Coding/decoding methods, coders/decoders, and method and device for finding optimally matched modules
A best matching and encoder technology, applied in the field of image coding, can solve the problems of not being able to improve coding efficiency better, and not being able to eliminate residual image correlation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
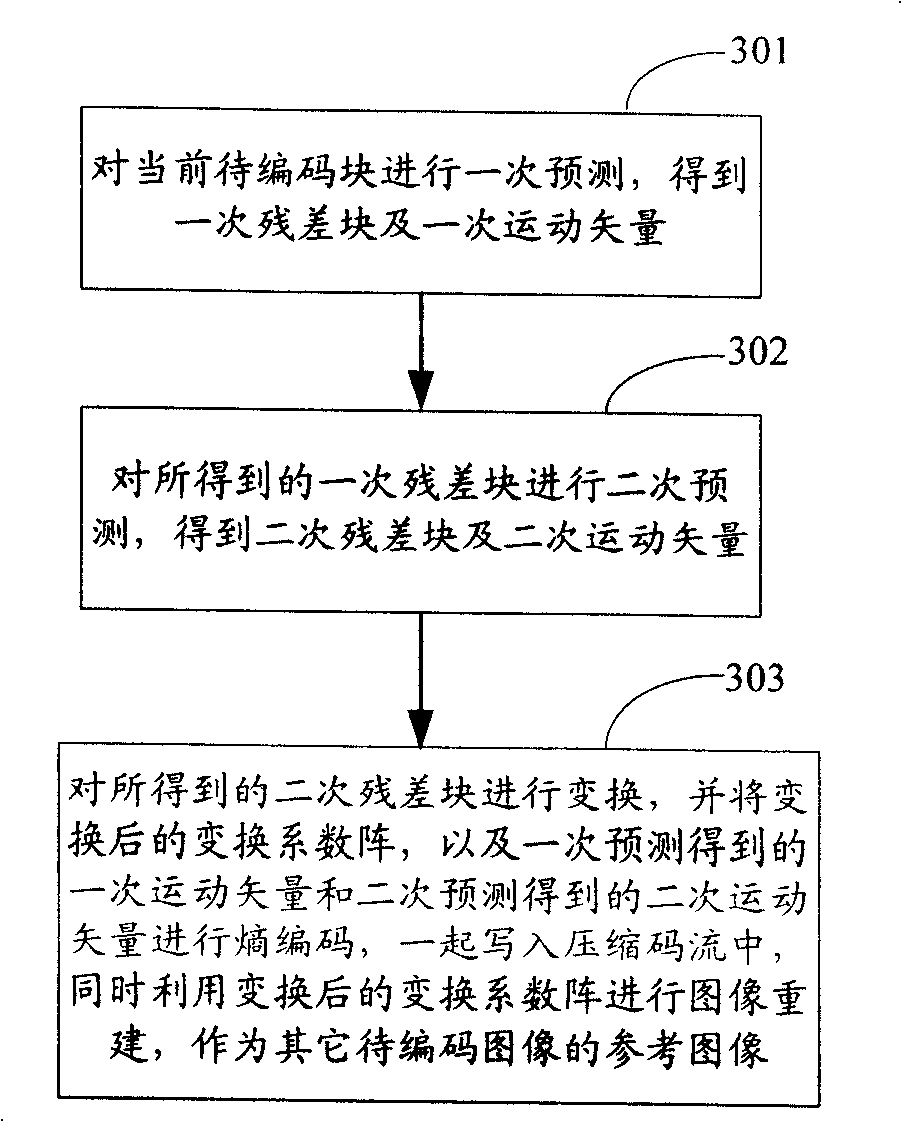
[0092] In this embodiment, the implementation manner in the first manner is described in detail. That is, the secondary prediction is directly performed on the primary residual image generated by the primary prediction, and the subsequent encoding process is performed on the secondary residual image generated by the secondary prediction. image 3 It is a flow chart of the image encoding method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In general, when inter-frame prediction is performed on the original image of the current image to be encoded, the prediction is performed in units of macroblocks or blocks, and the last block carries the end of the current image to be encoded, and then starts Perform the same inter-frame prediction on the next image to be encoded. Therefore, the flow of the image encoding method in this embodiment takes the encoding process of a macroblock of the image currently to be encoded as an example to describe the encoding method of the present inventio...
Embodiment 2
[0155] In this embodiment, the implementation of the second method is described in detail, that is, before the secondary prediction, the primary residual image is first transformed, and then the transformed primary residual image is converted to the secondary reference image corresponding to Secondary prediction is performed on the transformed secondary reference image, and subsequent encoding processing is performed on the secondary residual image generated after the secondary prediction.
[0156] In this embodiment, in order to distinguish it from method 1, the primary residual image generated after transforming the primary residual image is called the primary residual image transformation coefficient matrix, and correspondingly, the primary residual image generated after transforming the primary residual block is The primary residual block is called the primary residual block transformation coefficient matrix, and the secondary residual image generated by performing secondar...
Embodiment 3
[0210] In this embodiment, the image encoding method and decoding method in Embodiment 1, and the image encoding method and decoding method in Embodiment 2 can be applied simultaneously. Correspondingly, the encoder and the decoder have both the implementation functions of the encoder and the decoder in the first and second embodiments above, and the implementation in the first embodiment is added on the basis of the second embodiment . Figure 15 It is a schematic structural diagram of the encoder in Embodiment 3 of the present invention. The encoder includes: a primary prediction module, a transformation module, a secondary prediction module, an encoding module, a secondary reconstruction module, an inverse transformation module and a primary reconstruction module. It includes the encoding process represented by the dotted line: the current image to be encoded→primary prediction module→secondary prediction module→transformation module→encoding module→code stream; reconstruc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com