Magneto-optical switching device and method for switching a magnetizable medium
A technology for converting media and converting devices, applied in recording/reproducing/deleting methods, magnetic recording, beam reproduction, etc., capable of solving problems such as high power consumption, high manufacturing cost of magnetic devices, and failure to simplify the magnetic recording process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
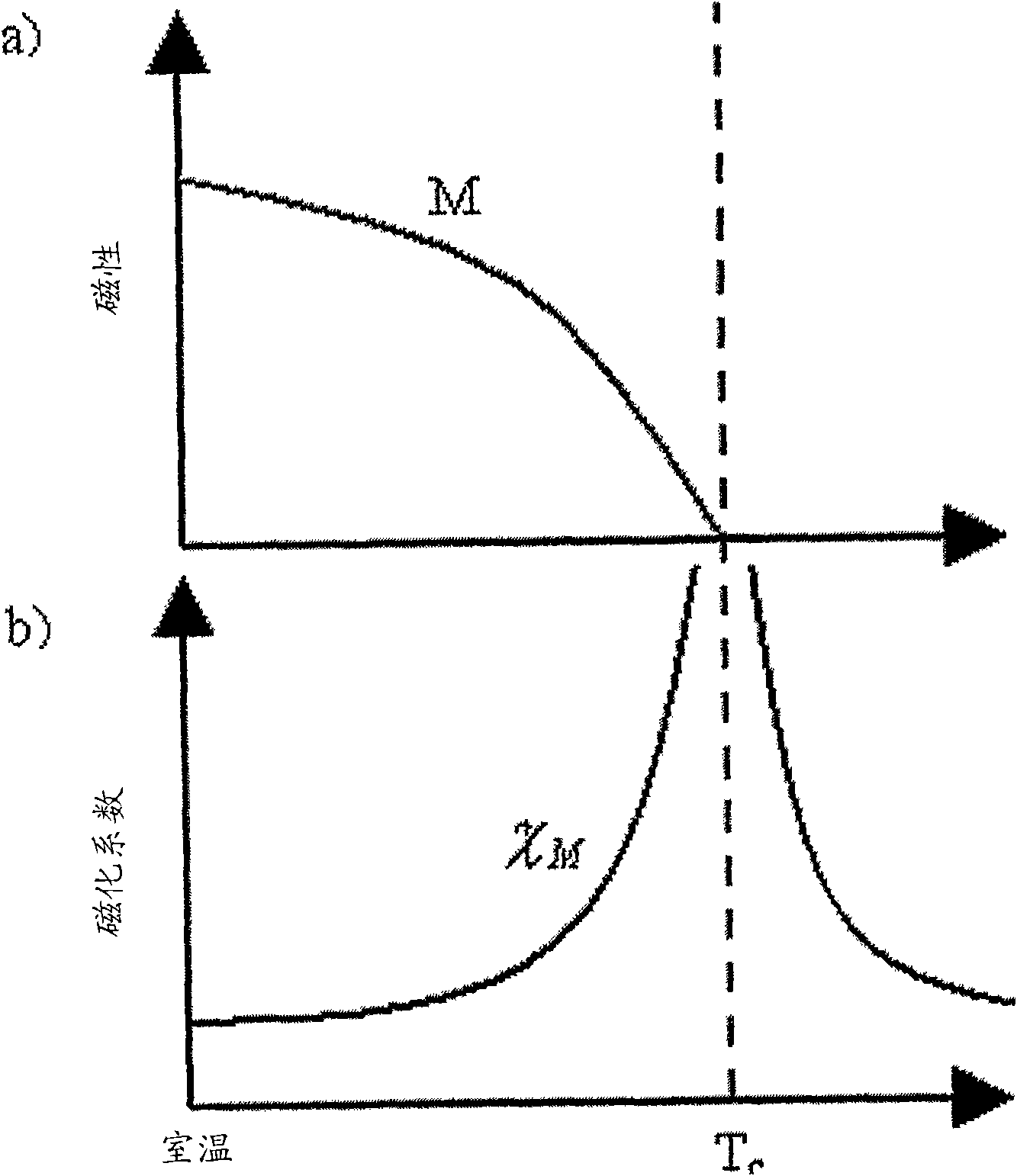
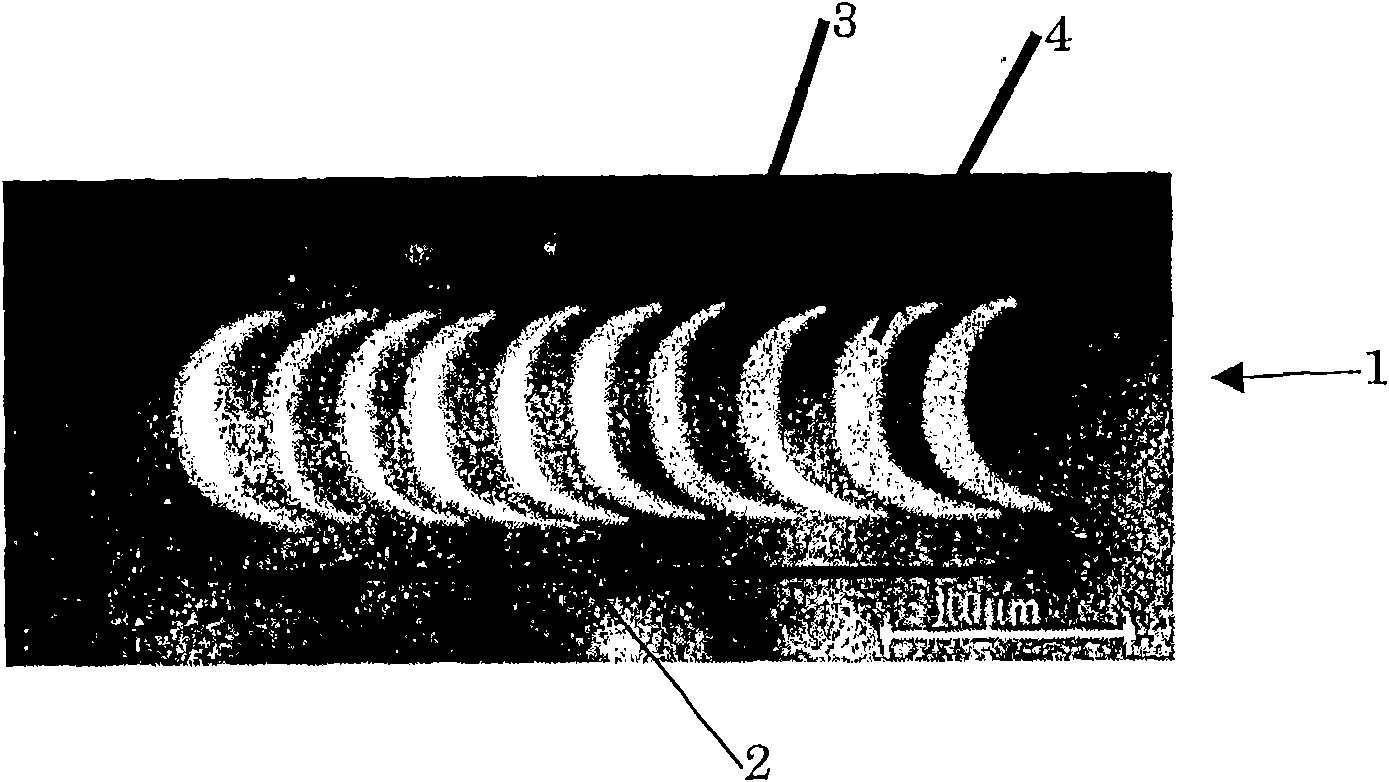
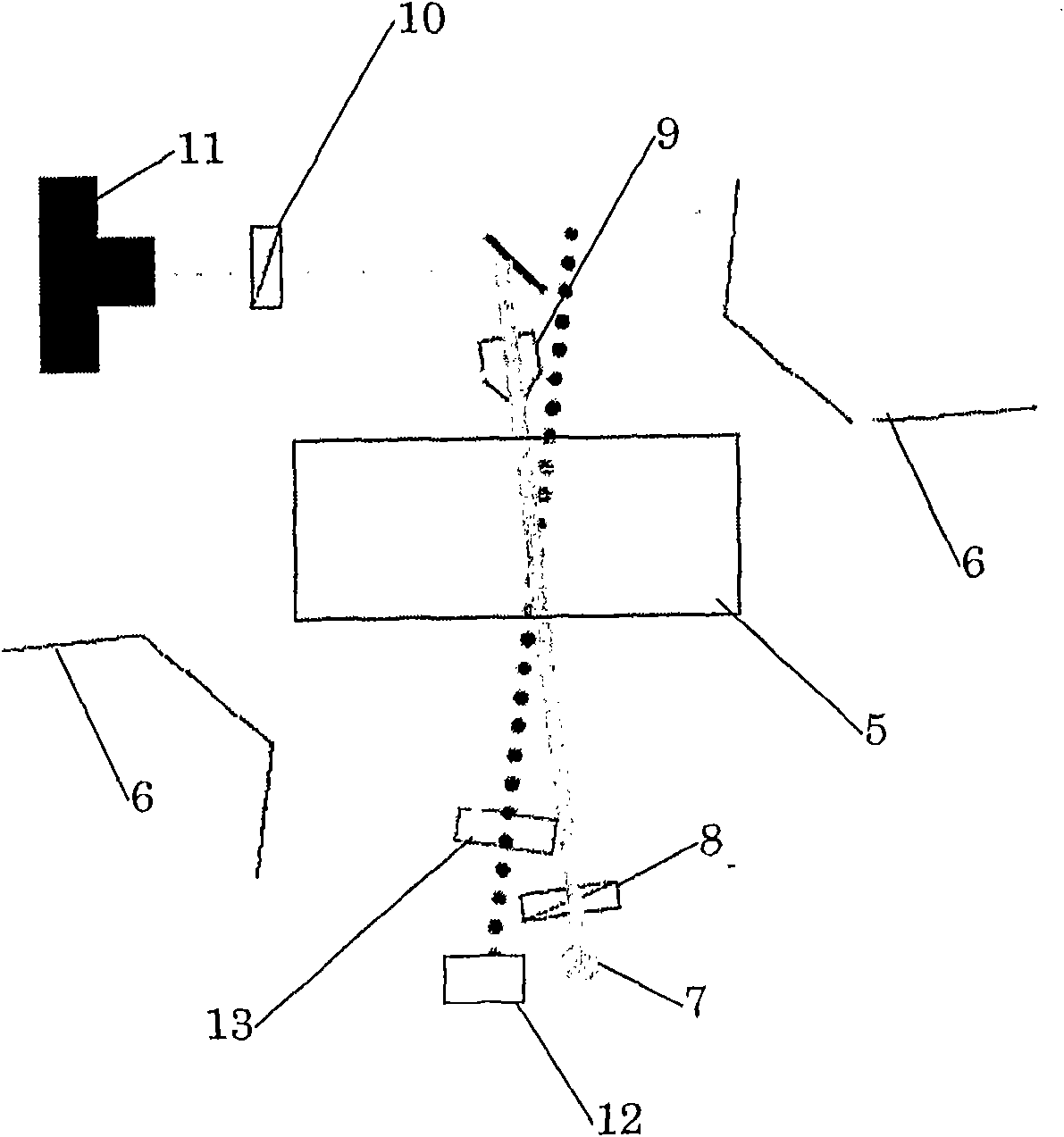
[0014] The interaction of light with magnetized media has been demonstrated in various magneto-optical phenomena. A good example is the Faraday effect, observed as a rotation of the plane of polarization of light passing through a magnetic medium:
[0015] α F = x n M · k [equation 1]
[0016] Among them, α F is the specific Faraday rotation, M is magnetism, n is the refractive index, k is the wave vector of light, and x is the magneto-optical susceptibility, which is a scalar in isotropic media value. Various devices such as magneto-optical insulators and modulators use large values of the Faraday rotation angle in light-transmitting magnetic compounds.
[0017] Less well known is the inverse Faraday effect, in which high-intensity laser radiation acts as a magnetic field on the medium and induces a static magnetism M(0):
[0018] M ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com