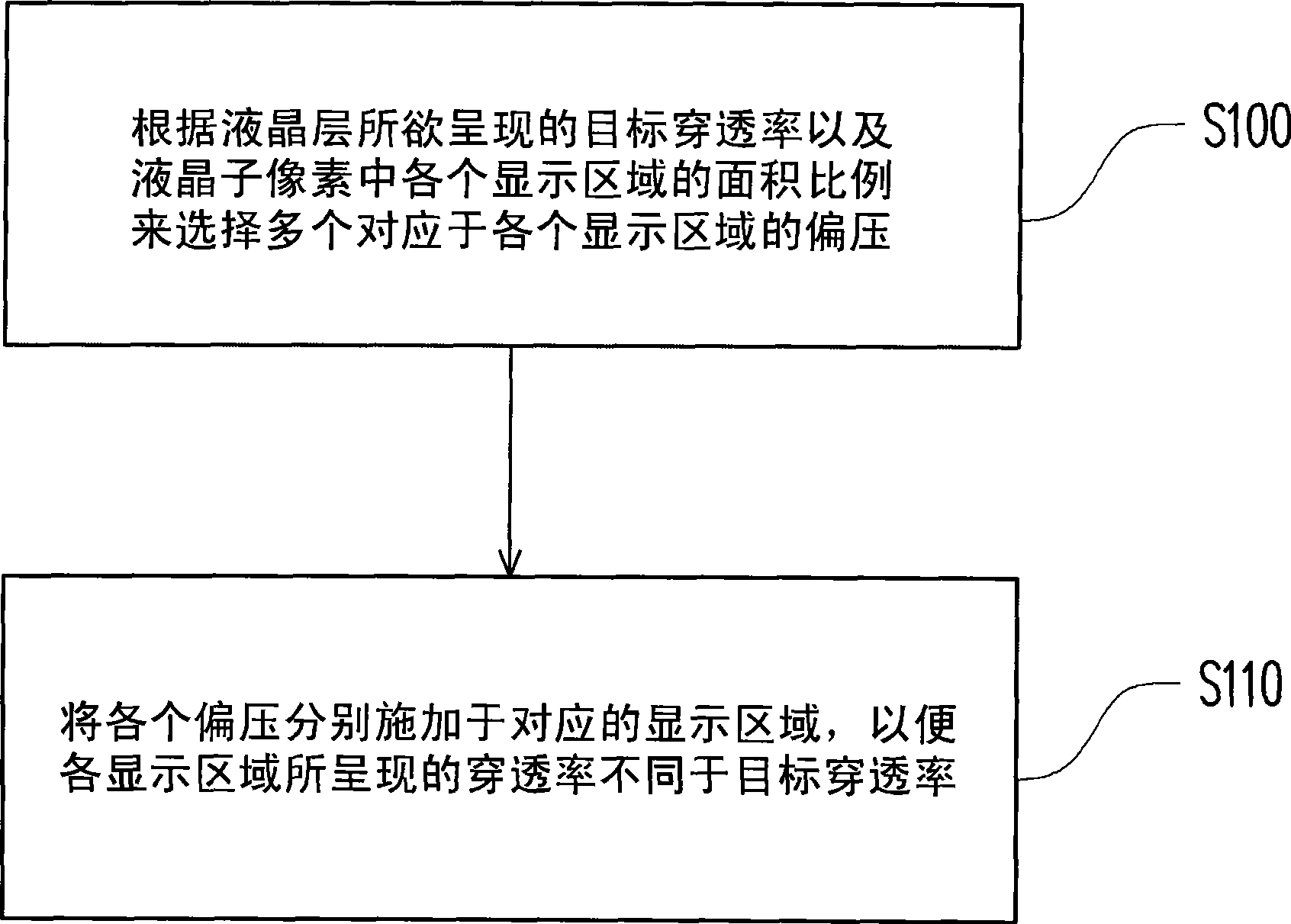
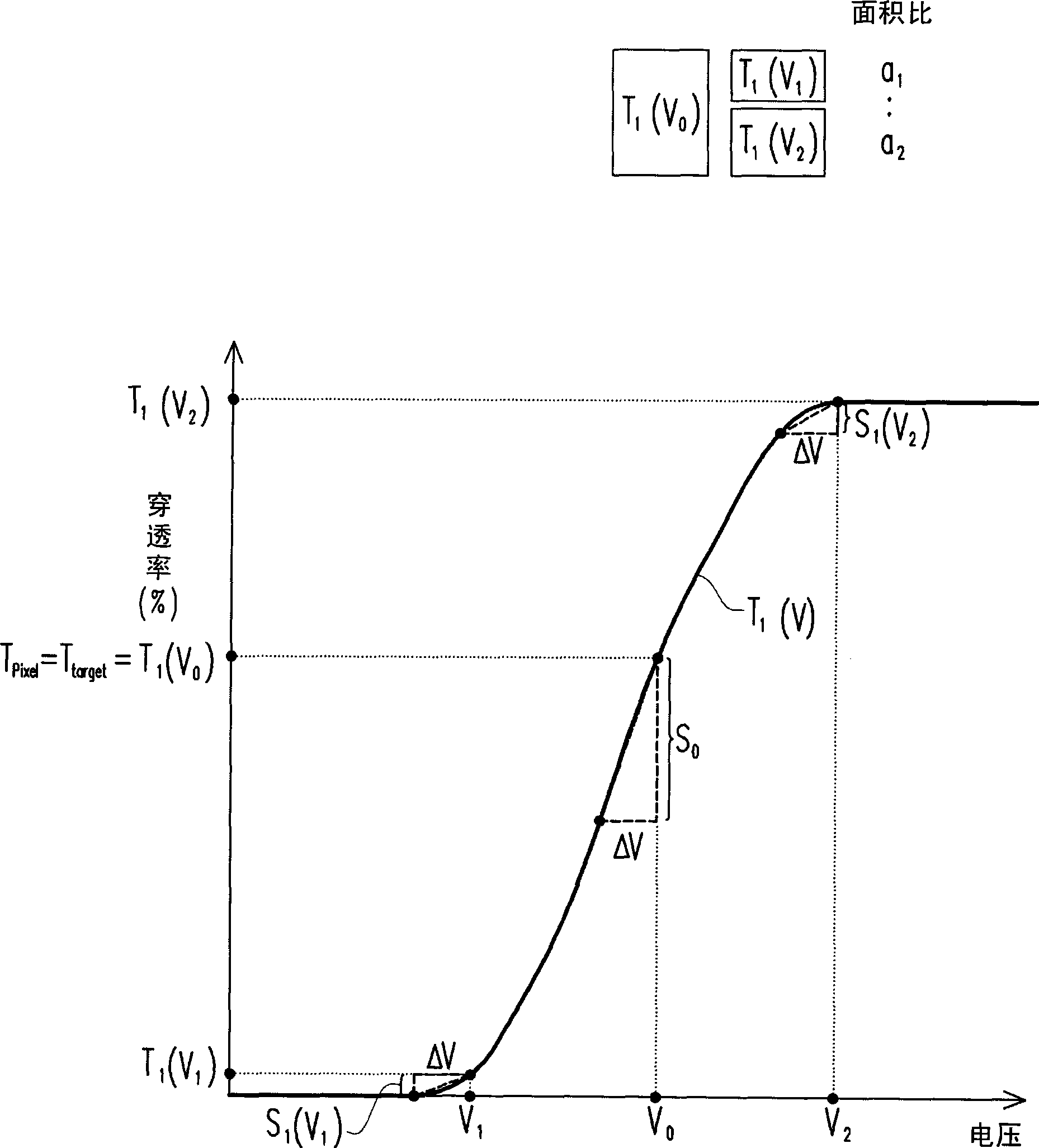
[0037] figure 1 is a flow chart of the driving method according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to figure 1 , the driving method of this embodiment is suitable for determining a target transmittance T to be presented by a liquid crystal layer in a liquid crystal sub-pixel target (n), wherein the liquid crystal sub-pixel has a plurality of display areas that can be individually controlled, when the bias voltage applied to each display area is the same, and the transmittance presented by the liquid crystal layer is the target transmittance T target (n), and when the bias voltage varies by ΔV, the transmittance of the liquid crystal layer in the liquid crystal sub-pixel varies as S 0 . Here, the bias voltage variation ΔV is caused by, for example, charged impurities or ions in the liquid crystal layer, and the reason thereof has been described in the prior art, so it will not be repeated here.
[0038] The driving method of this embodiment inclu...
no. 2 example
[0057] Please refer to relational expression (1) and relational expression (2) in the first embodiment, when n=2, a 1 ≠a 2 , and the voltage-transmittance curves of the liquid crystal layers in each display area are different, the aforementioned relational expression (1) and relational expression (2) can be simplified as follows:
[0058] T pixel = a 1 × T 1 ( V 1 ) + a 2 × T 2 ( V 2 ) a 1 + ...
no. 3 example
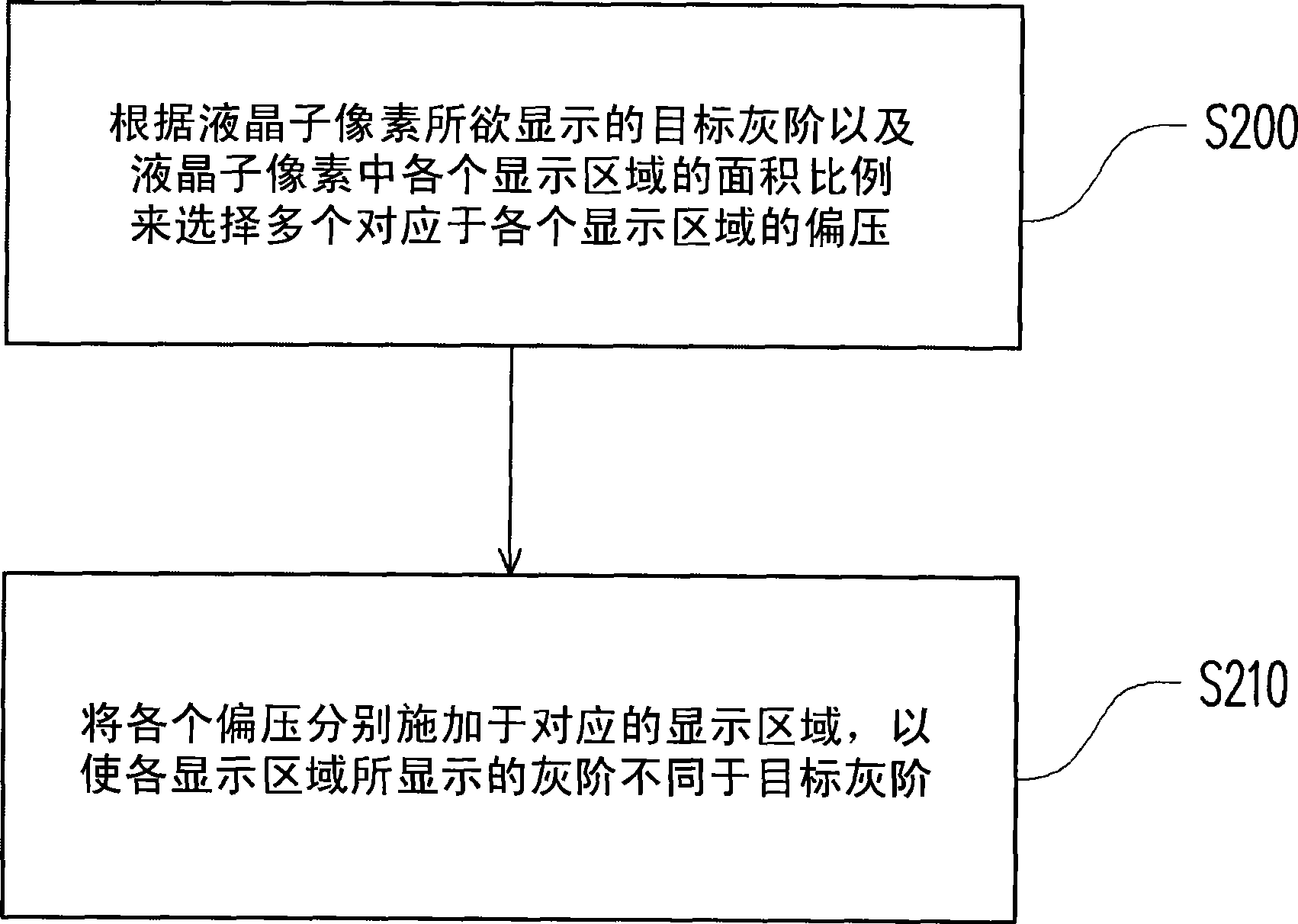
[0066] Since the transmittance of the liquid crystal layer in the liquid crystal pixel has a certain correlation with the grayscale brightness that the liquid crystal pixel can display, this embodiment uses the grayscale brightness and the variation of the grayscale brightness as the basis for selecting the bias voltage applied to each display area. in accordance with.
[0067] image 3 is a flow chart of the driving method according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to image 3 , the driving method of this embodiment is suitable for making a liquid crystal sub-pixel display a target grayscale brightness L target (n), wherein the liquid crystal sub-pixel has a plurality of display areas that can be individually controlled, when the bias voltage applied to each display area is the same, and the gray-scale brightness displayed by the liquid crystal sub-pixel is the target gray-scale brightness L target (n), and when the bias voltage varies by ΔV, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com